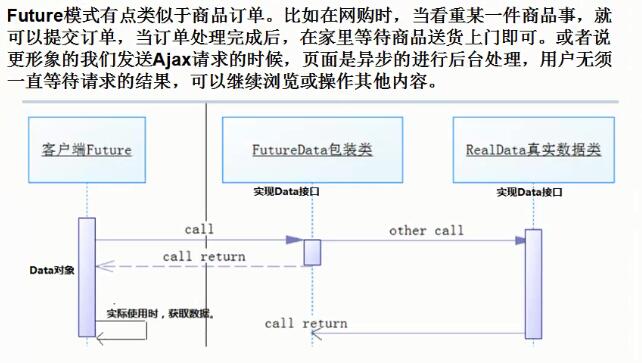
代码示例:

public interface Data { String getRequest(); } public class FutureData implements Data{ private RealData realData ; private boolean isReady = false; public synchronized void setRealData(RealData realData) { //如果已经装载完毕了,就直接返回 if(isReady){ return; } //如果没装载,进行装载真实对象 this.realData = realData; isReady = true; //进行通知 notify(); } @Override public synchronized String getRequest() { //如果没装载好 程序就一直处于阻塞状态 while(!isReady){ try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //装载好直接获取数据即可 return this.realData.getRequest(); } } public class RealData implements Data{ private String result ; public RealData (String queryStr){ System.out.println("根据" + queryStr + "进行查询,这是一个很耗时的操作.."); try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("操作完毕,获取结果"); result = "查询结果"; } @Override public String getRequest() { return result; } } public class FutureClient { public Data request(final String queryStr){ //1 我想要一个代理对象(Data接口的实现类)先返回给发送请求的客户端,告诉他请求已经接收到,可以做其他的事情 final FutureData futureData = new FutureData(); //2 启动一个新的线程,去加载真实的数据,传递给这个代理对象 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //3 这个新的线程可以去慢慢的加载真实对象,然后传递给代理对象 RealData realData = new RealData(queryStr); futureData.setRealData(realData); } }).start(); return futureData; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { FutureClient fc = new FutureClient(); Data data = fc.request("请求参数"); System.out.println("请求发送成功!"); System.out.println("做其他的事情..."); String result = data.getRequest(); System.out.println(result); } }
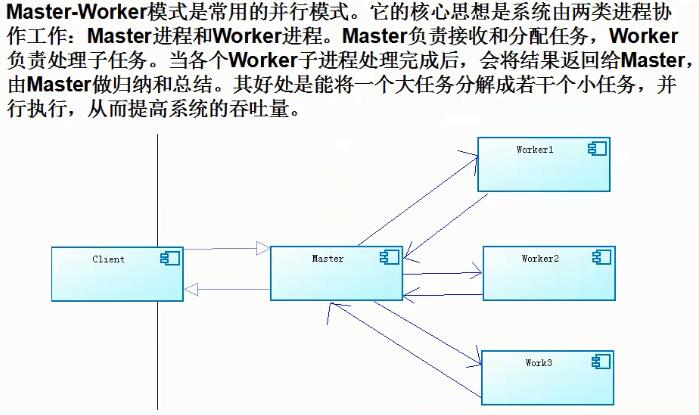
具体一点,代码实现流程应该是这样的:
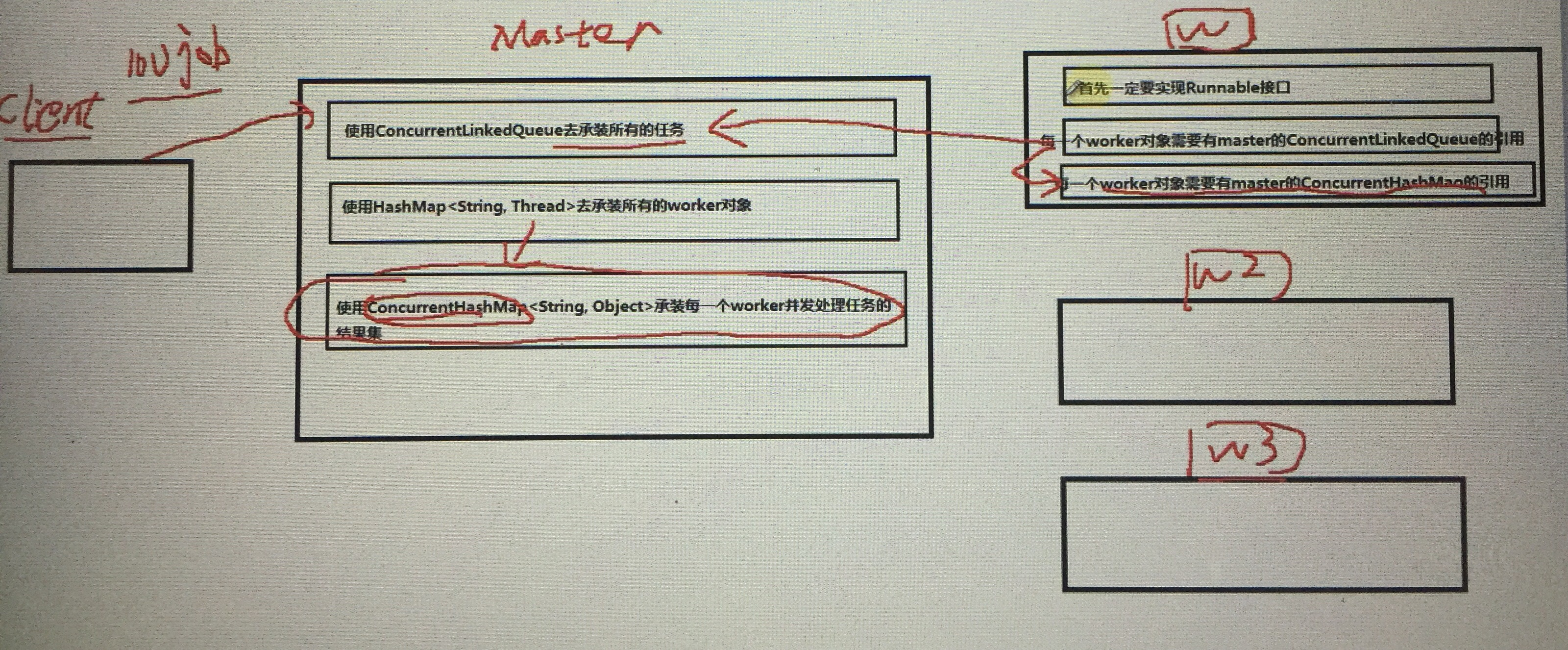
代码示例:

public class Task { private int id; private int price ; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } } public class Master { //1 有一个盛放任务的容器 private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Task> workQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Task>(); //2 需要有一个盛放worker的集合 private HashMap<String, Thread> workers = new HashMap<String, Thread>(); //3 需要有一个盛放每一个worker执行任务的结果集合 private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> resultMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(); //4 构造方法 public Master(Worker worker , int workerCount){ worker.setWorkQueue(this.workQueue); worker.setResultMap(this.resultMap); for(int i = 0; i < workerCount; i ++){ this.workers.put(Integer.toString(i), new Thread(worker)); } } //5 需要一个提交任务的方法 public void submit(Task task){ this.workQueue.add(task); } //6 需要有一个执行的方法,启动所有的worker方法去执行任务 public void execute(){ for(Map.Entry<String, Thread> me : workers.entrySet()){ me.getValue().start(); } } //7 判断是否运行结束的方法 public boolean isComplete() { for(Map.Entry<String, Thread> me : workers.entrySet()){ if(me.getValue().getState() != Thread.State.TERMINATED){ return false; } } return true; } //8 计算结果方法 public int getResult() { int priceResult = 0; for(Map.Entry<String, Object> me : resultMap.entrySet()){ priceResult += (Integer)me.getValue(); } return priceResult; } } public class Worker implements Runnable { private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Task> workQueue; private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> resultMap; public void setWorkQueue(ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Task> workQueue) { this.workQueue = workQueue; } public void setResultMap(ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> resultMap) { this.resultMap = resultMap; } @Override public void run() { while(true){ Task input = this.workQueue.poll(); if(input == null) break; Object output = handle(input); this.resultMap.put(Integer.toString(input.getId()), output); } } private Object handle(Task input) { Object output = null; try { //处理任务的耗时。。 比如说进行操作数据库。。。 Thread.sleep(500); output = input.getPrice(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return output; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Master master = new Master(new Worker(), 20); Random r = new Random(); for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){ Task t = new Task(); t.setId(i); t.setPrice(r.nextInt(1000)); master.submit(t); } master.execute(); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); while(true){ if(master.isComplete()){ long end = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; int priceResult = master.getResult(); System.out.println("最终结果:" + priceResult + ", 执行时间:" + end); break; } } } }

代码示例:

public final class Data { private String id; private String name; public Data(String id, String name){ this.id = id; this.name = name; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString(){ return "{id: " + id + ", name: " + name + "}"; } } public class Consumer implements Runnable{ private BlockingQueue<Data> queue; public Consumer(BlockingQueue queue){ this.queue = queue; } //随机对象 private static Random r = new Random(); @Override public void run() { while(true){ try { //获取数据 Data data = this.queue.take(); //进行数据处理。休眠0 - 1000毫秒模拟耗时 Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(1000)); System.out.println("当前消费线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", 消费成功,消费数据为id: " + data.getId()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public class Provider implements Runnable{ //共享缓存区 private BlockingQueue<Data> queue; //多线程间是否启动变量,有强制从主内存中刷新的功能。即时返回线程的状态 private volatile boolean isRunning = true; //id生成器 private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(); //随机对象 private static Random r = new Random(); public Provider(BlockingQueue queue){ this.queue = queue; } @Override public void run() { while(isRunning){ try { //随机休眠0 - 1000 毫秒 表示获取数据(产生数据的耗时) Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(1000)); //获取的数据进行累计... int id = count.incrementAndGet(); //比如通过一个getData方法获取了 Data data = new Data(Integer.toString(id), "数据" + id); System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", 获取了数据,id为:" + id + ", 进行装载到公共缓冲区中..."); if(!this.queue.offer(data, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)){ System.out.println("提交缓冲区数据失败...."); //do something... 比如重新提交 } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public void stop(){ this.isRunning = false; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //内存缓冲区 BlockingQueue<Data> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Data>(10); //生产者 Provider p1 = new Provider(queue); Provider p2 = new Provider(queue); Provider p3 = new Provider(queue); //消费者 Consumer c1 = new Consumer(queue); Consumer c2 = new Consumer(queue); Consumer c3 = new Consumer(queue); //创建线程池运行,这是一个缓存的线程池,可以创建无穷大的线程,没有任务的时候不创建线程。空闲线程存活时间为60s(默认值) ExecutorService cachePool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); cachePool.execute(p1); cachePool.execute(p2); cachePool.execute(p3); cachePool.execute(c1); cachePool.execute(c2); cachePool.execute(c3); try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } p1.stop(); p2.stop(); p3.stop(); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // cachePool.shutdown(); // cachePool.shutdownNow(); } }
