一:什么是表达式树
Expression我们称为是表达式树,是一种数据结构体,用于存储需要计算,运算的一种结构,这种结构可以只是存储,而不进行运算。通常表达式目录树是配合Lambda一起来使用的,lambda可以是匿名方法,当然也可以使用Expression来动态的创建!下面我们举例来说明什么是表达式目录树。
先创建一个People的实体,下面会用到
/// <summary> /// 实体类 /// </summary> public class People { public int Age { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Id; }
我们可以通过下面创建表达式目录树,我们称之为A种方式:
Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda = x => x.Id.ToString().IndexOf("5") >= 0;
我们还可以使用Expression来动态创建,我们称之为B种方式:
var peopleParam = Expression.Parameter(typeof(People), "x");//创建一个x,类型为people //得到x.Id MemberExpression idParam = Expression.Field(peopleParam, "Id"); //得到ToString方法 MethodInfo toStringWay = typeof(int).GetMethod("ToString", new Type[] { }); //得到IndexOf的方法,然后new Type[]这个代表是得到参数为string的一个方法 MethodInfo indexOfWay = typeof(string).GetMethod("IndexOf", new Type[] { typeof(string) }); //通过下面方法得到x.Id.ToString() MethodCallExpression tostringResult = Expression.Call(idParam, toStringWay, new Expression[] { }); //通过下面方法得到x.Id.ToString().IndexOf("5") ,MethodCallExpression继承于Expression MethodCallExpression indexOfResult = Expression.Call(tostringResult, indexOfWay, new Expression[] { Expression.Constant("5") }); //x.Id.ToString().IndexOf("5")>=0 var lambdaBody = Expression.GreaterThanOrEqual(indexOfResult, Expression.Constant(0)); //得到x => x.Id.ToString().IndexOf("5") >= 0,后面的一个参数指的是x,如果有多个则指定多个 Expression<Func<People,bool>> lambdaResult = Expression.Lambda<Func<People, bool>>(lambdaBody, new ParameterExpression[] { peopleParam }); //通过lambdaResult.Compile()得到Func<People,bool>这样的委托,然后Invoke是调用委托 bool result = lambdaResult.Compile().Invoke(new People() { Id = 155 });
A种和B种得到的结果是一致的,只不过第一种是通过lambda匿名方法来构建,第二种是通过动态的Expression来构建。另外下面的原理也是一样的
//普通的Lambda表达式 Func<int,int,int> func = (x,y)=> x + y - 2; //表达式目录树的Lambda表达式声明方式 Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = (x, y) => x + y - 2;
//表达式目录树的拼接方式实现 ParameterExpression parameterx = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "x"); ParameterExpression parametery = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "y"); ConstantExpression constantExpression = Expression.Constant(2, typeof(int)); BinaryExpression binaryAdd = Expression.Add(parameterx, parametery); BinaryExpression binarySubtract = Expression.Subtract(binaryAdd, constantExpression); Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expressionMosaic = Expression.Lambda<Func<int, int, int>>(binarySubtract, new ParameterExpression[] { parameterx, parametery });
int ResultLambda = func(5, 2); int ResultExpression = expression.Compile()(5, 2); int ResultMosaic = expressionMosaic.Compile()(5, 2); Console.WriteLine($"func:{ResultLambda}"); Console.WriteLine($"expression:{ResultExpression}"); Console.WriteLine($"expressionMosaic:{ResultMosaic}");
下面举例说明以下Expression.Block
ParameterExpression varExpr = Expression.Variable(typeof(int), "x"); //add(int x); var ex1 = Expression.Assign(varExpr, Expression.Constant(1)); //x = 1; var ex1 = x; var ex2 = Expression.Add(ex1, Expression.Constant(5)); //var ex2 = ex1 + 5;//6 var ex4 = Expression.Add(ex2, Expression.Constant(9)); //var ex4 = ex2 + 9; //15 var ex5 = Expression.Add(ex4, Expression.Constant(8)); // var ex5 = ex4 + 8; //23 BlockExpression blockExpr = Expression.Block( new ParameterExpression[] { varExpr }, ex1, ex2, ex4, ex5 );
该代码等效于,返回的结果都以最后一个Expression为主,则为ex5这个表达式
public int add(int x) { x = 1; var ex1 = x; var ex2 = ex1 + 5;//6 var ex4 = ex2 + 9; //15 var ex5 = ex4 + 8; //23 return ex5; //23 }
Expression.Block没有返回值
{ Expression A = Expression.Constant("第一大"); Expression B = Expression.Constant("第二大"); Expression ex = Expression.GreaterThan(Expression.Constant(1), Expression.Constant(2)); var method = typeof(Console).GetMethod("WriteLine", new Type[] { typeof(string) }); var AM = Expression.Call(method, A); var BM = Expression.Call(method, B); var condition = Expression.IfThenElse(ex, AM, BM); var blockExpr = Expression.Block(condition); //IfThenElse是没有返回值的 foreach (var expr in blockExpr.Expressions) Console.WriteLine(expr.ToString()); var lambdaExpression = Expression.Lambda<Action>(blockExpr).Compile(); lambdaExpression(); }
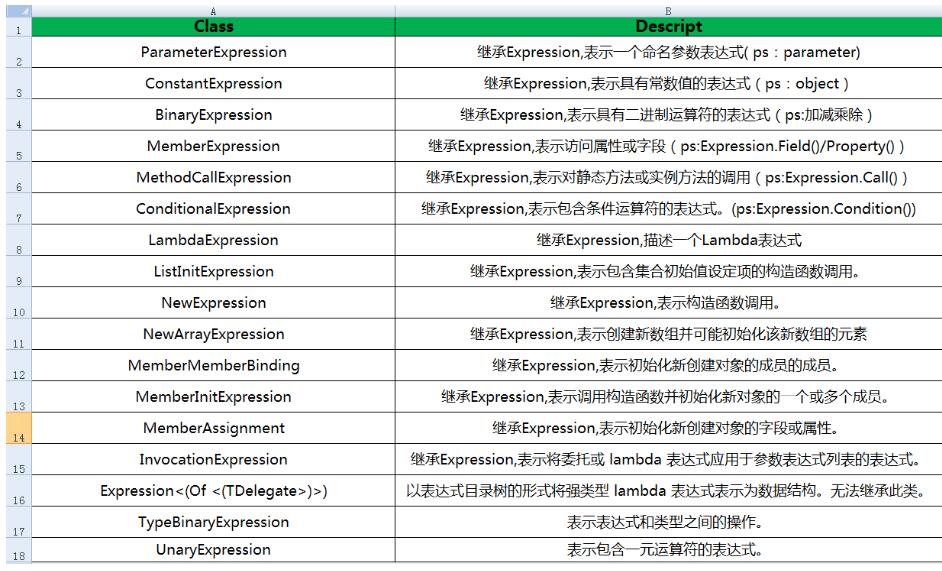
下图是Expression的一些变量
二:表达式目录树与委托
Expression一般都是都是配合委托一起来使用的,比如和委托Action(没有返回值),Func(至少有一个返回参数,且最后一个值为返回参数),Action,Func既可以直接传入一个与之匹配的实体方法,又可以传入lambda表达式这种匿名类(这种是声明lambda表达式的一种快捷方式)。Expression,Action,Func关键词是在.net 3.5之后出现的。Expression<Func<>>是可以转成Func的(通过compile()这个方法转换)。反过来则不行。我们可以理解为Func<>经过定义后,就无法改变它了。而表达式树(Expression<Func<>>则是可以进行变更的。Lambda
使用lambda表达声明表达式目录树的时候注意不能有{},即:
Func<int, int, int> func = (m, n) => m * n + 2;
上面这样是可以的。但是下面这样是不被允许的:
Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp1 = (m, n) => { return m * n + 2; };//不能有语句体 只能是一行,不能有大括号
下面的例子来解析一下委托和表达式目录树

1 #region PrivateMethod 2 private static void Do1(Func<People, bool> func) 3 { 4 List<People> people = new List<People>(); 5 people.Where(func); 6 } 7 private static void Do1(Expression<Func<People, bool>> func) 8 { 9 List<People> people = new List<People>() 10 { 11 new People(){Id=4,Name="123",Age=4}, 12 new People(){Id=5,Name="234",Age=5}, 13 new People(){Id=6,Name="345",Age=6}, 14 }; 15 16 List<People> peopleList = people.Where(func.Compile()).ToList(); 17 } 18 19 private static IQueryable<People> GetQueryable(Expression<Func<People, bool>> func) 20 { 21 List<People> people = new List<People>() 22 { 23 new People(){Id=4,Name="123",Age=4}, 24 new People(){Id=5,Name="234",Age=5}, 25 new People(){Id=6,Name="345",Age=6}, 26 }; 27 28 return people.AsQueryable<People>().Where(func); 29 } 30 #endregion
然后调用的时候为如下:
1 Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda1 = x => x.Age > 5; 2 Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda2 = x => x.Id > 5; 3 Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda3 = lambda1.And(lambda2); 4 Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda4 = lambda1.Or(lambda2); 5 Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda5 = lambda1.Not(); 6 Do1(lambda3); 7 Do1(lambda4); 8 Do1(lambda5);
三:使用Expression来进行不同对象的相同名字的属性映射
如果我们有一个新的对象和People属性基本上一致,如下:
/// <summary> /// 实体类Target /// PeopleDTO /// </summary> public class PeopleCopy { public int Age { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Id; }
现在我们想要把People的中Age,Name,Id等赋值给PeopleCopy,第一种我们直接想到的是硬编码,然后如下:
People people = new People() { Id = 11, Name = "加菲猫", Age = 31 }; //PeopleCopy copy = (PeopleCopy)people; //这种强制转换肯定是不行的 PeopleCopy peopleCopy = new PeopleCopy() { Id = people.Id, Name = people.Name, Age = people.Age };
但是如果有多个类型转换,要写N次,然后不同用且费力,所以我们会想到通用的方法,比如使用:【反射】,【序列化反序列化】,【缓存+表达式目录】,【泛型+表达式目录】,【AutoMapper】,我们可以用这五种方法都小试一下!
1:反射完成对象属性映射
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ExpressionDemo.MappingExtend { public class ReflectionMapper { /// <summary> /// 反射 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam> /// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam> /// <param name="tIn"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn) { TOut tOut = Activator.CreateInstance<TOut>(); foreach (var itemOut in tOut.GetType().GetProperties()) { var propIn = tIn.GetType().GetProperty(itemOut.Name); itemOut.SetValue(tOut, propIn.GetValue(tIn)); } foreach (var itemOut in tOut.GetType().GetFields()) { var fieldIn = tIn.GetType().GetField(itemOut.Name); itemOut.SetValue(tOut, fieldIn.GetValue(tIn)); } return tOut; } } }
2:使用序列化和反序列化来完成对象属性映射:
using Newtonsoft.Json; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ExpressionDemo.MappingExtend { /// <summary> /// 使用第三方序列化反序列化工具 /// /// 还有automapper /// </summary> public class SerializeMapper { /// <summary> /// 序列化反序列化方式 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam> /// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam> public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn) { return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<TOut>(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(tIn)); } } }
3:缓存+表达式目录树
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Linq.Expressions; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ExpressionDemo.MappingExtend { /// <summary> /// 生成表达式目录树 缓存 /// </summary> public class ExpressionMapper { /// <summary> /// 字典缓存--hash分布 /// </summary> private static Dictionary<string, object> _Dic = new Dictionary<string, object>(); /// <summary> /// 字典缓存表达式树 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam> /// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam> /// <param name="tIn"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn) { string key = string.Format("funckey_{0}_{1}", typeof(TIn).FullName, typeof(TOut).FullName); if (!_Dic.ContainsKey(key)) { ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(TIn), "p"); List<MemberBinding> memberBindingList = new List<MemberBinding>(); foreach (var item in typeof(TOut).GetProperties()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(TIn).GetProperty(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } foreach (var item in typeof(TOut).GetFields()) { MemberExpression property = Expression.Field(parameterExpression, typeof(TIn).GetField(item.Name)); MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); } MemberInitExpression memberInitExpression = Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(TOut)), memberBindingList.ToArray()); Expression<Func<TIn, TOut>> lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<TIn, TOut>>(memberInitExpression, new ParameterExpression[] { parameterExpression }); Func<TIn, TOut> func = lambda.Compile();//拼装是一次性的 _Dic[key] = func; } return ((Func<TIn, TOut>)_Dic[key]).Invoke(tIn); } } }
4:泛型+表达式目录树
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq.Expressions; 4 5 namespace ExpressionDemo.MappingExtend 6 { 7 /// <summary> 8 /// 生成表达式目录树 泛型缓存 9 /// </summary> 10 /// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam> 11 /// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam> 12 public class ExpressionGenericMapper<TIn, TOut>//Mapper`2 13 { 14 private static Func<TIn, TOut> _FUNC = null; 15 static ExpressionGenericMapper() 16 { 17 ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(TIn), "p"); 18 List<MemberBinding> memberBindingList = new List<MemberBinding>(); 19 foreach (var item in typeof(TOut).GetProperties()) 20 { 21 MemberExpression property = Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(TIn).GetProperty(item.Name)); //p.Age 22 MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); //Age=p.Age 23 memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); 24 } 25 foreach (var item in typeof(TOut).GetFields()) 26 { 27 MemberExpression property = Expression.Field(parameterExpression, typeof(TIn).GetField(item.Name)); 28 MemberBinding memberBinding = Expression.Bind(item, property); 29 memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding); 30 } 31 //new PeopleCopy() {Age = p.Age, Name = p.Name, Id = p.Id} 32 MemberInitExpression memberInitExpression = Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(TOut)), memberBindingList.ToArray()); 33 //p => new PeopleCopy() {Age = p.Age, Name = p.Name, Id = p.Id} 34 Expression<Func<TIn, TOut>> lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<TIn, TOut>>(memberInitExpression, new ParameterExpression[] 35 { 36 parameterExpression 37 }); 38 _FUNC = lambda.Compile();//拼装是一次性的 39 } 40 public static TOut Trans(TIn t) 41 { 42 return _FUNC(t); 43 } 44 } 45 }
5:使用.netFramwork框架自带的AutoMapper,首先我们要nuget添加引用AutoMapper即可直接使用,具体代码为:

1 using AutoMapper; 2 3 namespace ExpressionDemo.MappingExtend 4 { 5 public class AutoMapperTest 6 { 7 public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn) 8 { 9 return Mapper.Instance.Map<TOut>(tIn); 10 } 11 } 12 }
五种方法我们分别调用一下,然后测试一下性能,代码如下:

1 { 2 People people = new People() 3 { 4 Id = 11, 5 Name = "加菲猫", 6 Age = 31 7 }; 8 //使用AutoMapper之前必须要初始化对应的关系 9 Mapper.Initialize(x => x.CreateMap<People, PeopleCopy>()); 10 11 long common = 0; 12 long generic = 0; 13 long cache = 0; 14 long reflection = 0; 15 long serialize = 0; 16 long autoMapper = 0; 17 { 18 Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); 19 watch.Start(); 20 for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) 21 { 22 PeopleCopy peopleCopy = new PeopleCopy() 23 { 24 Id = people.Id, 25 Name = people.Name, 26 Age = people.Age 27 }; 28 } 29 watch.Stop(); 30 common = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; 31 } 32 { 33 Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); 34 watch.Start(); 35 for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) 36 { 37 PeopleCopy peopleCopy = AutoMapperTest.Trans<People, PeopleCopy>(people); 38 } 39 watch.Stop(); 40 autoMapper = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; 41 } 42 { 43 Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); 44 watch.Start(); 45 for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) 46 { 47 PeopleCopy peopleCopy = ReflectionMapper.Trans<People, PeopleCopy>(people); 48 } 49 watch.Stop(); 50 reflection = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; 51 } 52 { 53 Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); 54 watch.Start(); 55 for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) 56 { 57 PeopleCopy peopleCopy = SerializeMapper.Trans<People, PeopleCopy>(people); 58 } 59 watch.Stop(); 60 serialize = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; 61 } 62 { 63 Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); 64 watch.Start(); 65 for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) 66 { 67 PeopleCopy peopleCopy = ExpressionMapper.Trans<People, PeopleCopy>(people); 68 } 69 watch.Stop(); 70 cache = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; 71 } 72 { 73 Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); 74 watch.Start(); 75 for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) 76 { 77 PeopleCopy peopleCopy = ExpressionGenericMapper<People, PeopleCopy>.Trans(people); 78 } 79 watch.Stop(); 80 generic = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds; 81 } 82 83 Console.WriteLine($"common = { common} ms"); 84 Console.WriteLine($"reflection = { reflection} ms"); 85 Console.WriteLine($"serialize = { serialize} ms"); 86 Console.WriteLine($"cache = { cache} ms"); 87 Console.WriteLine($"generic = { generic} ms"); 88 Console.WriteLine($"automapper = { autoMapper} ms"); 89 //性能比automapper还要高 90 }
运行结果如下:

通过结果发现:反射和序列化运用的时间最多,而我们惊奇的发现表达式目录树+泛型缓存比框架自带的AutoMapper时间还短!有木有感觉超级腻害~!
四:ORM与表达式树目录的关系
我们平常项目中经常用到EF,其实都是继承Queryable,然后我们使用的EF通常都会使用 var items = anserDo.GetAll().Where(x => x.OrganizationId == input.oid || input.oid == 0) ,where其实传的就是表达式目录树。那我们来一步一步解析EF底层实现的具体逻辑。
lambada表达式上面说了能使用Expression来动态拼接,当然它还有一个神奇的功能,能动态的解耦。Expression有个类ExpressionVisitor
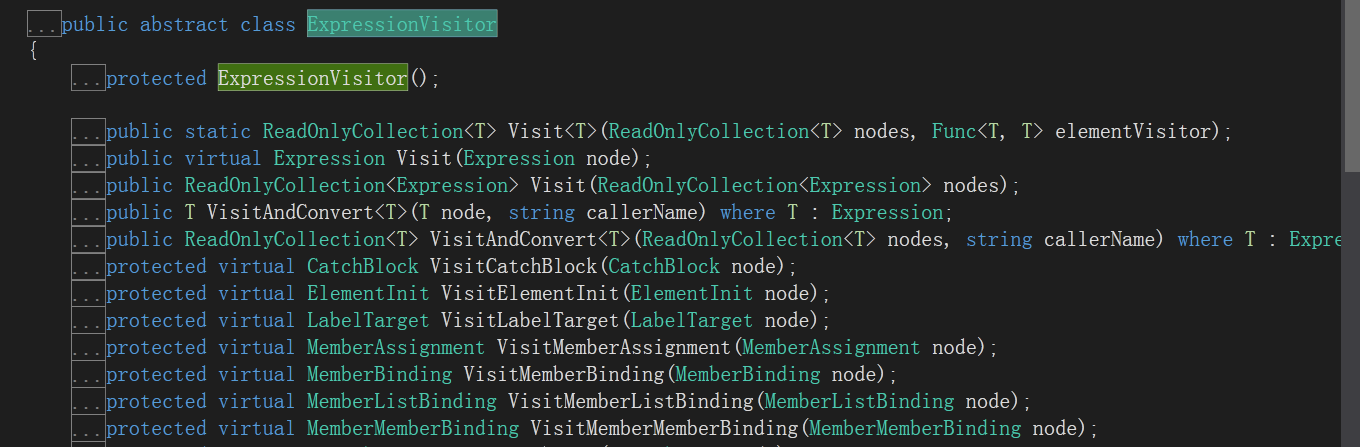
这个类中的Visit(Expression node)是解读表达式的入口,然后能够神奇的区分参数和方法体,然后将表达式调度到此类中更专用的访问方法中,然后一层一层的解析下去,一直到最终的叶节点!
将表达式调度到此类中更专用的访问方法中:我们来举例说明:

1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Linq.Expressions; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace ExpressionDemo.Visitor 9 { 10 public class OperationsVisitor : ExpressionVisitor 11 { 12 public Expression Modify(Expression expression) 13 { 14 return this.Visit(expression); 15 } 16 17 protected override Expression VisitBinary(BinaryExpression b) 18 { 19 if (b.NodeType == ExpressionType.Add) 20 { 21 Expression left = this.Visit(b.Left); 22 Expression right = this.Visit(b.Right); 23 return Expression.Subtract(left, right); 24 } 25 26 return base.VisitBinary(b); 27 } 28 29 protected override Expression VisitConstant(ConstantExpression node) 30 { 31 return base.VisitConstant(node); 32 } 33 } 34 }
下面调用:
1 { 2 //修改表达式目录树 3 Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp = (m, n) => m * n + 2; 4 OperationsVisitor visitor = new OperationsVisitor(); 5 Expression expNew = visitor.Modify(exp); 6 }
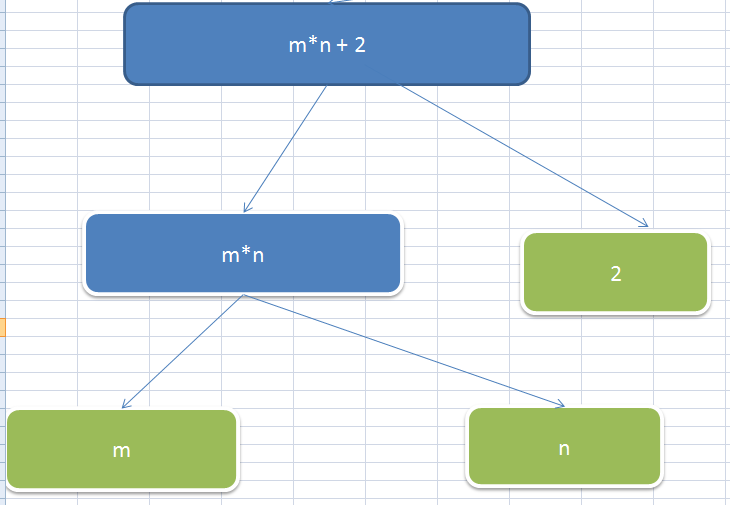
visit这个这个方法能够识别出来 m*n+2 是个二叉树,会通过下面的图然后一步一步的进行解析,如果遇到m*n 这会直接调用VisitBinary(BinaryExpression b)这个方法,如果遇到m或者n会调用VisitParameter(ParameterExpression node)这个方法,
如果遇到2常量则会调用VisitConstant(ConstantExpression node),这就是visit神奇的调度功能!
我们EF写的where等lambda表达式,就是通过ExpressionVisitor这个类来反解析的!之前没有学习过表达式目录树,以为ef本来就应该这样写,有没有和我一样认为的?
我们现在模拟写一个lambda转换sql的方法

1 using ExpressionDemo.DBExtend; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq.Expressions; 5 6 namespace ExpressionDemo.Visitor 7 { 8 public class ConditionBuilderVisitor : ExpressionVisitor 9 { 10 private Stack<string> _StringStack = new Stack<string>(); 11 12 public string Condition() 13 { 14 string condition = string.Concat(this._StringStack.ToArray()); 15 this._StringStack.Clear(); 16 return condition; 17 } 18 19 /// <summary> 20 /// 如果是二元表达式 21 /// </summary> 22 /// <param name="node"></param> 23 /// <returns></returns> 24 protected override Expression VisitBinary(BinaryExpression node) 25 { 26 if (node == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("BinaryExpression"); 27 28 this._StringStack.Push(")"); 29 base.Visit(node.Right);//解析右边 30 this._StringStack.Push(" " + node.NodeType.ToSqlOperator() + " "); 31 base.Visit(node.Left);//解析左边 32 this._StringStack.Push("("); 33 34 return node; 35 } 36 /// <summary> 37 /// 38 /// </summary> 39 /// <param name="node"></param> 40 /// <returns></returns> 41 protected override Expression VisitMember(MemberExpression node) 42 { 43 if (node == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("MemberExpression"); 44 this._StringStack.Push(" [" + node.Member.Name + "] "); 45 return node; 46 } 47 /// <summary> 48 /// 常量表达式 49 /// </summary> 50 /// <param name="node"></param> 51 /// <returns></returns> 52 protected override Expression VisitConstant(ConstantExpression node) 53 { 54 if (node == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("ConstantExpression"); 55 this._StringStack.Push(" '" + node.Value + "' "); 56 return node; 57 } 58 /// <summary> 59 /// 方法表达式 60 /// </summary> 61 /// <param name="m"></param> 62 /// <returns></returns> 63 protected override Expression VisitMethodCall(MethodCallExpression m) 64 { 65 if (m == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("MethodCallExpression"); 66 67 string format; 68 switch (m.Method.Name) 69 { 70 case "StartsWith": 71 format = "({0} LIKE {1}+'%')"; 72 break; 73 74 case "Contains": 75 format = "({0} LIKE '%'+{1}+'%')"; 76 break; 77 78 case "EndsWith": 79 format = "({0} LIKE '%'+{1})"; 80 break; 81 82 default: 83 throw new NotSupportedException(m.NodeType + " is not supported!"); 84 } 85 this.Visit(m.Object); 86 this.Visit(m.Arguments[0]); 87 string right = this._StringStack.Pop(); 88 string left = this._StringStack.Pop(); 89 this._StringStack.Push(String.Format(format, left, right)); 90 91 return m; 92 } 93 } 94 }

1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Linq.Expressions; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace ExpressionDemo.DBExtend 9 { 10 internal static class SqlOperator 11 { 12 internal static string ToSqlOperator(this ExpressionType type) 13 { 14 switch (type) 15 { 16 case (ExpressionType.AndAlso): 17 case (ExpressionType.And): 18 return "AND"; 19 case (ExpressionType.OrElse): 20 case (ExpressionType.Or): 21 return "OR"; 22 case (ExpressionType.Not): 23 return "NOT"; 24 case (ExpressionType.NotEqual): 25 return "<>"; 26 case ExpressionType.GreaterThan: 27 return ">"; 28 case ExpressionType.GreaterThanOrEqual: 29 return ">="; 30 case ExpressionType.LessThan: 31 return "<"; 32 case ExpressionType.LessThanOrEqual: 33 return "<="; 34 case (ExpressionType.Equal): 35 return "="; 36 default: 37 throw new Exception("不支持该方法"); 38 } 39 40 } 41 } 42 }
然后调用的时候如下:

1 { 2 //修改表达式目录树 3 Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp = (m, n) => m * n + 2; 4 OperationsVisitor visitor = new OperationsVisitor(); 5 Expression expNew = visitor.Modify(exp); 6 } 7 8 { 9 Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda = x => x.Age > 5 && x.Id > 5 10 && x.Name.StartsWith("1") 11 && x.Name.EndsWith("1") 12 && x.Name.Contains("1"); 13 14 string sql = string.Format("Delete From [{0}] WHERE {1}" 15 , typeof(People).Name 16 , " [Age]>5 AND [ID] >5" 17 ); 18 ConditionBuilderVisitor vistor = new ConditionBuilderVisitor(); 19 vistor.Visit(lambda); 20 Console.WriteLine(vistor.Condition()); 21 } 22 { 23 Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda = x => x.Age > 5 && x.Name == "A" || x.Id > 5; 24 ConditionBuilderVisitor vistor = new ConditionBuilderVisitor(); 25 vistor.Visit(lambda); 26 Console.WriteLine(vistor.Condition()); 27 } 28 { 29 Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda = x => x.Age > 5 || (x.Name == "A" && x.Id > 5); 30 ConditionBuilderVisitor vistor = new ConditionBuilderVisitor(); 31 vistor.Visit(lambda); 32 Console.WriteLine(vistor.Condition()); 33 } 34 { 35 Expression<Func<People, bool>> lambda = x => (x.Age > 5 || x.Name == "A") && x.Id > 5; 36 ConditionBuilderVisitor vistor = new ConditionBuilderVisitor(); 37 vistor.Visit(lambda); 38 Console.WriteLine(vistor.Condition()); 39 }
目前Expression只支持ExpressionType的84种操作符Add, AndAlso等等,然后VisitMethodCall这个方法中表示lambda能解析出来的方法名字,如果需要可以自行修改会得到对应的sql语句的where条件!
