/*
* 多线程的实现方式:
* 方式1:一种方法是将类声明为 Thread 的子类。该子类应重写 Thread 类的 run 方法。接下来可以分配并启动该子类的实例
*
* Thread
* String getName() 返回该线程的名称。
* void setName(String name) 改变线程名称,使之与参数 name 相同。
*
*
* CPU执行程序的随机性*/
一、Thread类
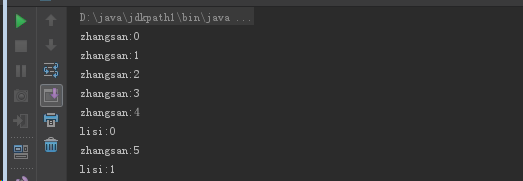
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { //重新Runnable的run方法 for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { System.out.println(getName()+ ":" + i); } } }
public class ThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread mt = new MyThread(); mt.setName("zhangsan"); mt.start(); MyThread mt2 = new MyThread(); mt2.setName("lisi"); mt2.start(); } }
输出: cpu执行程序的随机性
二、Runnable 接口
/*
* 创建线程的另一种方法是声明实现 Runnable 接口的类。该类然后实现 run 方法。
* 然后可以分配该类的实例,在创建 Thread 时作为一个参数来传递并启动
* Thread(Runnable target)
*
* 既然有了继承Thread为何还要整出来实现Runnable?
* 类单一继承,runnable是接口可以多继承
* */
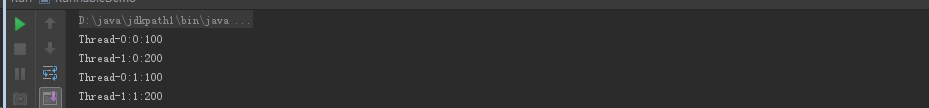
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable { int num; public MyRunnable(int num) { this.num = num; } @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i + ":" + num); } } }
public class RunnableDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { method1(); // method2(); } private static void method2() { MyRunnable mt = new MyRunnable(100); Thread t = new Thread(mt);////构造方法:Thread(Runnable target) 分配新的 Thread 对象 t.start(); Thread t2 = new Thread(mt); t2.start(); } private static void method1() { MyRunnable mt = new MyRunnable(100); Thread t = new Thread(mt); t.start(); MyRunnable mt2 = new MyRunnable(200); Thread t2 = new Thread(mt2); t2.start(); } }