连通性问题
目标:编写一个程序来过滤序列中所有无意义的整数对
程序输入p,q,如果已知的所有整数都不能说明p,q是相连的,则将这对整数写到输出中,如果已知数据已经可以证明,则忽略。
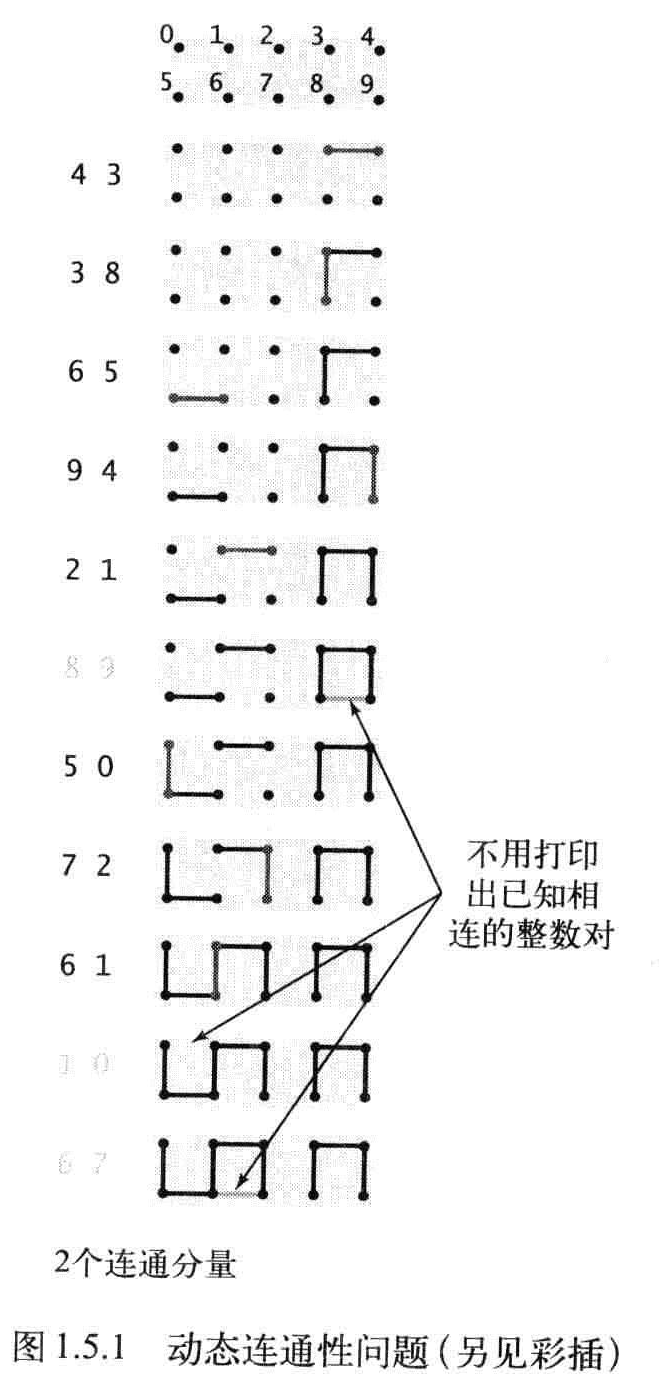
将对象称为触电,将整数对称为连接。将等价类称为连通分量。简称分量

Quck-find算法
该算法的目标就是让所有连通的触电(索引)对应的值都相同。


public class QuickFindUF
{
private int[] _id;
private int _length;
public QuickFindUF(int length)
{
_length = length;
_id = new int[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
_id[i] = i;
}
public int Length()
{
return _length;
}
public int Find(int p)
{
validate(p);
return _id[p];
}
// validate that p is a valid index
private void validate(int p)
{
int n = _id.Length;
if (p < 0 || p >= n)
{
throw new ArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n - 1));
}
}
public bool Connected(int p, int q)
{
validate(p);
validate(q);
return _id[p] == _id[q];
}
public void Union(int p, int q)
{
validate(p);
validate(q);
//将p和q归并到相同的分量中
int pID = _id[p]; // needed for correctness
int qID = _id[q]; // to reduce the number of array accesses
// 如果p和q已经在相同的分量之中则不需要采取任何行动
if (pID == qID) return;
//将p的分量重命名为q的名称
for (int i = 0; i < _id.Length; i++)
if (_id[i] == pID) _id[i] = qID;
_length--;
}
}
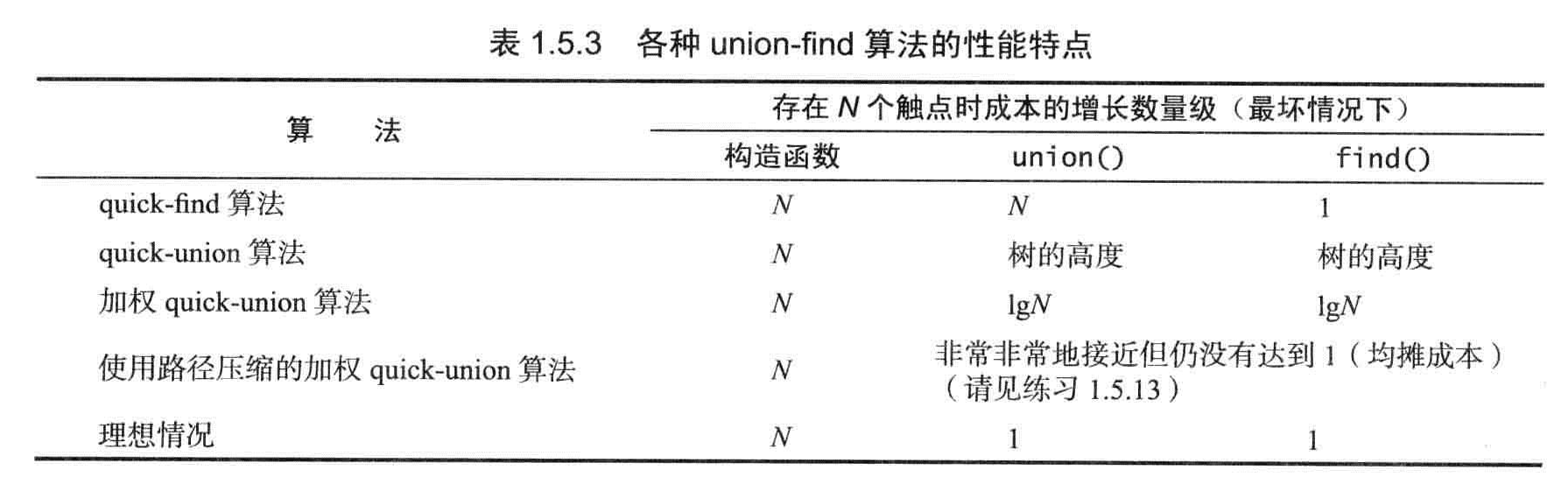
命题F:在Quick-find算法中,每次find()调用只需要访问id[]数组一次。而归并两个分量的union()操作访问数组的次数在(N+3)到(2N+1)之间。
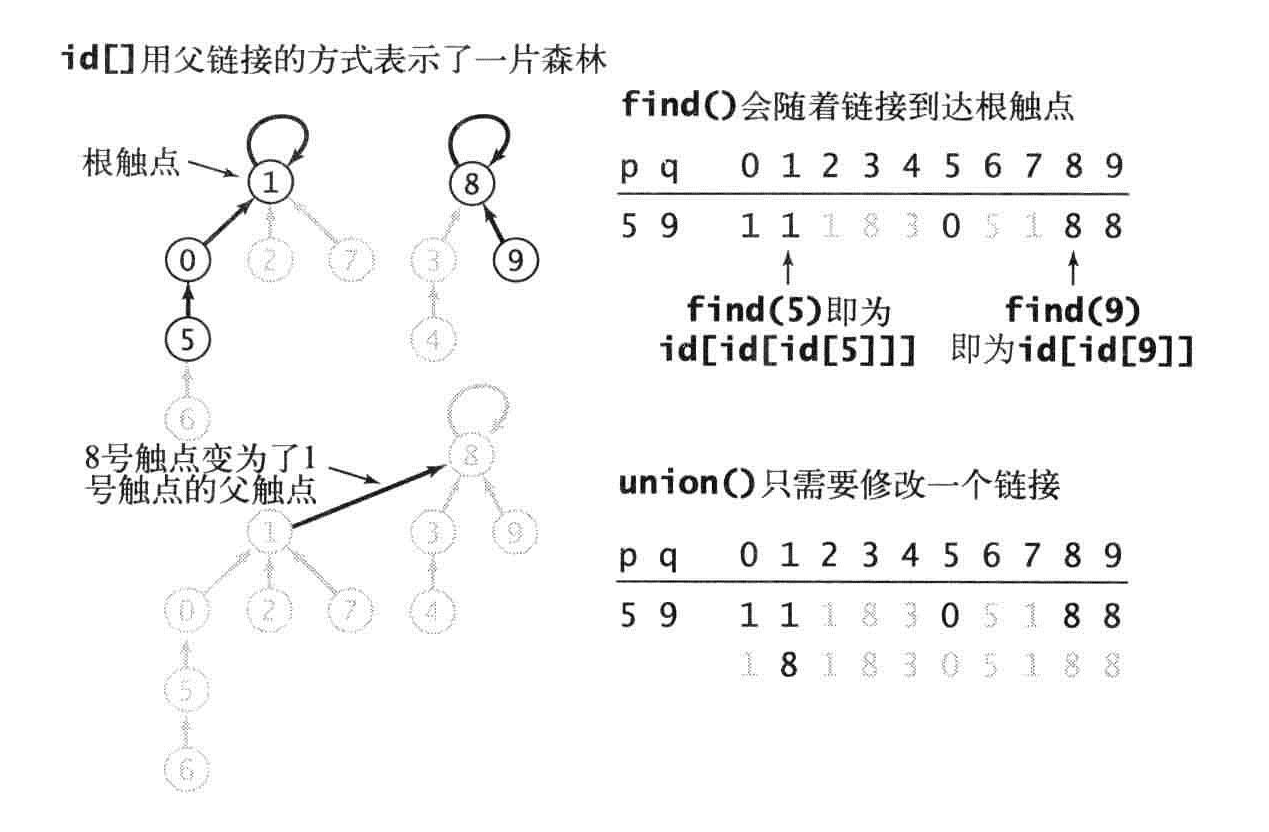
Quick-unit算法
还是以触点作为索引。每个触电对应的值是另一个触点(也可以是自己),这称为连接,find方法,从第一个触点开始,得到第二个触点,在得到第4个触点。
public class QuickUnionUF
{
private int[] _parent;
private int _length;
public QuickUnionUF(int length)
{
_parent = new int[length];
_length = length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
_parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int Length()
{
return _length;
}
public int Find(int p)
{
validate(p);
while (p != _parent[p])//找出分量
p = _parent[p];
return p;
}
// validate that p is a valid index
private void validate(int p)
{
int n = _parent.Length;
if (p < 0 || p >= n)
{
throw new ArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n - 1));
}
}
public bool Connected(int p, int q)
{
return Find(p) == Find(q);
}
public void Union(int p, int q)
{
//将P和Q的根节点统一
int rootP = Find(p);
int rootQ = Find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
_parent[rootP] = rootQ;
_length--;
}
}
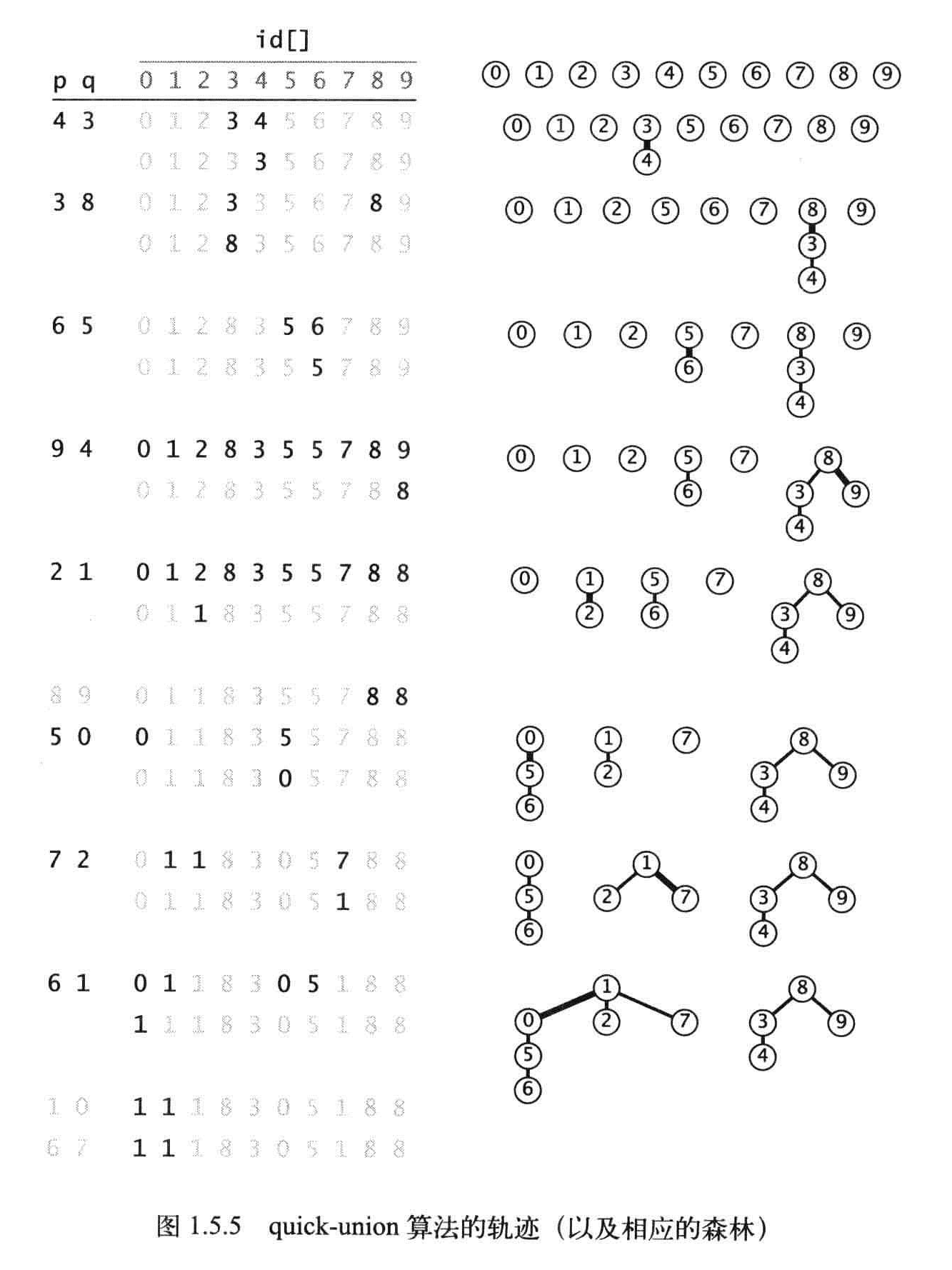
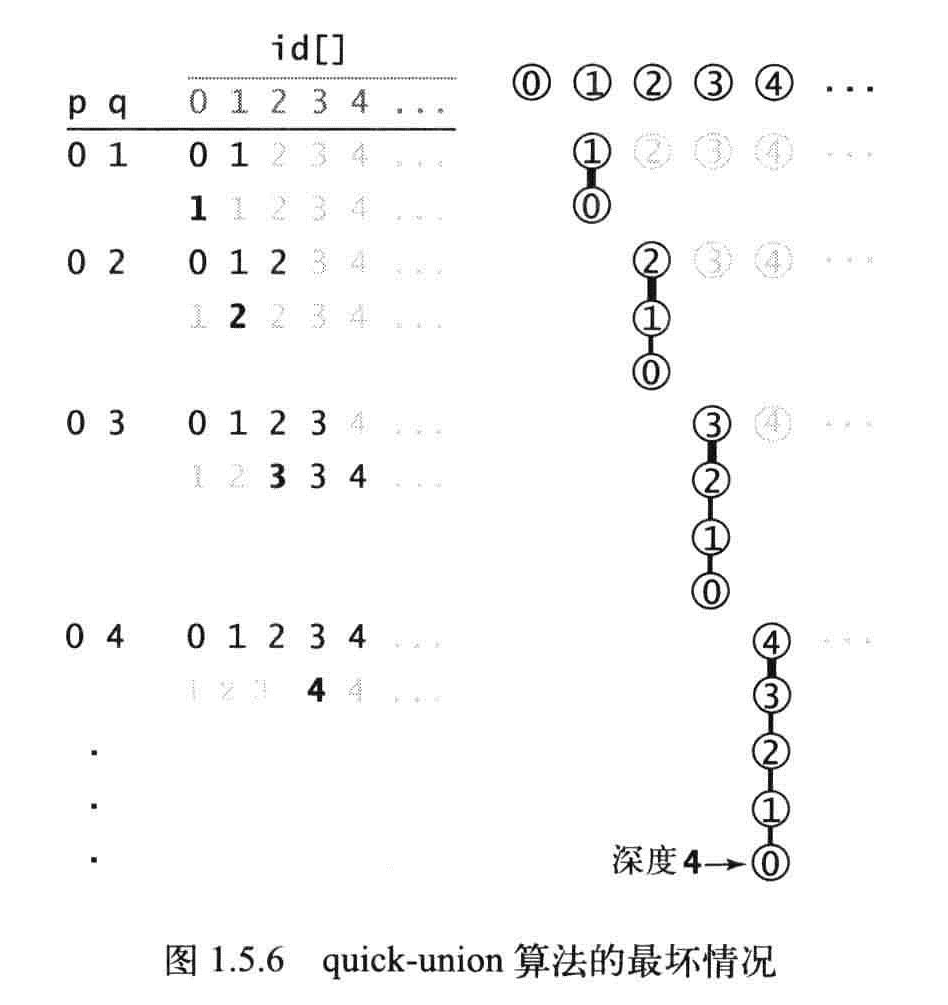
定义:一颗树的带下是它的结点的数量,树中的一个节点的深度是它到根节点的路径上的链接数。树的高度是它的所有节点中的最大深度。
命题G:Quick-Union算法中find()方法访问数组的次数为1加上给定触点对应的节点的深度的两倍,union和connected访问数组的次数为两次find操作。
最坏情况下还是N^2
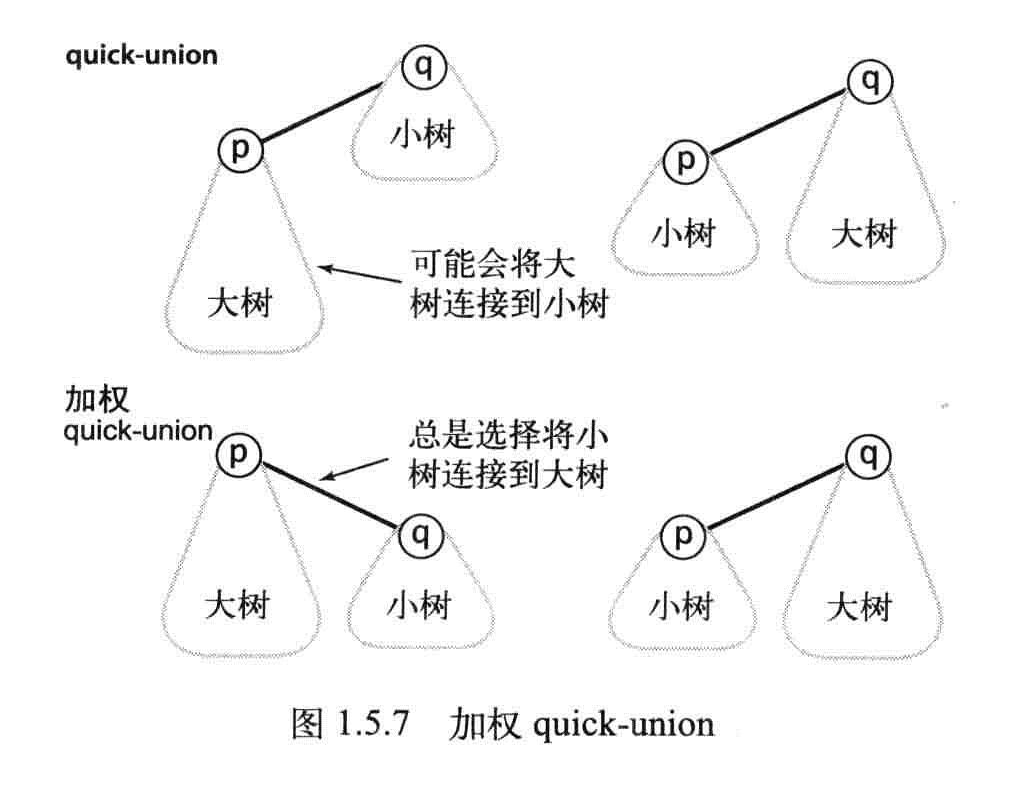
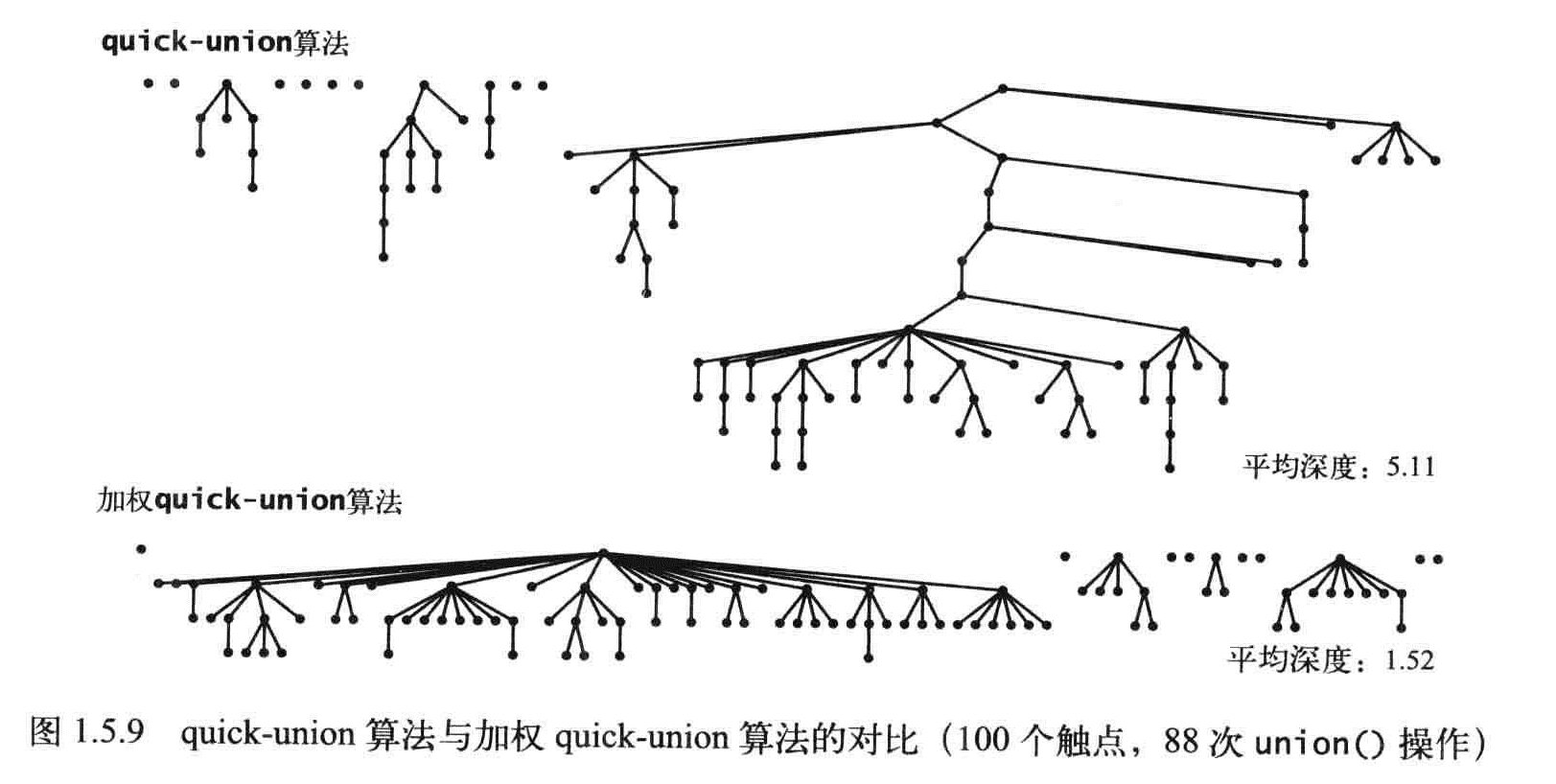
加权Quick-union算法
记录每棵树的大小并总是将较小的树连接到较大的树上。
public class WeightedQuickUnionUF
{
/// <summary>
/// 父链接数组(触点索引)
/// </summary>
private int[] _parent;
/// <summary>
/// 各个节点所对应权重的大小
/// </summary>
private int[] _size;
/// <summary>
/// 连通分量的数量
/// </summary>
private int _length;
public WeightedQuickUnionUF(int length)
{
_length = length;
_parent = new int[length];
_size = new int[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
_parent[i] = i;
_size[i] = 1;//刚开始所有权重为1
}
}
public int Length()
{
return _length;
}
public bool Connected(int p, int q)
{
return Find(p) == Find(q);
}
private void validate(int p)
{
int n = _parent.Length;
if (p < 0 || p >= n)
{
throw new ArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n - 1));
}
}
public int Find(int p)
{
validate(p);
while (p != _parent[p])
p = _parent[p];
return p;
}
public void Union(int p, int q)
{
int rootP = Find(p);
int rootQ = Find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
//将小树的根节点链接到大树的根节点
if (_size[rootP] < _size[rootQ])
{
_parent[rootP] = rootQ;
_size[rootQ] += _size[rootP];
}
else
{
_parent[rootQ] = rootP;//
_size[rootP] += _size[rootQ];
}
_length--;
}
}
命题H:对于N个触点,加权quick-union算法构造的森林中的任意节点的深度最多为logN。
推论:对于加权quick-union算法和N个触点,在最坏情况下find(),connected()和uniond的成本的增长数量级为logN。
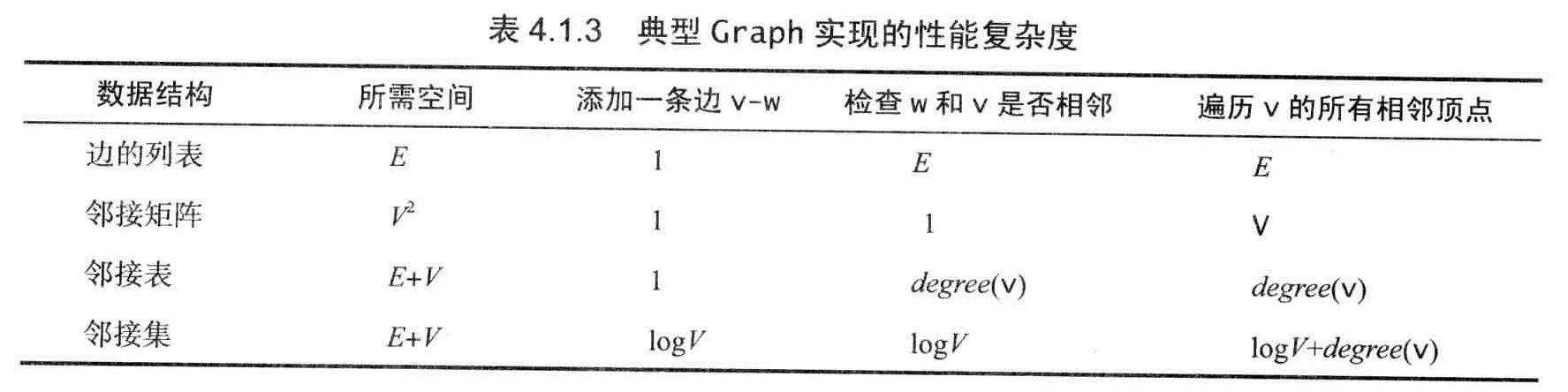
无向图
无向图:图是由一组顶点和一组能够将连个顶点相连的边组成的。
一般使用0-(V-1)来表示一张含有V个顶点的图中的各个顶点。用V-W的记法来表示连接V和W的边。
由两种特殊的图:
- 自环:一条连接一个顶点和自身的边
- 连接同一对顶点的两条边称为平行边。
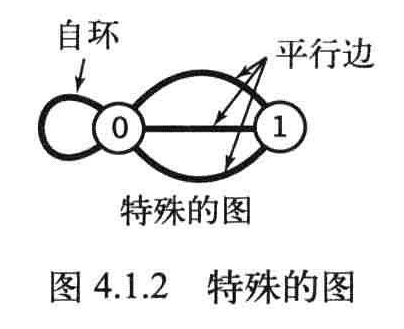
图的定义和绘出的图像无关
两个顶点通过同一条边相连时,称为这两个顶点是相邻的。并称该连接依附于这两个顶点。
顶点的度数表示依附于它的边总数,也就是连接到该顶点的边的条数。
子图是一幅图的所有边的一个子集(以及它们所依附的所有顶点)组成的图。
路径是边顺序连接一系列顶点。
简单路径是一条没有重复顶点的路径。
环是一条至少含有一条边且起点和终点相同的路径。
简单环:一条(除了起点和终点必须相同之外)不含有重复顶点和边的环。
长度:路径和环的长度为其包含的边数。
连通:如果两个顶点之间存在一条连接双方的路径时,一个顶点和另一个顶点是连通的。路径用u-v-w-x来表示这条u到x的路径。
连通图:从任意一个顶点都存在一条路径到达另一个任意顶点。
极大连通子图:一个非连通的图由若干连通子图组成。
无环图:不包含环的图。
树:一幅无环连通图。
森林:互不相连的树组成的集合。
连通图的生成树:是连通图的一个子集,它包含连通图中所有顶点并是一颗树。
图的生成树森林:所有连通子图的生成树的集合。

树的辨别条件,一幅含有V个结点的图G,满足一点就是树:
- G有V-1条边且不含有环;
- G有V-1条边是连通的;
- G是连通的,但删除任意一条边都会使它不再连通
- G是无环图,但添加任意一条边都会产生一条环。
- G中任意一对顶点之间仅存一条简单的路径。
图的密度:已经连接的顶点对占所有可能被连接顶点对的比列。
二分图:能够将所有结点分为两部分的图,图的每条边所连接的两个顶点都分别属于不同的部分。
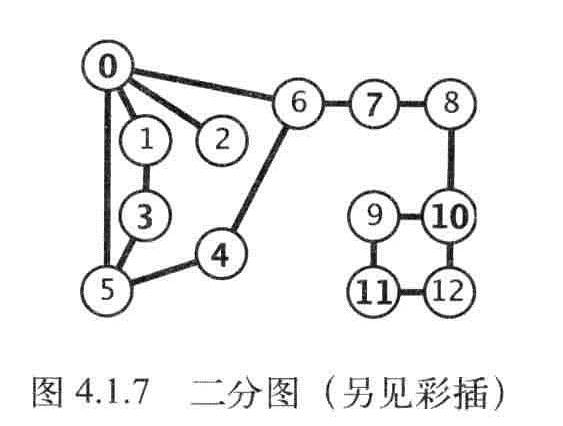
加粗的是一类,不加粗的是另一类
图的实现
图的数据表示:
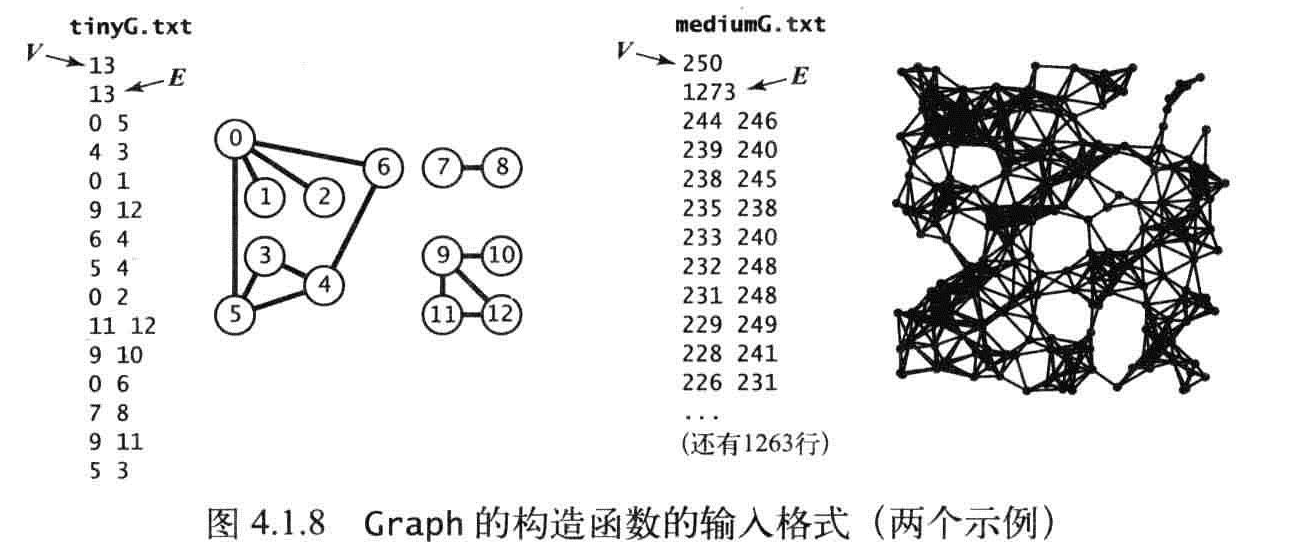
图的代码表示需要满足以下两个条件:
- 预留出足够的空间
- Graph的实例方法实现一定要快
代码是实现
- 邻接矩阵:使用一个V乘V的布尔矩阵,需要V^2个布尔值的空间,空间是不可能满足的,造成很多浪费。
- 边的数组,使用Edge类,含有两个int实例变量,不满足第二个。
- 邻接标数组:零点为索引的列表数组,每个元素都是和该顶点相邻的列表数组。
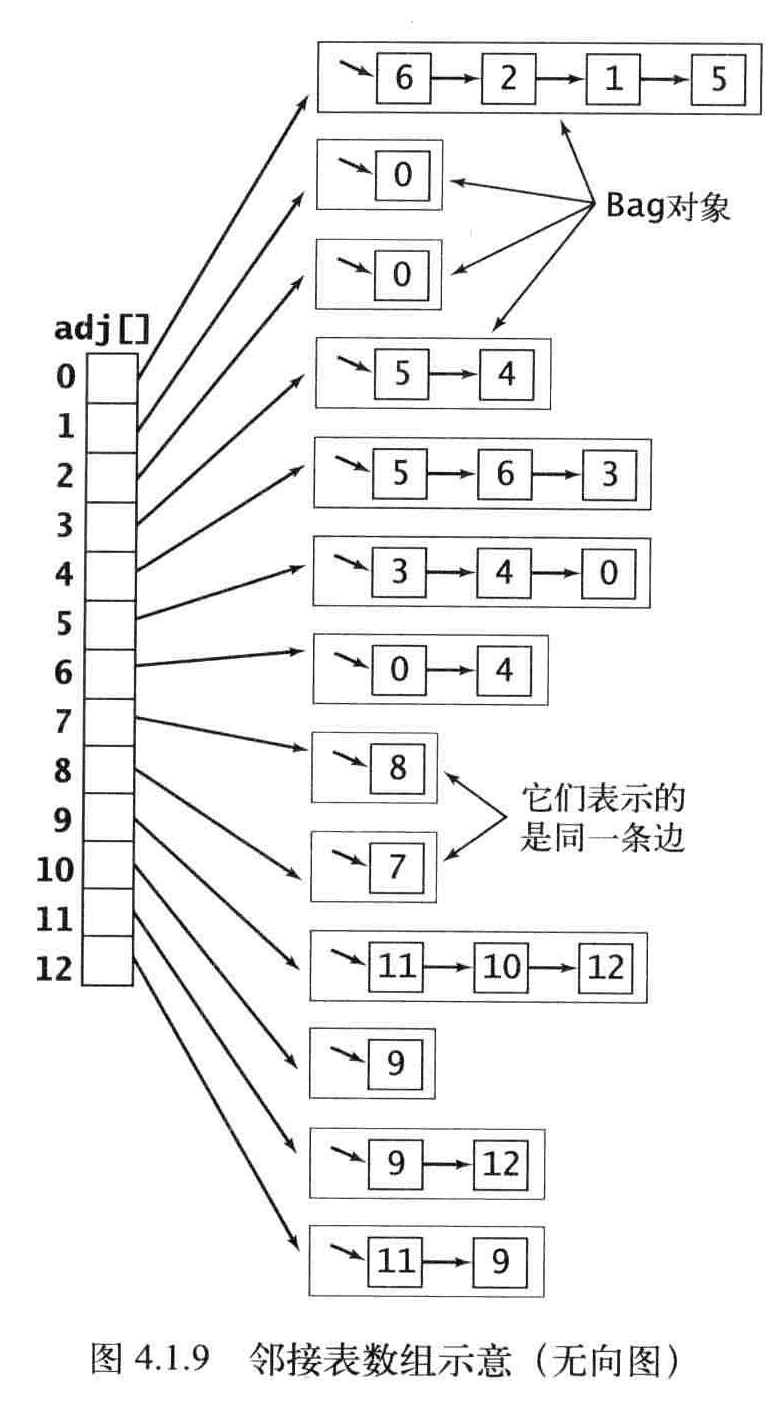
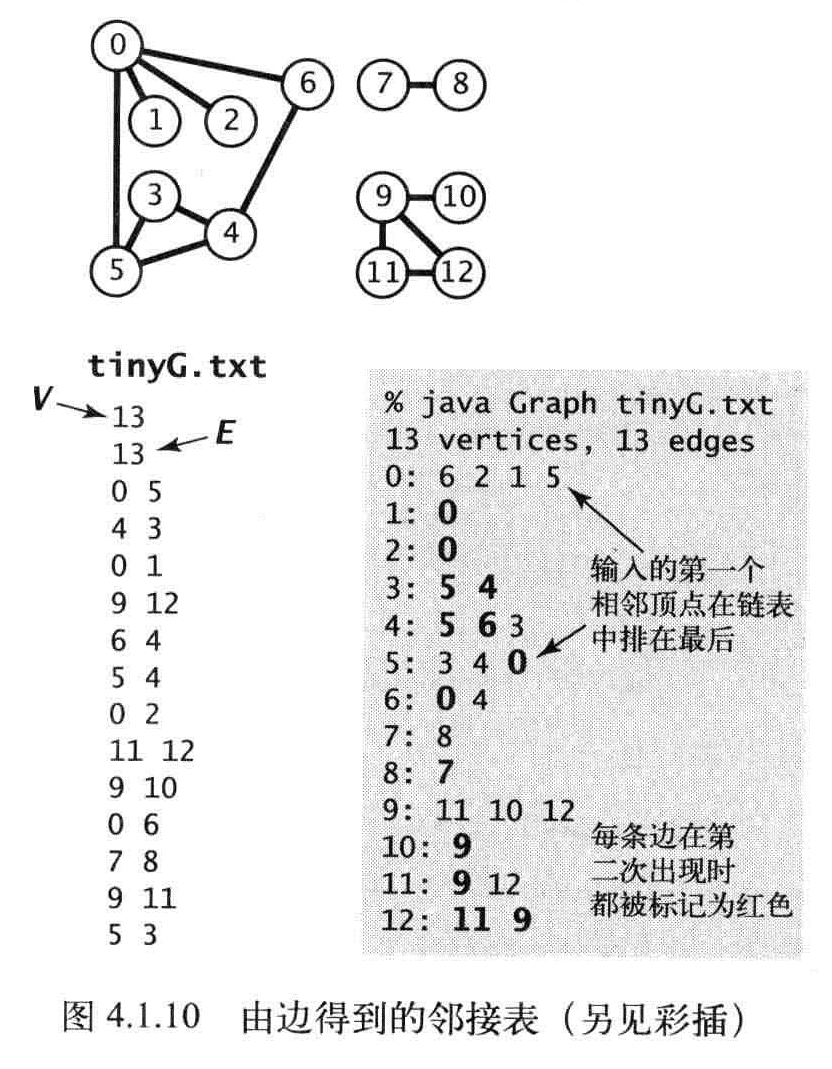
邻接标的特性:
- 使用的空间和V+E成正比;
- 添加一条边所需的时间为常数。
- 遍历顶点V的所有相邻点所需的时间和V的度数成正比(处理每个相邻顶点所需的时间为常数)
public class Graph
{
private static readonly string NEWLINE = System.Environment.NewLine;
private readonly int _vertices;
private int _edge;
private LinkedBagNet<int>[] _adj;
public int Vertices => _vertices;
public Graph(int vertices)
{
if (vertices < 1) throw new ArgumentException("this vertices is less than zero");
this._vertices = vertices;
this._edge = 0;
_adj = new LinkedBagNet<int>[vertices];
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
{
_adj[i] = new LinkedBagNet<int>();
}
}
public Graph(StreamReader stream)
{
if (stream == null) throw new ArgumentException("this stream is null");
try
{
var vertices = int.Parse(stream.ReadLine());
if (vertices < 1) throw new ArgumentException("this vertices value is too small");
this._vertices = vertices;
_adj = new LinkedBagNet<int>[vertices];
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
{
_adj[i] = new LinkedBagNet<int>();
}
int edge = int.Parse(stream.ReadLine());
if (edge < 1) throw new ArgumentException("this edges is too small");
for (int i = 0; i < edge; i++)
{
string line = stream.ReadLine();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(line) && line.Split(' ').Count() == 2)
{
int v =int.Parse( line.Split(' ')[0]);
int w =int.Parse( line.Split(' ')[1]);
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
AddEdge(v, w);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new ArgumentException("this readstream is not legitimate");
}
}
public Graph(Graph graph)
{
this._vertices = graph._vertices;
this._edge = graph._edge;
if(_vertices<1) throw new ArgumentException("this vertices is too small");
_adj=new LinkedBagNet<int>[_vertices];
for (int i = 0; i < _vertices; i++)
{
_adj[i]=new LinkedBagNet<int>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < _vertices; i++)
{
foreach (var value in graph._adj[i])
{
_adj[i].Add(value);
}
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
if (v < 0 || v > _vertices) throw new ArgumentException("this v does not in range");
}
public void AddEdge(int v, int w)
{
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
_edge++;
_adj[v].Add(w);
_adj[w].Add(v);
}
public int Degree(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _adj[v].Length;
}
}
图生成器
public static class GraphGenerator
{
private class Edge : IComparable<Edge>
{
private int _v;
private int _w;
public Edge(int v, int w)
{
if (v < w)
{
this._v = v;
this._w = w;
}
else
{
this._v = w;
this._w = v;
}
}
public int CompareTo(Edge other)
{
if (ReferenceEquals(this, other)) return 0;
if (ReferenceEquals(null, other)) return 1;
var vComparison = _v.CompareTo(other._v);
if (vComparison != 0) return vComparison;
var wComparison = _w.CompareTo(other._w);
if (wComparison != 0) return wComparison;
return 0;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 生成简单图
/// </summary>
/// <param name="V">顶点数量</param>
/// <param name="E">边的数量</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static Graph Simple(int V, int E)
{
if (E > (long)V * (V - 1) / 2) throw new ArgumentException("Too many edges");
if (E < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Too few edges");
Graph G = new Graph(V);
List<Edge> set = new List<Edge>();
var random=new Random();
while (G.Edge < E)
{
int v = random.Next(V);
int w = random.Next(V);
Edge e = new Edge(v, w);
if ((v != w) && !set.Contains(e))
{
set.Add(e);
G.AddEdge(v, w);
}
}
return G;
}
/// <summary>
/// 生成简单图
/// </summary>
/// <param name="V">顶点的数量</param>
/// <param name="p">选择边的概率</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static Graph Simple(int V, double p)
{
if (p < 0.0 || p > 1.0)
throw new ArgumentException("Probability must be between 0 and 1");
Graph G = new Graph(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
for (int w = v + 1; w < V; w++)
if (new Random().NextDouble()<p)
G.AddEdge(v, w);
return G;
}
public static Graph Complete(int V)
{
return Simple(V, 1.0);
}
/// <summary>
/// 在V1和V2顶点上返回完整的二分图
/// </summary>
/// <param name="V1"></param>
/// <param name="V2"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static Graph CompleteBipartite(int V1, int V2)
{
return Bipartite(V1, V2, V1 * V2);
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="V1"></param>
/// <param name="V2"></param>
/// <param name="E">边数</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static Graph Bipartite(int V1, int V2, int E)
{
if (E > (long)V1 * V2) throw new ArgumentException("Too many edges");
if (E < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Too few edges");
Graph G = new Graph(V1 + V2);
int[] vertices = new int[V1 + V2];
for (int i = 0; i < V1 + V2; i++)
vertices[i] = i;
vertices.Shuffle();
List<Edge> set = new List<Edge>();
Random randon=new Random();
while (G.Edge < E)
{
int i = randon.Next(V1);
int j = V1 + randon.Next(V2);
Edge e = new Edge(vertices[i], vertices[j]);
if (!set.Contains(e))
{
set.Add(e);
G.AddEdge(vertices[i], vertices[j]);
}
}
return G;
}
public static Graph Bipartite(int V1, int V2, double p)
{
if (p < 0.0 || p > 1.0)
throw new ArgumentException("Probability must be between 0 and 1");
int[] vertices = new int[V1 + V2];
for (int i = 0; i < V1 + V2; i++)
vertices[i] = i;
vertices.Shuffle();
Graph G = new Graph(V1 + V2);
for (int i = 0; i < V1; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < V2; j++)
if (new Random().NextDouble() < p)
G.AddEdge(vertices[i], vertices[V1 + j]);
return G;
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="V"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static Graph Path(int V)
{
Graph G = new Graph(V);
int[] vertices = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
vertices[i] = i;
vertices.Shuffle();
for (int i = 0; i < V - 1; i++)
{
G.AddEdge(vertices[i], vertices[i + 1]);
}
return G;
}
/// <summary>
/// 树图
/// </summary>
/// <param name="V">顶点数</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static Graph BinaryTree(int V)
{
Graph G = new Graph(V);
int[] vertices = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
vertices[i] = i;
vertices.Shuffle();
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++)
{
G.AddEdge(vertices[i], vertices[(i - 1) / 2]);
}
return G;
}
/// <summary>
/// 环图
/// </summary>
/// <param name="V"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static Graph Cycle(int V)
{
Graph G = new Graph(V);
int[] vertices = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
vertices[i] = i;
vertices.Shuffle();
for (int i = 0; i < V - 1; i++)
{
G.AddEdge(vertices[i], vertices[i + 1]);
}
G.AddEdge(vertices[V - 1], vertices[0]);
return G;
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="V"></param>
/// <param name="E"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static Graph EulerianCycle(int V, int E)
{
if (E <= 0)
throw new ArgumentException("An Eulerian cycle must have at least one edge");
if (V <= 0)
throw new ArgumentException("An Eulerian cycle must have at least one vertex");
Graph G = new Graph(V);
int[] vertices = new int[E];
Random random=new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
vertices[i] =random.Next(V);
for (int i = 0; i < E - 1; i++)
{
G.AddEdge(vertices[i], vertices[i + 1]);
}
G.AddEdge(vertices[E - 1], vertices[0]);
return G;
}
public static Graph EulerianPath(int V, int E)
{
if (E < 0)
throw new ArgumentException("negative number of edges");
if (V <= 0)
throw new ArgumentException("An Eulerian path must have at least one vertex");
Graph G = new Graph(V);
int[] vertices = new int[E + 1];
Random random=new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < E + 1; i++)
vertices[i] = random.Next(V);
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
G.AddEdge(vertices[i], vertices[i + 1]);
}
return G;
}
public static Graph Wheel(int V)
{
if (V <= 1) throw new ArgumentException("Number of vertices must be at least 2");
Graph G = new Graph(V);
int[] vertices = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
vertices[i] = i;
vertices.Shuffle();
// simple cycle on V-1 vertices
for (int i = 1; i < V - 1; i++)
{
G.AddEdge(vertices[i], vertices[i + 1]);
}
G.AddEdge(vertices[V - 1], vertices[1]);
// connect vertices[0] to every vertex on cycle
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++)
{
G.AddEdge(vertices[0], vertices[i]);
}
return G;
}
public static Graph Star(int V)
{
if (V <= 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of vertices must be at least 1");
Graph G = new Graph(V);
int[] vertices = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
vertices[i] = i;
vertices.Shuffle();
// connect vertices[0] to every other vertex
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++)
{
G.AddEdge(vertices[0], vertices[i]);
}
return G;
}
public static Graph Regular(int V, int k)
{
if (V * k % 2 != 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of vertices * k must be even");
Graph G = new Graph(V);
// create k copies of each vertex
int[] vertices = new int[V * k];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++)
{
vertices[v + V * j] = v;
}
}
// pick a random perfect matching
vertices.Shuffle();
for (int i = 0; i < V * k / 2; i++)
{
G.AddEdge(vertices[2 * i], vertices[2 * i + 1]);
}
return G;
}
public static Graph Tree(int V)
{
Graph G = new Graph(V);
// special case
if (V == 1) return G;
// Cayley's theorem: there are V^(V-2) labeled trees on V vertices
// Prufer sequence: sequence of V-2 values between 0 and V-1
// Prufer's proof of Cayley's theorem: Prufer sequences are in 1-1
// with labeled trees on V vertices
int[] prufer = new int[V - 2];
Random random=new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < V - 2; i++)
prufer[i] = random.Next(V);
// degree of vertex v = 1 + number of times it appers in Prufer sequence
int[] degree = new int[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
degree[v] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < V - 2; i++)
degree[prufer[i]]++;
// pq contains all vertices of degree 1
MinPQNet<int> pq = new MinPQNet<int>();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (degree[v] == 1) pq.Insert(v);
// repeatedly delMin() degree 1 vertex that has the minimum index
for (int i = 0; i < V - 2; i++)
{
int v = pq.DeleteMin();
G.AddEdge(v, prufer[i]);
degree[v]--;
degree[prufer[i]]--;
if (degree[prufer[i]] == 1) pq.Insert(prufer[i]);
}
G.AddEdge(pq.DeleteMin(), pq.DeleteMin());
return G;
}
public static int[] Shuffle(this int[] stack)
{
var random=new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < stack.Length; i++)
{
int temindex = random.Next(stack.Length);
if (i != temindex)
{
int tem = stack[i];
stack[i] = stack[temindex];
stack[temindex] = tem;
}
}
return stack;
}
public static void TestFunction(int V,int E)
{
int V1 = V / 2;
int V2 = V - V1;
Console.WriteLine("complete graph");
Console.WriteLine(Complete(V));
Console.WriteLine("simple");
Console.WriteLine(Simple(V, E));
Console.WriteLine("Erdos-Renyi");
double p = (double)E / (V * (V - 1) / 2.0);
Console.WriteLine(Simple(V, p));
Console.WriteLine("complete bipartite");
Console.WriteLine(CompleteBipartite(V1, V2));
Console.WriteLine("bipartite");
Console.WriteLine(Bipartite(V1, V2, E));
Console.WriteLine("Erdos Renyi bipartite");
double q = (double)E / (V1 * V2);
Console.WriteLine(Bipartite(V1, V2, q));
Console.WriteLine("path");
Console.WriteLine(Path(V));
Console.WriteLine("cycle");
Console.WriteLine(Cycle(V));
Console.WriteLine("binary tree");
Console.WriteLine(BinaryTree(V));
Console.WriteLine("tree");
Console.WriteLine(Tree(V));
Console.WriteLine("4-regular");
Console.WriteLine(Regular(V, 4));
Console.WriteLine("star");
Console.WriteLine(Star(V));
Console.WriteLine("wheel");
Console.WriteLine(Wheel(V));
}
}
图的处理算法
图的表示和实现是分开的
Search(Graph graph, int s):找到和起点S连通的所有顶点。
Marked(int v):v和s是连通的吗
从图中起点开始沿着路径到达其他顶点并标记每个路过的顶点。
深度优先算法(DFS)
查找所有节点
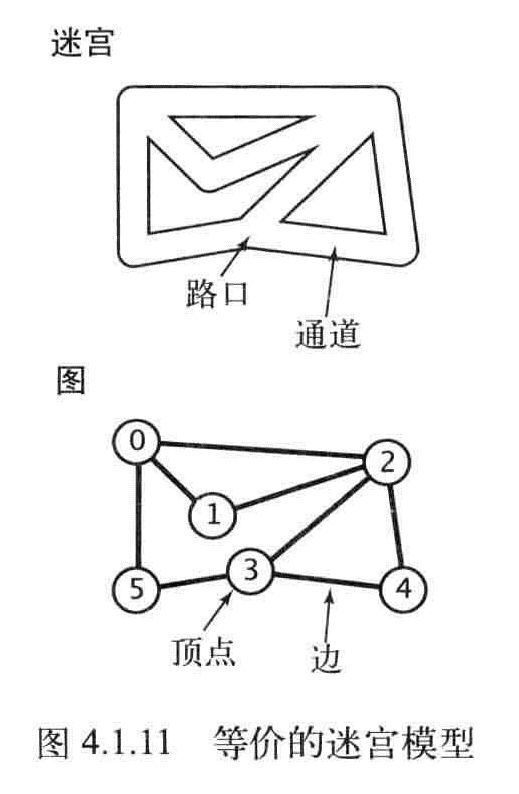
Tremaux搜索:
- 选择一条没有标记过的通道,在走过的路上铺一条绳子
- 标记所有第一次路过的路口和通道
- 当回退到路口已没有可走的通道时继续回退。
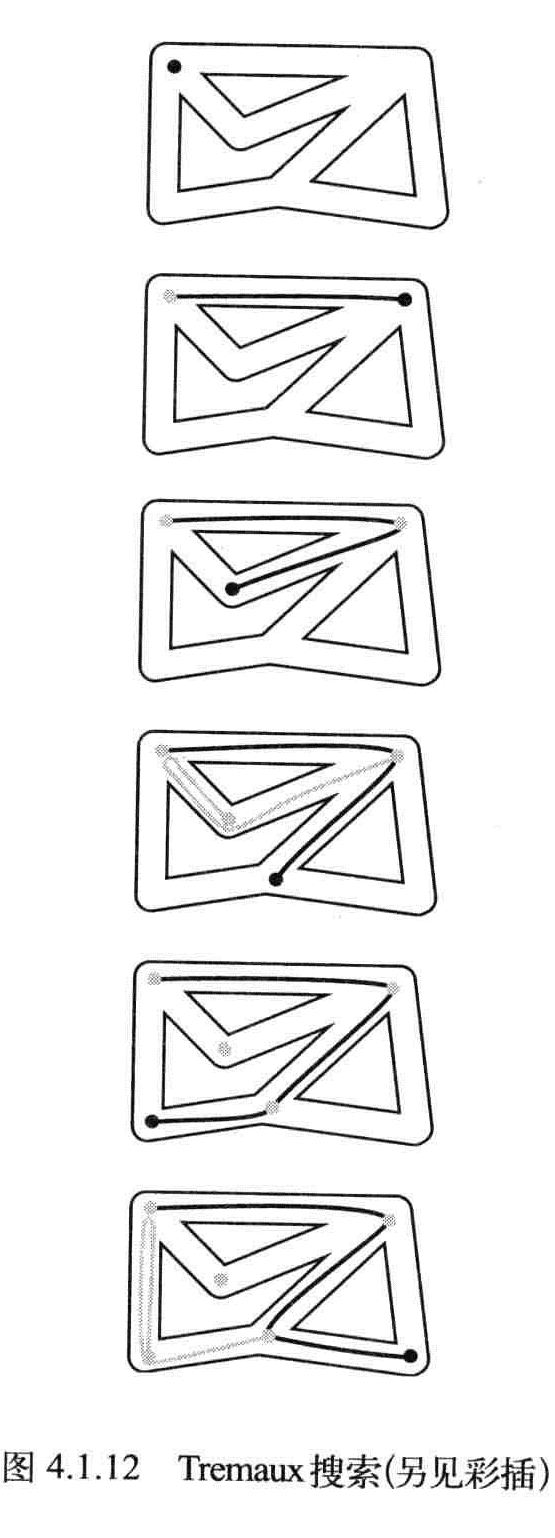
Tremaux可以保证找到一条路,但不能保证完全探索整张图。
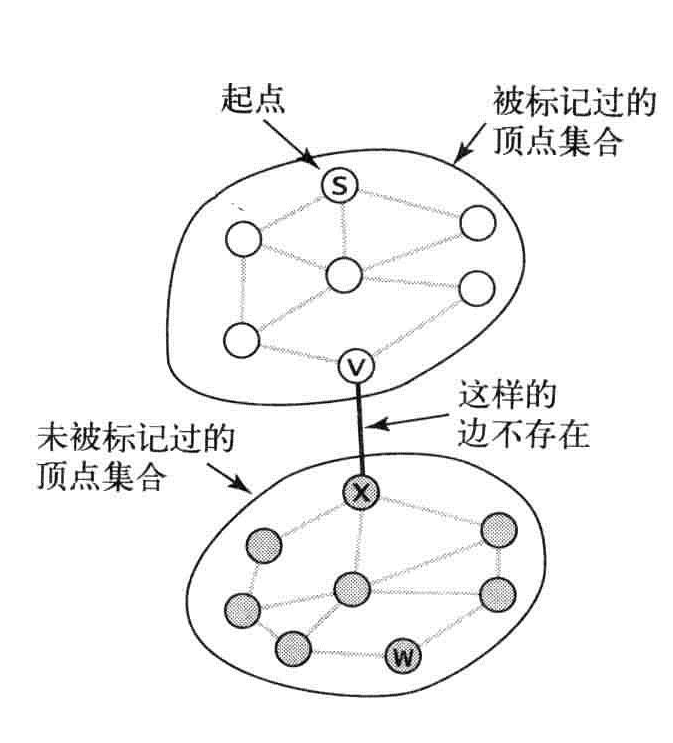
深度优先搜索:利用递归遍历所有的边和顶点,在访问一个顶点时,将它标记为已访问,递归地访问它所有没有被标记过的邻居顶点。
命题A:深度优先搜索标记与起点连通的所有顶点所需的时间和顶点的度数之和成正比。
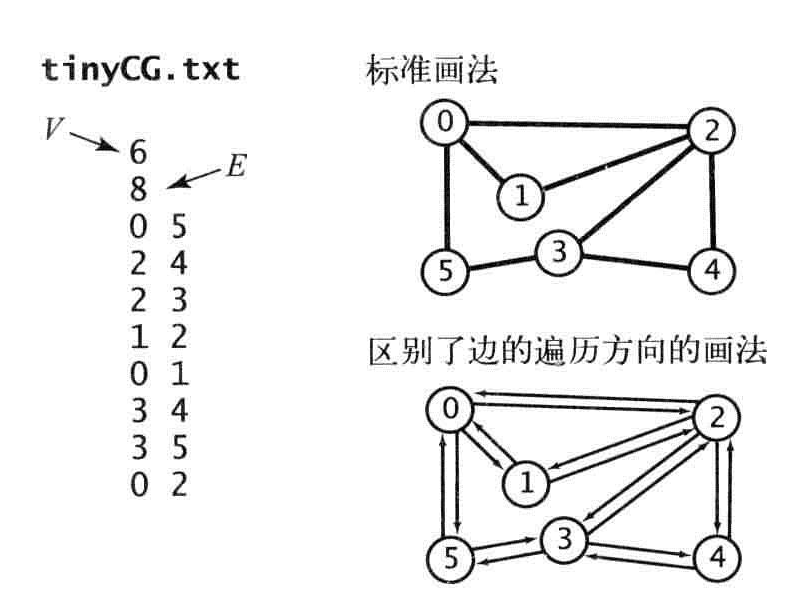
将图会化成单向通道,当V-W时,要么递归调用(w没有被标记过),要么跳过这条边(w已经被标记过),第二次从w-v遇到这条边,会忽略它,因为另一端v肯定被访问过。
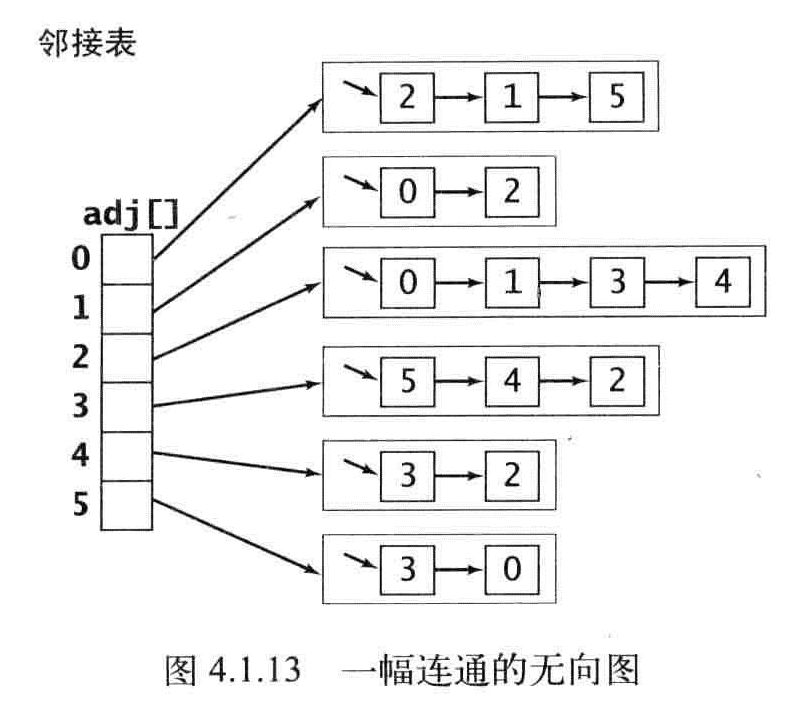
深度搜索每条边都被访问两次,第一次访问标记,第二次访问会发现这个顶点被标记过。
深度优先搜索示例
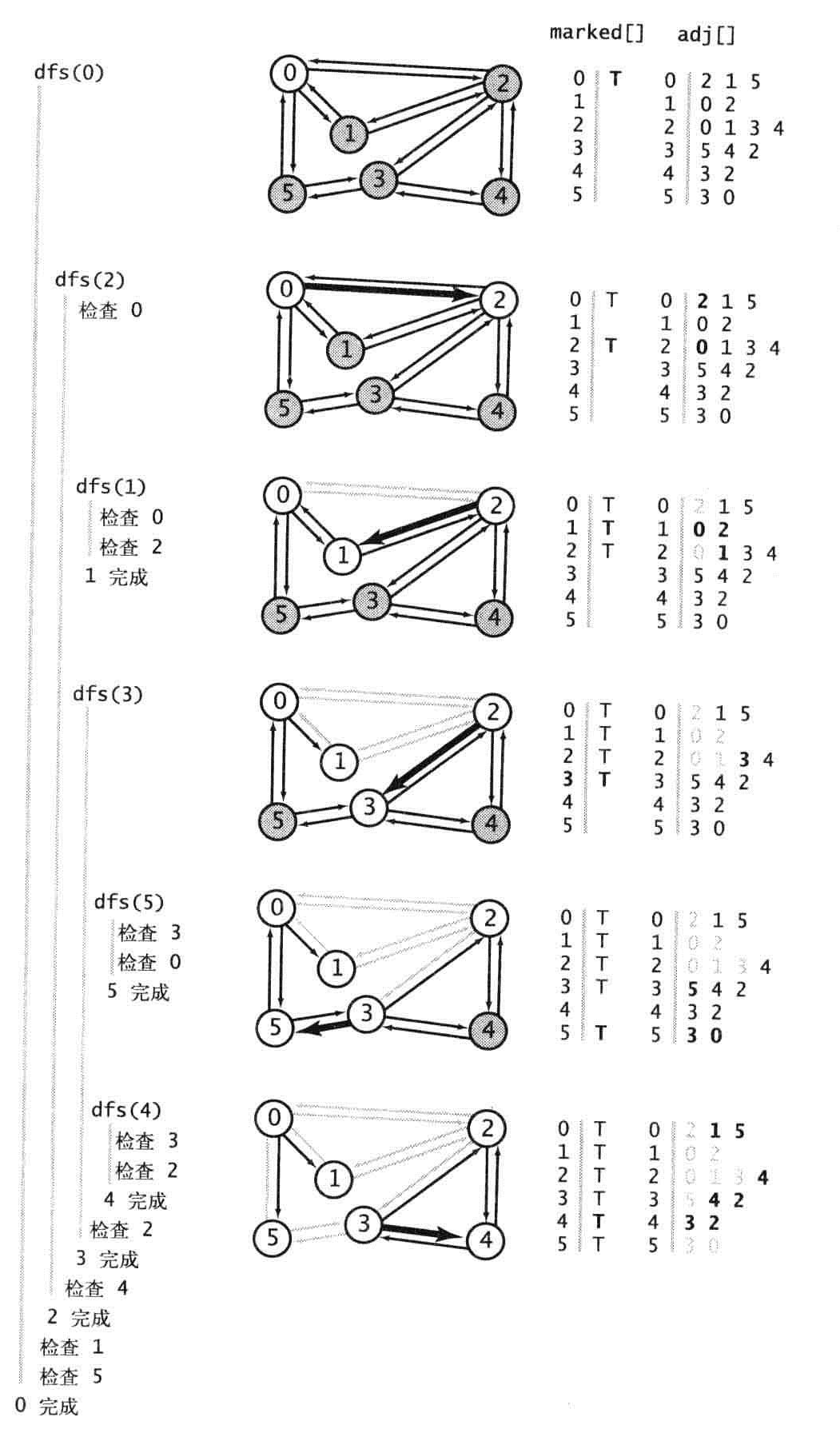
0邻接表2,1,5,优先访问2,
2邻接表0,1,3,4,0标记过,然后访问1,
1邻接表0,2,都标记过,访问3的邻接标
3邻接表,5,4,2,先访问5,再访问4,2被标记过,
这边应该再检查2邻接表中的4,所有点都访问过。
需要解决的问题:两个给定的顶点是否连通?有多少个连通子图?
public class DepthFirstSearch
{
private bool[] _marked;//s-v的路径记录
private int _count;//连接到s的顶点数量
public int Count => _count;
public DepthFirstSearch(Graph graph, int s)
{
_marked = new bool[graph.Vertices];
validateVertex(s);
dfs(graph,s);
}
private void dfs(Graph G, int v)
{
_count++;
_marked[v] = true;//访问过的节点为true
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
dfs(G, w);//递归调用
}
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
public bool Marked(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _marked[v];
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void DepthFirstTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\tinyG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph graph = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph(stream);
Console.WriteLine($"Graph vertices:{graph.Vertices}");
DepthFirstSearch search = new DepthFirstSearch(graph, 1);
for (int v = 0; v < graph.Vertices; v++)
{
if(search.Marked(v))
Console.Write(v+" ");
}
}
}
//Graph vertices:13
//0 1 2 3 4 5 6
深度搜索:无递归
/// <summary>
/// 深度优先算法,无递归
/// </summary>
public class NonrecursiveDFS
{
private bool[] _marked;
public NonrecursiveDFS(Graph G, int s)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
validateVertex(s);
// 保存邻接表
IEnumerator[] adj = new IEnumerator<int>[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
adj[v] = G.Adj.GetEnumerator();
// 需要一个额外的栈来存放节点
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
_marked[s] = true;
stack.Push(s);
while (stack.Any())
{
int v = stack.Peek();
if (adj[v].MoveNext())
{
int w =(int) adj[v].Current;
if (!_marked[w])
{
//标记节点
_marked[w] = true;
stack.Push(w);//压栈
}
}
else
{
stack.Pop();//访问完该节点的所有邻接点,出栈
}
}
}
public bool Marked(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _marked[v];
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
深度优先算法是查找所有的节点。
寻找所有路径

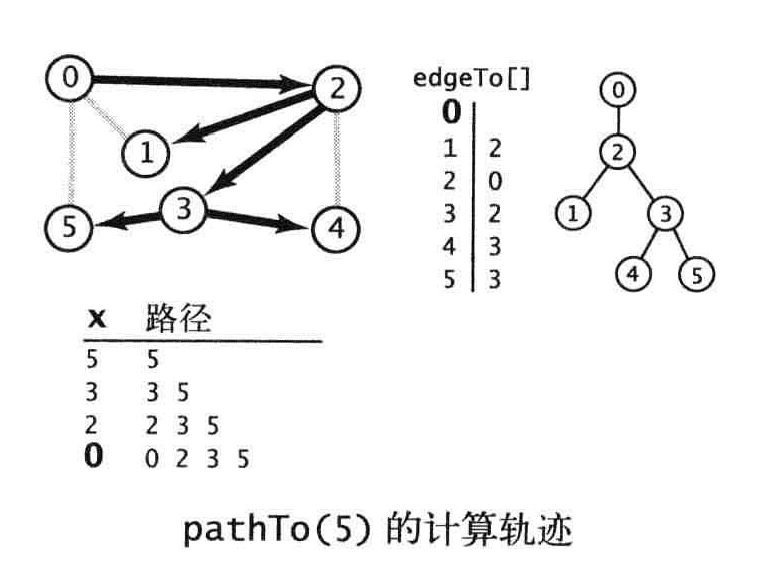
通过添加实例变量edgeTo()整型数组来模仿Tremaux搜索中绳子的作用。它用来记录每个顶点到起点的路径。
public class DepthFirstPaths
{
private bool[] _marked;
private int[] _edgeTo;
/// <summary>
/// start
/// </summary>
private readonly int _start;
public DepthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s)
{
this._start = s;
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
validateVertex(s);
dfs(G, s);
}
private void dfs(Graph G, int v)
{
_marked[v] = true;
foreach(int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
_edgeTo[w] = v;//通到w是v
dfs(G, w);
}
}
}
public bool HasPathTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _marked[v];
}
public IEnumerable<int> PathTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
if (!HasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<int> path = new Stack<int>();//通过栈先进后出
for (int x = v; x != _start; x = _edgeTo[x])
path.Push(x);
path.Push(_start);
return path;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试代码:
[TestMethod()]
public void DepthFirstPathsTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\tinyG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph graph = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph(stream);
Console.WriteLine($"Graph vertices:{graph.Vertices}");
DepthFirstPaths dfs = new DepthFirstPaths(graph, 1);
for (int v = 0; v < graph.Vertices; v++)
{
if (dfs.HasPathTo(v))
{
Console.Write($"1 to {v}: ");
foreach (int x in dfs.PathTo(v))
{
if (x == 1) Console.Write(x);
else Console.Write("-" + x);
}
Console.Write(System.Environment.NewLine);
}
else
{
Console.Write($"1 to {v}: not connected
");
}
}
}
//Graph vertices:13
//1 to 0: 1 - 0
//1 to 1: 1
//1 to 2: 1 - 0 - 2
//1 to 3: 1 - 0 - 6 - 4 - 5 - 3
//1 to 4: 1 - 0 - 6 - 4
//1 to 5: 1 - 0 - 6 - 4 - 5
//1 to 6: 1 - 0 - 6
//1 to 7: not connected
//1 to 8: not connected
//1 to 9: not connected
//1 to 10: not connected
//1 to 11: not connected
//1 to 12: not connected
}
edgeTo的轨迹
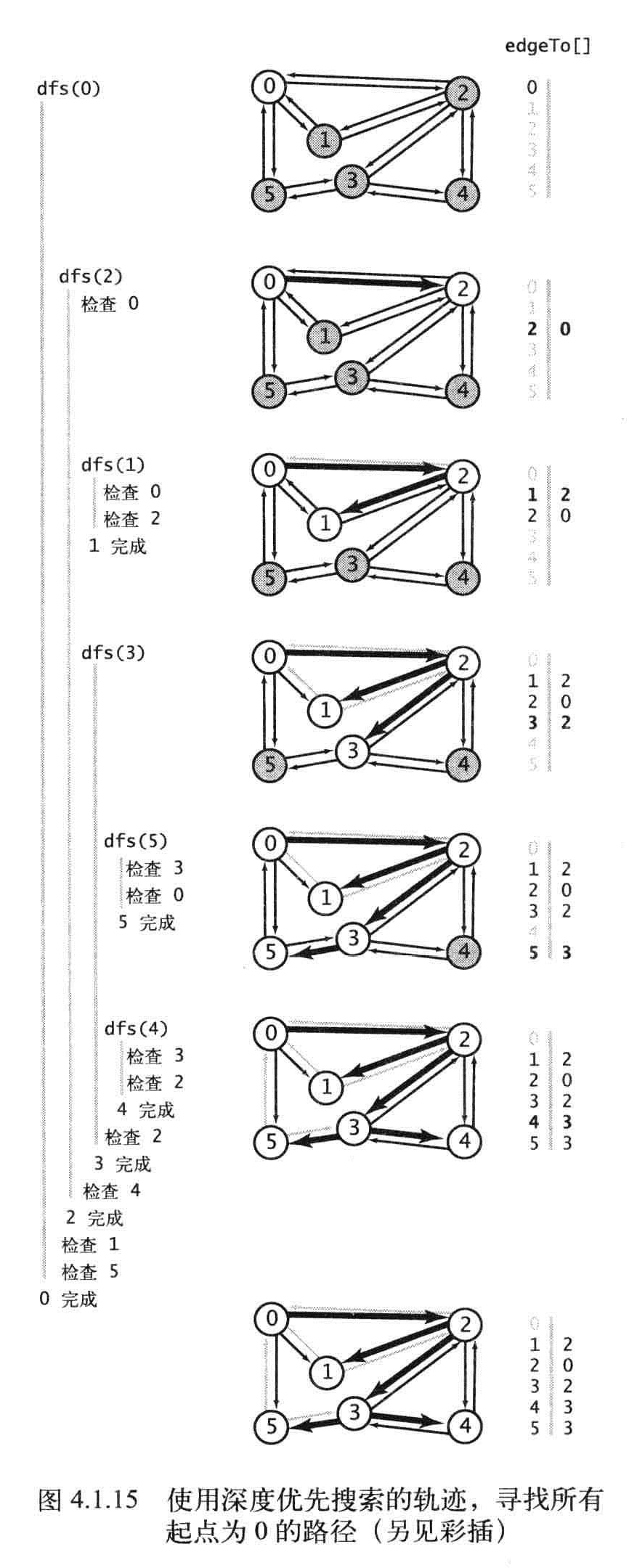
命题A:使用深度优先搜索得到从给定起点到任意标记顶点的路径所需的时间与路径的长度成正比。
连通分量
找出图中所有的连通分量,与……连通。
public class CC
{
private bool[] _marked;
private int[] _id; // id[v] ,v所在连通分量的标识符
private int _count; // 连通分量的数量
public CC(Graph G)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_id = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
if (!_marked[v])
{
dfs(G, v);
_count++;//从不同顶点开始遍历,遇到没有标记过的顶点,连通分量加一
}
}
}
private void dfs(Graph G, int v)
{
_marked[v] = true;
_id[v] = _count;
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])//这边使用的是深度优先
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
dfs(G, w);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// v所在连通分量表示符
/// </summary>
/// <param name="v"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Id(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _id[v];
}
public int Count()
{
return _count;
}
public bool Connected(int v, int w)
{
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return Id(v) == Id(w);
}
public bool AreConnected(int v, int w)
{
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return Id(v) == Id(w);
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试代码
[TestMethod()]
public void CCTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\tinyG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph(stream);
CC cc = new CC(G);
// number of connected components
int m = cc.Count();
Console.WriteLine(m + " components ");
// compute list of vertices in each connected component
Queue<int>[] components = new Queue<int>[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
components[i] = new Queue<int>();
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
components[cc.Id(v)].Enqueue(v);
}
// print results
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
foreach (int v in components[i])
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.Write(System.Environment.NewLine);
}
//3 components
//0 1 2 3 4 5 6
//7 8
//9 10 11 12
}
}
命题C:深度优先搜索的预处理使用的时间和空间与V+E成正比且可以在常数时间内处理关于图的连通性查询。

二分图
二分图:能够将所有结点分为两部分的图,图的每条边所连接的两个顶点都分别属于不同的部分。
/// <summary>
/// 二分图:能够将所有结点分为两部分的图,图的每条边所连接的两个顶点都分别属于不同的部分。
/// 深度优先搜索
/// </summary>
public class Bipartite
{
/// <summary>
/// 是否是二分图
/// </summary>
private bool _isBipartite;
/// <summary>
/// 用来区分节点颜色
/// </summary>
private bool[] _color;
/// <summary>
/// 是否被访问过
/// </summary>
private bool[] _marked;
private int[] _edgeTo;
/// <summary>
/// 用来保存一次奇循环
/// </summary>
private Stack<int> _cycle;
public bool IsBipartite => _isBipartite;
public Bipartite(Graph G)
{
_isBipartite = true;
_color = new bool[G.Vertices];
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
if (!_marked[v])
{
dfs(G, v);
}
}
}
private void dfs(Graph G, int v)
{
_marked[v] = true;
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
// short circuit if odd-length cycle found
if (_cycle != null) return;
// found uncolored vertex, so recur
if (!_marked[w])
{
_edgeTo[w] = v;
_color[w] = !_color[v];//颜色与顶点颜色想反
dfs(G, w);//深度优先算法
}
else if (_color[w] == _color[v])//如果被访问过,顶点颜色又一样,那么肯定不是二分图
{
_isBipartite = false;
_cycle = new Stack<int>();//记录连通分量
_cycle.Push(w);
for (int x = v; x != w; x = _edgeTo[x])
{
_cycle.Push(x);
}
_cycle.Push(w);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 节点颜色
/// </summary>
/// <param name="v"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Color(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
if (!_isBipartite)
throw new ArgumentException("graph is not bipartite");
return _color[v];
}
public IEnumerable<int> oddCycle()
{
return _cycle;
}
private bool check(Graph G)
{
// graph is bipartite
if (_isBipartite)
{
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (_color[v] == _color[w])
{
Console.Write($"edge {v}-{w} with {v} and {w} in same side of bipartition
");
return false;
}
}
}
}
// graph has an odd-length cycle
else
{
// verify cycle
int first = -1, last = -1;
foreach (int v in oddCycle())
{
if (first == -1) first = v;
last = v;
}
if (first != last)
{
Console.Write($"cycle begins with {first} and ends with {last}
", first, last);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void BipartiteTest()
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph G = GraphGenerator.Bipartite(6, 6, 10);
//Random random=new Random();
//for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
//{
// int v = random.Next(10);
// int w = random.Next(10);
// G.AddEdge(v, w);
//}
Bipartite b=new Bipartite(G);
if (b.IsBipartite)
{
Console.Write("Graph is bipartite: ");
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
Console.Write(v + ": " + b.Color(v)+"; ");
}
}
else
{
Console.Write("Graph has an odd-length cycle: ");
foreach (int x in b.oddCycle())
{
Console.Write(x + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
无环图
public class Cycle
{
private bool[] _marked;
private int[] _edgeTo;
private Stack<int> _cycle;
public Cycle(Graph G)
{
if (hasSelfLoop(G)) return;
if (hasParallelEdges(G)) return;
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (!_marked[v])
dfs(G, -1, v);
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查自环
/// </summary>
/// <param name="G"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool hasSelfLoop(Graph G)
{
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (v == w)
{
_cycle = new Stack<int>();
_cycle.Push(v);
_cycle.Push(v);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查平行边
/// </summary>
/// <param name="G"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool hasParallelEdges(Graph G)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
//平行边就是邻接矩阵中有相同项
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (_marked[w])
{
_cycle = new Stack<int>();
_cycle.Push(v);
_cycle.Push(w);
_cycle.Push(v);
return true;
}
_marked[w] = true;
}
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
_marked[w] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
public bool HasCycle()
{
return _cycle != null;
}
public IEnumerable<int> GetCycle()
{
return _cycle;
}
private void dfs(Graph G, int u, int v)
{
_marked[v] = true;
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (_cycle != null) return;
if (!_marked[w])
{
_edgeTo[w] = v;
dfs(G, v, w);
}
else if (w != u)//如果周围的项有重复并且不是自环
{
_cycle = new Stack<int>();
for (int x = v; x != w; x = _edgeTo[x])
{
_cycle.Push(x);
}
_cycle.Push(w);
_cycle.Push(v);
}
}
}
}
测试:
[TestMethod()]
public void CycleTest()
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph G = GraphGenerator.Cycle(15);
Cycle finder=new Cycle(G);
if (finder.HasCycle())
{
foreach (int v in finder.GetCycle())
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Graph is acyclic");
}
}
欧拉环
欧拉环:恰好包含了所有的边且没用重复的环,欧拉环就是欧拉路径起点和终点一样。
/// <summary>
/// 欧拉环:恰好包含所有的边且没有重复的环
/// </summary>
public class EulerianCycle
{
private Stack<int> _cycle = new Stack<int>();
/// <summary>
/// 无状态边
/// 指示是否被使用
/// </summary>
private class Edge
{
public int V;
public int W;
public bool IsUsed;
public Edge(int v, int w)
{
this.V = v;
this.W = w;
IsUsed = false;
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回边的另一个顶点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="vertex"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Other(int vertex)
{
if (vertex == V) return W;
else if (vertex == W) return V;
else throw new ArgumentException("Illegal endpoint");
}
}
public EulerianCycle(Graph G)
{
// 至少含有一个边
if (G.Edge == 0) return;
// 所有的顶点都具有偶数度
// 否则会找到的欧拉路径肯能不是环
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (G.Degree(v) % 2 != 0)
return;
// 创建邻接表本地副本,一次迭代一个顶点
Queue<Edge>[] adj = new Queue<Edge>[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
adj[v] = new Queue<Edge>();
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
int selfLoops = 0;
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
//小心自环
if (v == w)
{
if (selfLoops % 2 == 0)
{
Edge e = new Edge(v, w);
adj[v].Enqueue(e);//顶点对应的边
adj[w].Enqueue(e);
}
selfLoops++;//自环统计
}
else if (v < w)
{
Edge e = new Edge(v, w);
adj[v].Enqueue(e);
adj[w].Enqueue(e);
}
}
}
// 非单独的顶点,确定起始点
int s = nonIsolatedVertex(G);
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
stack.Push(s);
//使用深度搜索
_cycle = new Stack<int>();
while (stack.Any())
{
int v = stack.Pop();
while (adj[v].Any())
{
Edge edge = adj[v].Dequeue();
if (edge.IsUsed) continue;
edge.IsUsed = true;
stack.Push(v);
v = edge.Other(v);
}
_cycle.Push(v);
}
// 确定所有的边都是用
if (_cycle.Count != G.Vertices + 1)
_cycle = null;
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回欧拉环的顶点
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerable<int> GetCycle()
{
return _cycle;
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否存在欧拉环
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool hasEulerianCycle()
{
return _cycle != null;
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回单独的顶点,如果不是单独的顶点返回该顶点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="G"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private static int nonIsolatedVertex(Graph G)
{
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (G.Degree(v) > 0)
return v;
return -1;
}
private static bool satisfiesNecessaryAndSufficientConditions(Graph G)
{
// Condition 0: at least 1 edge
if (G.Edge == 0) return false;
// Condition 1: degree(v) is even for every vertex
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (G.Degree(v) % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Condition 2: graph is connected, ignoring isolated vertices
int s = nonIsolatedVertex(G);
BreadthFirstPaths bfs = new BreadthFirstPaths(G, s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (G.Degree(v) > 0 && !bfs.HasPathTo(v))
return false;
return true;
}
private bool certifySolution(Graph G)
{
// internal consistency check
if (hasEulerianCycle() == (GetCycle() == null)) return false;
// hashEulerianCycle() returns correct value
if (hasEulerianCycle() != satisfiesNecessaryAndSufficientConditions(G)) return false;
// nothing else to check if no Eulerian cycle
if (_cycle == null) return true;
// check that cycle() uses correct number of edges
if (_cycle.Count() != G.Edge + 1) return false;
// check that cycle() is a cycle of G
// TODO
// check that first and last vertices in cycle() are the same
int first = -1, last = -1;
foreach (int v in GetCycle())
{
if (first == -1) first = v;
last = v;
}
if (first != last) return false;
return true;
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void EulerianCycleTest()
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph G = GraphGenerator.EulerianCycle(5, 5);
EulerianCycle euler = new EulerianCycle(G);
if (euler.hasEulerianCycle())
{
foreach (int v in euler.GetCycle())
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.Write("none");
}
Console.WriteLine();
//1 2 3 3 3 1
}
欧拉路径
欧拉路径:一个路径包括每个边恰好一次
public class EulerianPath
{
private Stack<int> _path = null;
private class Edge
{
public int V;
public int W;
public bool IsUsed;
public Edge(int v, int w)
{
this.V = v;
this.W = w;
IsUsed = false;
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回边的另一个顶点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="vertex"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Other(int vertex)
{
if (vertex == V) return W;
else if (vertex == W) return V;
else throw new ArgumentException("Illegal endpoint");
}
}
public EulerianPath(Graph G)
{
// 查找欧拉路径的起点
// 如果有顶点的度数是奇数,那么不符合欧拉路径
// 每个顶点至少有偶数度
int oddDegreeVertices = 0;
int s = nonIsolatedVertex(G);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
if (G.Degree(v) % 2 != 0)
{
oddDegreeVertices++;
s = v;
}
}
// 一个图的奇数顶点最多只有2个起点和终点。
if (oddDegreeVertices > 2) return;
// 一种特殊的没有边的图
if (s == -1) s = 0;
// 创建本地邻接表
Queue<Edge>[] adj = new Queue<Edge>[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
adj[v] = new Queue<Edge>();
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
int selfLoops = 0;
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
// 自环
if (v == w)
{
if (selfLoops % 2 == 0)
{
Edge e = new Edge(v, w);
adj[v].Enqueue(e);
adj[w].Enqueue(e);
}
selfLoops++;
}
else if (v < w)
{
Edge e = new Edge(v, w);
adj[v].Enqueue(e);
adj[w].Enqueue(e);
}
}
}
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
stack.Push(s);
// 深度搜索
_path = new Stack<int>();
while (stack.Any())
{
int v = stack.Pop();
while (adj[v].Any())//所有的边
{
Edge edge = adj[v].Dequeue();//使用过的边就弹出
if (edge.IsUsed) continue;
edge.IsUsed = true;
stack.Push(v);
v = edge.Other(v);//探索边的另一个顶点
}
// 记录路径
_path.Push(v);
}
// 如果所有的边都用了
if (_path.Count != G.Edge + 1)
_path = null;
}
public IEnumerable<int> Path()
{
return _path;
}
public bool HasEulerianPath()
{
return _path != null;
}
private static int nonIsolatedVertex(Graph G)
{
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (G.Degree(v) > 0)
return v;
return -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 必要和充分条件
/// </summary>
/// <param name="G"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private static bool satisfiesNecessaryAndSufficientConditions(Graph G)
{
if (G.Edge == 0) return true;
// Condition 1: degree(v) is even except for possibly two
int oddDegreeVertices = 0;
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (G.Degree(v) % 2 != 0)
oddDegreeVertices++;
if (oddDegreeVertices > 2) return false;
// Condition 2: graph is connected, ignoring isolated vertices
int s = nonIsolatedVertex(G);
BreadthFirstPaths bfs = new BreadthFirstPaths(G, s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (G.Degree(v) > 0 && !bfs.HasPathTo(v))
return false;
return true;
}
private bool certifySolution(Graph G)
{
// internal consistency check
if (HasEulerianPath() == (_path == null)) return false;
// hashEulerianPath() returns correct value
if (HasEulerianPath() != satisfiesNecessaryAndSufficientConditions(G)) return false;
// nothing else to check if no Eulerian path
if (_path == null) return true;
// check that path() uses correct number of edges
if (_path.Count != G.Edge + 1) return false;
// check that path() is a path in G
// TODO
return true;
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void EulerianPathTest()
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph G = GraphGenerator.EulerianCycle(5, 5);
EulerianPath euler = new EulerianPath(G);
if (euler.HasEulerianPath())
{
foreach (int v in euler.Path())
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.Write("none");
}
Console.WriteLine();
//2 4 4 3 3 2
}
广度优先搜索(BFS)
最短路径
广度优先搜索(BFS)解决了单点最短路径的问题。
深度搜索就像一个人在走迷宫,广度搜索就像一组人在走迷宫,每个人都有绳子,当两个人相遇的时候,会合并使用较短绳子的那个人。
在深度搜索中,使用了LIFO(后进先出)栈来描述走过的路径。
在广度搜索中,按照距离与起点的距离的顺序来遍历所有顶点,使用FIFO先进先出队列来替换LIFO后进先出队列。
public class BreadthFirstPaths
{
private static readonly int INFINITY = int.MaxValue;
private bool[] _marked; //到达该顶点的最短路径是否已知
private int[] _edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = s 表示指向顶点v的顶点是s,也表示边s-V
private int[] _distTo; // distTo[v] = s 表示s到达到v的边的数量
public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_distTo = new int[G.Vertices];
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
validateVertex(s);
bfs(G, s);
}
public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph G, IEnumerable<int> sources)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_distTo = new int[G.Vertices];
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
_distTo[v] = INFINITY;
validateVertices(sources);
bfs(G, sources);
}
private void bfs(Graph G, int s)
{
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
_distTo[v] = INFINITY;
_distTo[s] = 0;
_marked[s] = true;
q.Enqueue(s);
while (q.Any())
{
int v = q.Dequeue();
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
_edgeTo[w] = v;
_distTo[w] = _distTo[v] + 1;
_marked[w] = true;
q.Enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
private void bfs(Graph G, IEnumerable<int> sources)
{
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
foreach (int s in sources)
{
_marked[s] = true;
_distTo[s] = 0;
q.Enqueue(s);
}
while (q.Any())
{
int v = q.Dequeue();
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
_edgeTo[w] = v;
_distTo[w] = _distTo[v] + 1;
_marked[w] = true;
q.Enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
public bool HasPathTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _marked[v];
}
public int DistTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _distTo[v];
}
public IEnumerable<int> PathTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
if (!HasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<int> path = new Stack<int>();
int x;
for (x = v; _distTo[x] != 0; x = _edgeTo[x])
path.Push(x);
path.Push(x);
return path;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
private void validateVertices(IEnumerable<int> vertices)
{
if (vertices == null)
{
throw new ArgumentException("argument is null");
}
int V = _marked.Length;
foreach (int v in vertices)
{
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
{
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
}
}
测试:
[TestMethod()]
public void BreadthFirstPathsTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\tinyG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph(stream);
int s =1;
BreadthFirstPaths bfs = new BreadthFirstPaths(G, s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
if (bfs.HasPathTo(v))
{
Console.Write($"{s} to {v} ({bfs.DistTo(v)}): ");
foreach (int x in bfs.PathTo(v))
{
if (x == s) Console.Write(x);
else Console.Write("-" + x);
}
Console.Write(System.Environment.NewLine);
}
else
{
Console.Write($"{s} to{v} (-): not connected
");
}
}
}
//1 to 0(1): 1 - 0
//1 to 1(0): 1
//1 to 2(2): 1 - 0 - 2
//1 to 3(3): 1 - 0 - 5 - 3
//1 to 4(3): 1 - 0 - 6 - 4
//1 to 5(2): 1 - 0 - 5
//1 to 6(2): 1 - 0 - 6
//1 to7(-): not connected
//1 to8(-): not connected
//1 to9(-): not connected
//1 to10(-): not connected
//1 to11(-): not connected
//1 to12(-): not connected
}
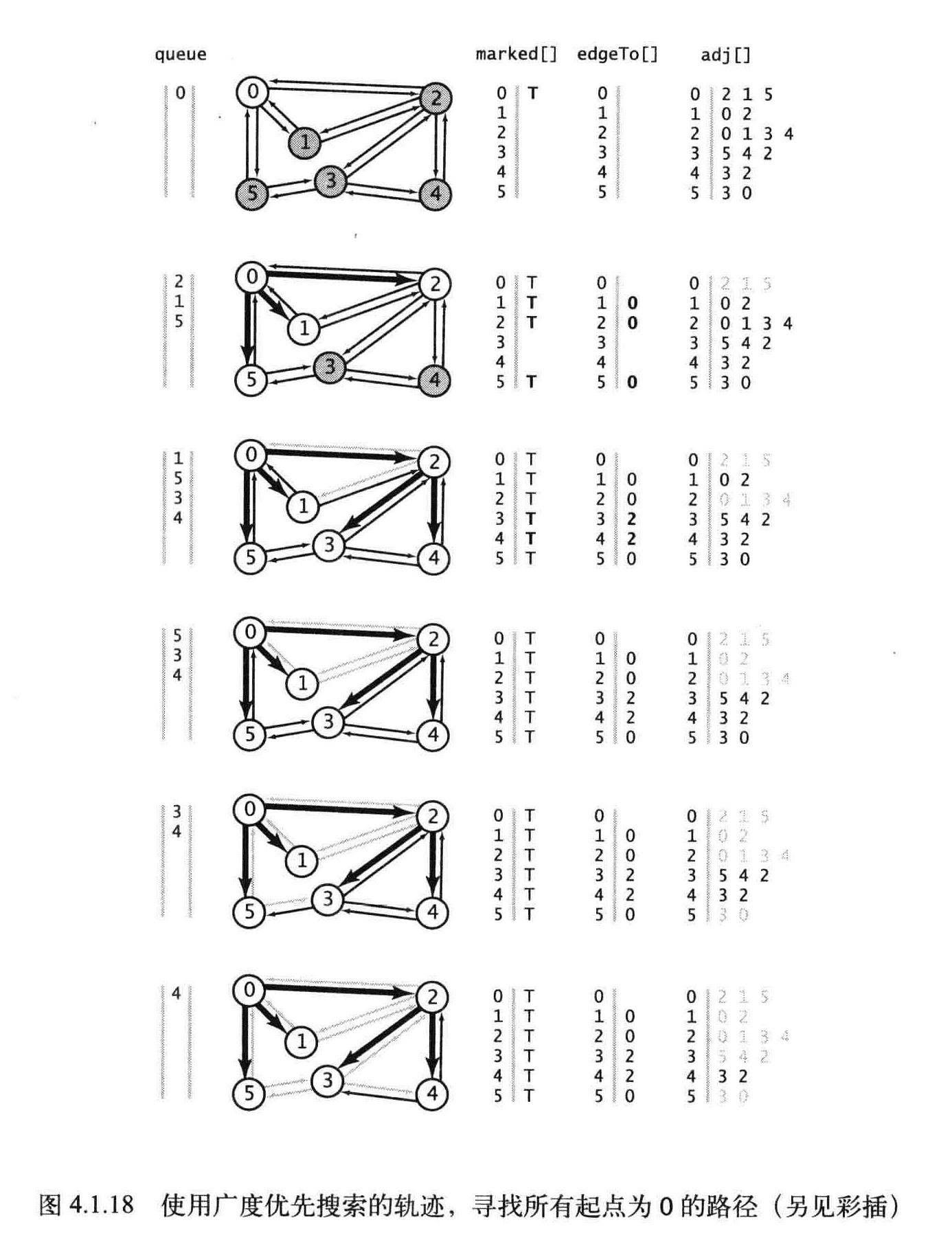
命题B:对于从S可达的任意顶点V,edgeTo[]数组在第二步之后就已经完成了。和深度优先搜索一样,一旦所有的顶点都已经被标记,余下的计算工作就只是在检查连接到各个已被标记的顶点的边而已。
命题B:广度搜索所需的时间在最坏情况下和V+E成正比。
二分图
/// <summary>
/// 使用广度优先搜索
/// </summary>
public class BipartiteX
{
private static readonly bool WHITE = false;
private static readonly bool BLACK = true;
private bool _isBipartite;
private bool[] _color;
private bool[] _marked;
private int[] _edgeTo;
private Queue<int> _cycle;
public bool IsBipartite => _isBipartite;
public BipartiteX(Graph G)
{
_isBipartite = true;
_color = new bool[G.Vertices];
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices && _isBipartite; v++)
{
if (!_marked[v])
{
bfs(G, v);
}
}
}
private void bfs(Graph G, int s)
{
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
_color[s] = WHITE;
_marked[s] = true;
q.Enqueue(s);
while (q.Any())
{
int v = q.Dequeue();
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
_marked[w] = true;
_edgeTo[w] = v;
_color[w] = !_color[v];
q.Enqueue(w);
}
else if (_color[w] == _color[v])
{
_isBipartite = false;//不是二分图
//奇循环:整个路径的构成 (w-x)+(x-v)+(v-w)
_cycle = new Queue<int>();
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
int x = v, y = w;
while (x != y)
{
stack.Push(x);
_cycle.Enqueue(y);
x = _edgeTo[x];
y = _edgeTo[y];
}
stack.Push(x);
while (stack.Any())//将上面的顶点和下面的顶点合并
_cycle.Enqueue(stack.Pop());
_cycle.Enqueue(w);
return;
}
}
}
}
public bool Color(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
if (!_isBipartite)
throw new ArgumentException("Graph is not bipartite");
return _color[v];
}
public IEnumerable<int> OddCycle()
{
return _cycle;
}
private bool check(Graph G)
{
// graph is bipartite
if (_isBipartite)
{
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (_color[v] == _color[w])
{
Console.Write($"edge {v}-{w} with {v} and {w} in same side of bipartition
");
return false;
}
}
}
}
// graph has an odd-length cycle
else
{
// verify cycle
int first = -1, last = -1;
foreach (int v in OddCycle())
{
if (first == -1) first = v;
last = v;
}
if (first != last)
{
Console.Write($"cycle begins with {first} and ends with {last}
", first, last);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试:
[TestMethod()]
public void BipartiteXTest()
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph G = GraphGenerator.Bipartite(6, 6, 20);
Random random = new Random();
//for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++)
//{
// int v = random.Next(12);
// int w = random.Next(12);
// G.AddEdge(v, w);
//}
BipartiteX b = new BipartiteX(G);
if (b.IsBipartite)
{
Console.Write("Graph is bipartite: ");
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
Console.Write(v + ": " + b.Color(v) + "; ");
}
}
else
{
Console.Write("Graph has an odd-length cycle: ");
foreach (int x in b.OddCycle())
{
Console.Write(x + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
深度搜索和广度搜索
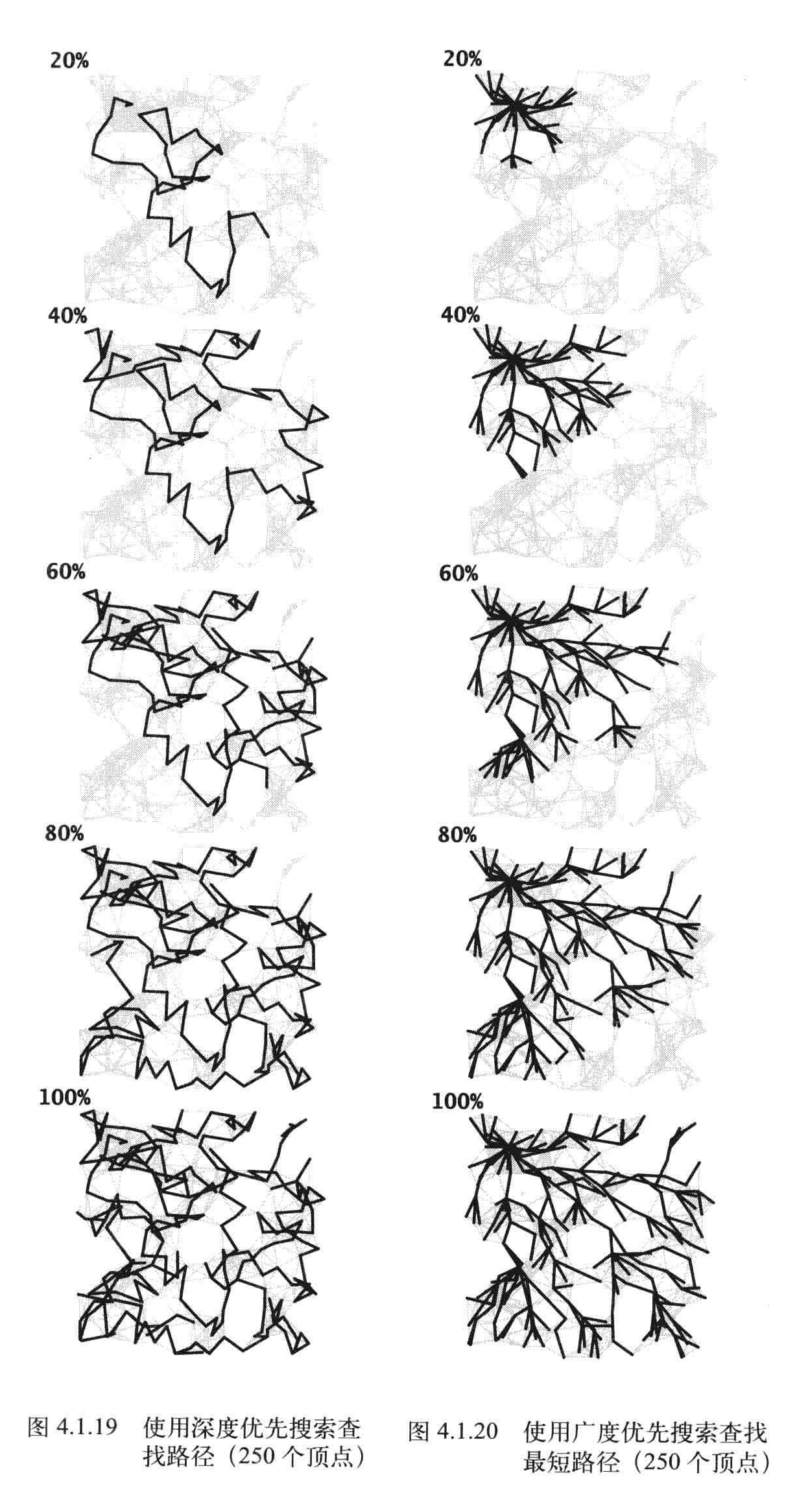
深度优先:不断深入图,栈中保存了所有分叉的顶点
广度优先:像扇面扫描一样,队列中保存了所有访问过的最前端节点。
连通分量
深度搜索比Union-Find快,但实际Union-Find更快,因为Union-Find不需要完整构建整个图,
当只需要判断连通性,需要有大量连通性查询和插入混合操作时,推荐使用Union-Find算法
当需要图的抽象数据类型的时候,推荐使用深度优先。
符号图
在实际使用中,图都是通过文件和网页定义了,使用的是字符串来代替顶点。
- 顶点为字符串
- 用指定分隔符来隔开顶点名
- 每一行都表示一组边的集合。
- 顶点总数V和边的总数都是隐式定义的。

public class SymbolGraph
{
private ST<String, int> _st; //符号名-索引
private String[] _keys; // 索引-符号名
private Graph _graph; // 图
public SymbolGraph(String filename, String delimiter)
{
_st = new ST<String, int>();
var stream = new StreamReader(filename);
while (!stream.EndOfStream) {//第一遍构造顶点
String[] a = stream.ReadLine().Split(delimiter.ToCharArray());
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
if (!_st.Contains(a[i]))//为每个不同的字符串关联一个索引
_st.Add(a[i], _st.Count());
}
}
_keys = new String[_st.Count()];//用来获得顶点名的反向索引是一个数组
foreach (String name in _st.Keys())
{
_keys[_st.Get(name)] = name;
}
_graph = new Graph(_st.Count());
stream = new StreamReader(filename);//第二遍构造边
while (!stream.EndOfStream) {
String[] a = stream.ReadLine().Split(delimiter.ToCharArray());//将每一行的顶点和该行的其他顶点相连
int v = _st.Get(a[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < a.Length; i++)
{
int w = _st.Get(a[i]);
_graph.AddEdge(v, w);
}
}
}
public bool Contains(String s)
{
return _st.Contains(s);
}
public int Index(String s)
{
return _st.Get(s);
}
public int IndexOf(String s)
{
return _st.Get(s);
}
public String Name(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _keys[v];
}
public String NameOf(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _keys[v];
}
public Graph Graph()
{
return _graph;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _graph.Vertices;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试:
[TestMethod()]
public void SymbolGraph()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\routes.txt");
SymbolGraph sg = new SymbolGraph(data, " ");
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Graph graph = sg.Graph();
StreamReader reader=new StreamReader(data);
while (!reader.EndOfStream)
{
String source = reader.ReadLine().Split(' ')[0];
if (sg.Contains(source))
{
Console.Write($"{source} :");
int s = sg.Index(source);
foreach (int v in graph.Adj[s])
{
Console.Write(" " + sg.Name(v));
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("input not contain '" + source + "'");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// JFK: ORD ATL MCO
// ORD : ATL JFK PHX DFW HOU DEN
// ORD: ATL JFK PHX DFW HOU DEN
// DFW: HOU ORD PHX
// JFK : ORD ATL MCO
// ORD : ATL JFK PHX DFW HOU DEN
// ORD: ATL JFK PHX DFW HOU DEN
// ATL: MCO ORD HOU JFK
// DEN: LAS PHX ORD
// PHX : LAS LAX DEN ORD DFW
// JFK : ORD ATL MCO
// DEN : LAS PHX ORD
// DFW : HOU ORD PHX
// ORD : ATL JFK PHX DFW HOU DEN
// LAS: PHX LAX DEN
// ATL : MCO ORD HOU JFK
// HOU: MCO DFW ATL ORD
// LAS: PHX LAX DEN
}