一、关于Attention,关于NMT
未完待续、、、
以google 的 nmt 代码引入 探讨下端到端:
项目地址:https://github.com/tensorflow/nmt
机器翻译算是深度学习在垂直领域应用最成功的之一了,深度学习在垂直领域的应用的确能解决很多之前繁琐的问题,但是缺乏范化能力不足,这也是各大公司一直解决的问题;
最近开源的模型:
lingvo:一种新的侧重于sequence2sequence的框架;
bert :一种基于深度双向Transform的语言模型预训练策略;
端到端的解决方案,依然是目前很多NLP任务中常用的模型框架;
二、tensorflow 中的attention:
tensorflow 中主要有两种Attention:
1、Bahdanau 的 Attention
2、Luong 的 Attention
两种的计算如下所示:
分别来自两篇NMT的论文也是nmt 最经典的两篇论文:(深扒的话还是看论文吧)
1、Bahdanau 的 Attention
NEURAL MACHINE TRANSLATION BY JOINTLY LEARNING TO ALIGN AND TRANSLATE
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.0473.pdf
2、Luong 的 Attention
Effective Approaches to Attention-based Neural Machine Translation
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1508.04025.pdf
以下是两篇论文中如何使用Attention:
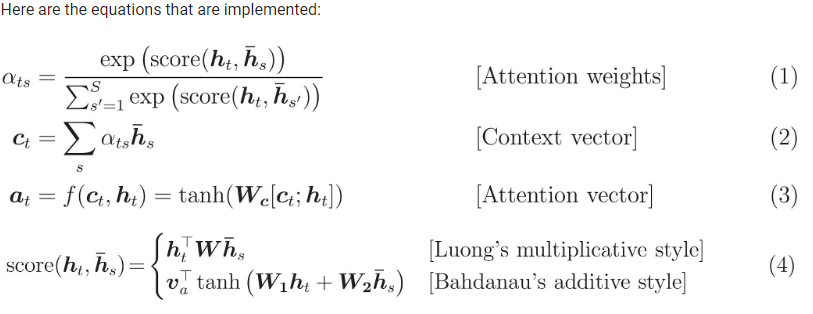
图:两个attention
两者的区别:
主要区别在于如何评估当前解码器输入和编码器输出之间的相似性。
tensorflow代码中封装好的,共有四个attention函数:
1、加入了得分偏置 bias 的 Bahdanau 的 attention
class BahdanauMonotonicAttention()
2、无得分偏置的Bahdanau 的 attention
class BahdanauAttention()
3、加入了得分偏置 bias 的Luong 的 attention
class LuongMonotonicAttention()
4、无得分偏置的Luong 的 attention
class LuongAttention()
贴一个直接封装好的代码encode 和 decoder 的代码:详细代码稍后续上
主要用到有以下几个函数:attention + beamsearch
tf.contrib.seq2seq.tile_batch
tf.contrib.seq2seq.LuongAttention
tf.contrib.seq2seq.BahdanauAttention
tf.contrib.seq2seq.AttentionWrapper
tf.contrib.seq2seq.TrainingHelper
代码片段:
def decoder(mode,encoder_outputs,encoder_state,X_len,word2id_tar,embeddings_Y,embedded_Y): k_initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer() with tf.variable_scope('decoder'): net_mode = hp.dec_mode beam_width = hp.beam_size batch_size = hp.batch_size memory = encoder_outputs num_layers = hp.dec_num_layers if mode == 'infer': memory = tf.contrib.seq2seq.tile_batch(memory, beam_width) X_len = tf.contrib.seq2seq.tile_batch(X_len, beam_width) encoder_state = tf.contrib.seq2seq.tile_batch(encoder_state, beam_width) bs = batch_size * beam_width else: bs = batch_size attention = tf.contrib.seq2seq.LuongAttention(hp.dec_hidden_size, memory, X_len, scale=True) # multiplicative # attention = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BahdanauAttention(hidden_size, memory, X_len, normalize=True) # additive cell = multi_cells(num_layers * 2,mode,net_mode) cell = tf.contrib.seq2seq.AttentionWrapper(cell, attention, hp.dec_hidden_size, name='attention') decoder_initial_state = cell.zero_state(bs, tf.float32).clone(cell_state=encoder_state) with tf.variable_scope('projected'): output_layer = tf.layers.Dense(len(word2id_tar), use_bias=False, kernel_initializer=k_initializer) if mode == 'infer': start = tf.fill([batch_size], word2id_tar['<s>']) decoder = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BeamSearchDecoder(cell, embeddings_Y, start, word2id_tar['</s>'], decoder_initial_state, beam_width, output_layer) outputs, final_context_state, _ = tf.contrib.seq2seq.dynamic_decode(decoder, output_time_major=True, maximum_iterations=1 * tf.reduce_max(X_len)) sample_id = outputs.predicted_ids print ("sample_id shape") print (sample_id.get_shape()) return "",sample_id else: helper = tf.contrib.seq2seq.TrainingHelper(embedded_Y, [hp.maxlen - 1 for b in range(batch_size)]) decoder = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BasicDecoder(cell, helper, decoder_initial_state, output_layer) outputs, final_context_state, _ = tf.contrib.seq2seq.dynamic_decode(decoder, output_time_major=True) logits = outputs.rnn_output logits = tf.transpose(logits, (1, 0, 2)) print(logits) return logits,""
贴一下 google nmt 的代码:google 里面写的也很详细了
主要三部分: attention,encoder,decoder,计算方式如上图,流程如以下代码所描述;
#两个 attention代码:依据的是: 上图:两个attention class LuongAttentionAttention(tf.keras.Model): def __init__(self, units): super(LuongAttention, self).__init__() self.W = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units) def call(self, query, values): # hidden shape == (batch_size, hidden size) # hidden_with_time_axis shape == (batch_size, 1, hidden size) # we are doing this to perform addition to calculate the score hidden_with_time_axis = tf.expand_dims(query, 1) # score shape == (batch_size, max_length, hidden_size) #矩阵转置 转置前:[batch_size,max_length,hidden_size] 转置后:[batch_size,hidden_size,max_length] score = tf.transpose(values, perm=[0, 2, 1])*self.W(hidden_with_time_axis))) # attention_weights shape == (batch_size, max_length, 1) # we get 1 at the last axis because we are applying score to self.V attention_weights = tf.nn.softmax(score, axis=1) # context_vector shape after sum == (batch_size, hidden_size) context_vector = attention_weights * values context_vector = tf.reduce_sum(context_vector, axis=1) return context_vector, attention_weights #BahdanauAttention:#计算 attention class BahdanauAttention(tf.keras.Model): def __init__(self, units): super(BahdanauAttention, self).__init__() self.W1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units) self.W2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units) self.V = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1) def call(self, query, values): # hidden shape == (batch_size, hidden size) # hidden_with_time_axis shape == (batch_size, 1, hidden size) # we are doing this to perform addition to calculate the score hidden_with_time_axis = tf.expand_dims(query, 1) # score shape == (batch_size, max_length, hidden_size) score = self.V(tf.nn.tanh( self.W1(values) + self.W2(hidden_with_time_axis))) # attention_weights shape == (batch_size, max_length, 1) # we get 1 at the last axis because we are applying score to self.V attention_weights = tf.nn.softmax(score, axis=1) # context_vector shape after sum == (batch_size, hidden_size) context_vector = attention_weights * values context_vector = tf.reduce_sum(context_vector, axis=1) return context_vector, attention_weights decoder 的部分代码 class Decoder(tf.keras.Model): def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, dec_units, batch_sz): super(Decoder, self).__init__() self.batch_sz = batch_sz self.dec_units = dec_units self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim) # 参数简说: self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.dec_units, return_sequences=True, return_state=True, recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform') self.fc = tf.keras.layers.Dense(vocab_size) # used for attention self.attention = BahdanauAttention(self.dec_units) def call(self, x, hidden, enc_output): # enc_output shape == (batch_size, max_length, hidden_size) #调用 attention 函数,传入,上个时刻的 hidden 和 encoder 的 outputs # context_vector 加权平均后的 Ci(论文中的),attention_weights 权重值 context_vector, attention_weights = self.attention(hidden, enc_output) # x shape after passing through embedding == (batch_size, 1, embedding_dim) x = self.embedding(x) # x shape after concatenation == (batch_size, 1, embedding_dim + hidden_size) # context_vector 和 embedding 后的 X 进行结合 x = tf.concat([tf.expand_dims(context_vector, 1), x], axis=-1) # passing the concatenated vector to the GRU # 此时的 output 应该 等于 state; output, state = self.gru(x) # output shape == (batch_size * 1, hidden_size) output = tf.reshape(output, (-1, output.shape[2])) # output shape == (batch_size, vocab) x = self.fc(output) # 输出 outputs 全连接之后的 x,隐藏层的state,attention 的score,x在训练的时候直接作为损失; return x, state, attention_weights #训练的部分代码: def train_step(inp, targ, enc_hidden): loss = 0 with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # encoder 部分的代码,直接取的所有的输出和最后的隐藏层; enc_output, enc_hidden = encoder(inp, enc_hidden) dec_hidden = enc_hidden dec_input = tf.expand_dims([targ_lang.word_index['<start>']] * BATCH_SIZE, 1) # Teacher forcing - feeding the target as the next input #按照句子的长度一个一个的进行输入; for t in range(1, targ.shape[1]): # passing enc_output to the decoder # 获得decoder 每一时刻的输出 和隐藏层的输出; predictions, dec_hidden, _ = decoder(dec_input, dec_hidden, enc_output) loss += loss_function(targ[:, t], predictions) # using teacher forcing dec_input = tf.expand_dims(targ[:, t], 1) batch_loss = (loss / int(targ.shape[1])) variables = encoder.trainable_variables + decoder.trainable_variables gradients = tape.gradient(loss, variables) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, variables)) return batch_loss