1. 什么是BDD
BDD全称Behavior Driven Development,译作"行为驱动开发",是基于TDD (Test Driven Development 测试驱动开发)的软件开发过程和方法。
BDD可以让项目成员(甚至是不懂编程的)使用自然语言来描述系统功能和场景,从而根据这些描述步骤进行系统自动化的测试。(详见附录4.1)
2. 常用BDD框架介绍
目前常用的BDD测试框架有Ruby中的Cucumber,Python中的Behave、Lettuce及Freshen等。
基本的流程如下图所示(Lettuce官方图):

简单来说就是"写用例->跑测试->看结果->写实现->看结果"这样的一个循环。
Behave网站列出了上面提到的几个自动化测试框架的对比(详见附录4.2),基于此原因,本文选择behave来介绍Python BDD自动化测试框架。
3. Behave示例
3.1 Behave安装
pip install behave # 全新安装 pip install -U behave # 更新
3.2 基础知识
3.2.1 Gherkin语法
上文提到的几种BDD框架均使用Gherkin语法,这是一种简单易懂的语言,使用关键字来定义系统特征和测试。
使用Gherkin语法编写的feature文件基本结构如下:
Title (one line describing the story/feature) As a [role] I want [feature] So that [benefit] Scenario: Title1 (for Behaviour 1) Given [context or setup] And [some more context]... When [event occurs] Then [expected outcome] And [another outcome]... Scenario: Title2 (for Behaviour 2) ...
3.2.2 断言模块
使用BDD测试框架前,需要选择一个好用的断言模块。Python有很多可用的断言模块(下表),本文我们选择hamcrest模块为例。
| Matcher Library | Description |
| Native assert | Starting point, but not enough information when assert fails. |
| hamcrest | First assertion matcher library, now part of JUnit4. Supports several programming languages: http://code.google.com/p/hamcrest/ |
| nose.tools | Part of the nose test framework |
| should-dsl | An interesting small matcher library, http://www.should-dsl.info/ |
| sure | Provided by the maker of lettuce, github:/gabrielfalcao/sure |
| compare | http://pypi.python.org/pypi/compare |
| describe | http://pypi.python.org/pypi/describe |
3.2.3 目录结构
Behave项目的目录格式如下:
$PROJECT/ +-- features/ -- Contains all feature files. | +-- steps/ | | +-- step_*.py -- Step definitions for features. | +-- environment.py -- Environment for global setup... | +-- tutorial*.feature -- Feature files.
3.3 Behave示例
我们以fibnacci数列计算为例,来了解下behave框架结构及如何使用(网上基本都是以阶乘或WEB页面为例,为显示本文的原创性,我们以fib数列为例)
首先,比较pythonic的实现fib数列的代码如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- def fibs(num): a=b=1 for i in range(num): yield a a,b=b,a+b print list(fibs(10))
使用behave进行自动化测试的详细步骤如下:
1. 新建目录fib,在此目录下新建文件fib.feature,内容如下
Feature:Calc Fib In order to introduce Behave We calc fib as example Scenario: Calc fib number Given we have the number 10 when we calc the fib then we get the fib number 55
2. 新建目录fib/steps,在此目录下新建文件fib.py,内容如下
from behave import * from hamcrest import * def fibs(num): a=b=1 for i in range(num): yield a a,b=b,a+b @given('we have the number {number}') def have_number(context,number): context.fib_number = int(number) @when('we calc the fib') def calc_fib(context): context.fib_number=list(fibs(context.fib_number))[-1] @then('we get the fib number {number}') def get_number(context,number): context.expected_number = int(number) assert_that(context.fib_number, equal_to(context.expected_number),"Calc fib number: %d" %context.fib_number)
这段Python代码主要分为三部分:
@given部分将输入的number=10转为整形并存入变量中
@when部分调用fib函数,计算fib数列值
@then 部分将计算出的fib值与预期值进行断言比较,判断结果是否相等
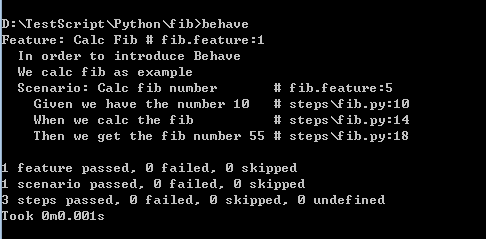
3. 切换到fib目录,执行behave命令,结果如下
4. Scenario Outlines场景大纲
有时相同的一个Scenario需要在很多不同的参数情况下运行,为了避免写过多重复的Scenario ,我们需要使用Scenario Outlines,如fib.feature文件内容可以修改如下:
Feature:Calc Fib In order to introduce Behave We calc fib as example Scenario Outline: Calc fib number Given we have the number <number> when we calc the fib then we get the fib number <fib_number> Examples: Some Numbers | number | fib_number | | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 2 | | 10 | 55 |
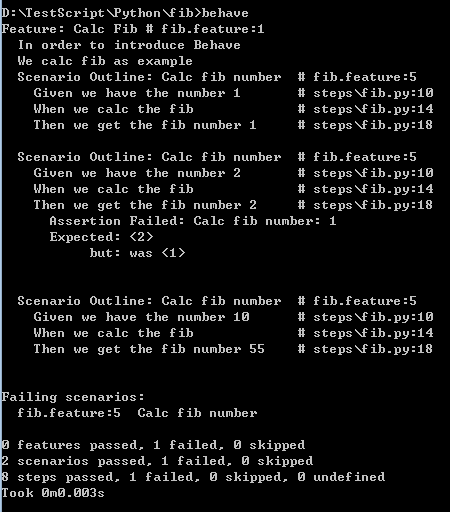
执行结果如下:
5. 更多的beahve示例可以参考附录4.4
4. 附录
本文只对Python BDD自动化测试框架进行了简单入门级介绍,若想更深入了解BDD,可参考如下资料:
4.1 BDD详细介绍:https://pythonhosted.org/behave/philosophy.html
4.2 常用测试框架对比:https://pythonhosted.org/behave/comparison.html
4.3 Hamcrest断言模块:https://github.com/hamcrest/PyHamcrest
4.4 Behave示例:http://jenisys.github.io/behave.example/