Java实验报告
班级 计科二班 学号 20188430 姓名 詹洋
完成时间 2019.10.07
评分等级
实验四 类的继承
- 实验目的
- 理解抽象类与接口的使用;
- 了解包的作用,掌握包的设计方法。
- 实验要求
- 掌握使用抽象类的方法。
- 掌握使用系统接口的技术和创建自定义接口的方法。
- 了解 Java 系统包的结构。
- 掌握创建自定义包的方法。
- 实验内容
(一)抽象类的使用
- 设计一个类层次,定义一个抽象类--形状,其中包括有求形状的面积的抽象方法。 继承该抽象类定义三角型、矩形、圆。 分别创建一个三角形、矩形、圆存对象,将各类图形的面积输出。
注:三角形面积s=sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)) 其中,a,b,c为三条边,p=(a+b+c)/2
2.编程技巧
(1) 抽象类定义的方法在具体类要实现;
(2) 使用抽象类的引用变量可引用子类的对象;
(3) 通过父类引用子类对象,通过该引用访问对象方法时实际用的是子类的方法。可将所有对象存入到父类定义的数组中。
(二)使用接口技术
1定义接口Shape,其中包括一个方法size(),设计“直线”、“圆”、类实现Shape接口。分别创建一个“直线”、“圆”对象,将各类图形的大小输出。
- 编程技巧
(1) 接口中定义的方法在实现接口的具体类中要重写实现;
(2) 利用接口类型的变量可引用实现该接口的类创建的对象。
实验源码:
abstract class shape { public abstract double print(); } class Triangle extends shape { private double num1; private double num2; private double num3; public Triangle(double a,double b,double c){ this.num1=a; this.num2=b; this.num3=c; } public double print() { double sum=(num1+num2+num3)/2; return Math.sqrt(sum*(sum-num1)*(sum-num2)*(sum-num3)); } } class Rectangle1 extends shape { private double width; private double height; public Rectangle1(double width, double height){ this.height=height; this.width=width; } public double print() { return width*height; } } class Circle1 extends shape { double radious; public Circle1(double radious){ this.radious=radious; } public double print() { return Math.PI*radious*radious; } } public class HUA { public static void main(String[] args){ shape s1=new Triangle(6,7,8); shape s2=new Rectangle1(5,9); shape s3=new Circle1(8); System.out.println("三角形的面积为:"+s1.print()); System.out.println("矩形的面积为:"+s2.print()); System.out.println("圆的面积为:"+s3.print()); } }
实验结果:
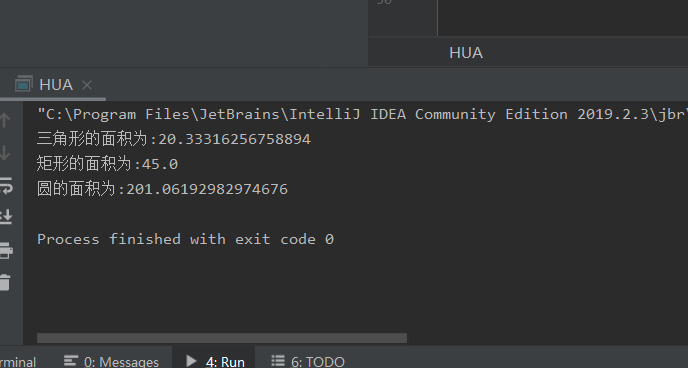
实验源码:
interface Shape { public void size(); } class StraightLine implements Shape{ private double length; public StraightLine(double s) { this.length = s; } public void size() { System.out.println("直线长度为"+this.length+"cm"); } } class Circle implements Shape{ private double a; private double area; public Circle(double r) { this.a=r; this.area=Math.PI*Math.pow(r,2); } public void size() { System.out.println("圆的半径为"+this.a+" 圆面积大小为"+this.area); } } public class YAN { public static void main (String args[]) { Shape form=new StraightLine(18); Shape form2=new Circle(4); form.size(); form2.size(); } }
实验结果:
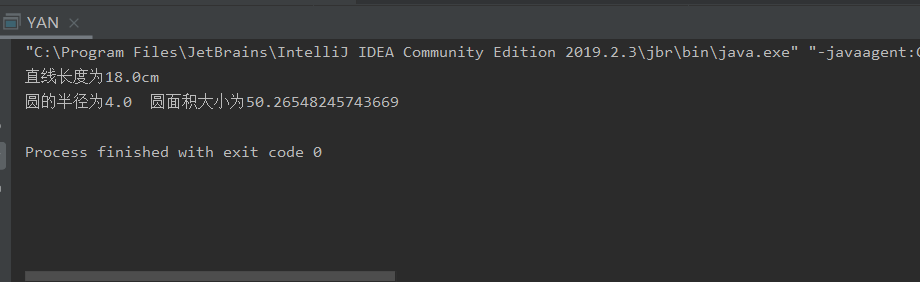 、
、
实验总结:
知道一些编辑的小技巧
(1) 抽象类定义的方法在具体类要实现;
(2) 使用抽象类的引用变量可引用子类的对象;
(3) 通过父类引用子类对象,通过该引用访问对象方法时实际用的是子类的方法。可将所有对象存入到父类定义的数组中。
读会这些方法题目思路就会清晰很多。
这周还学习object,它是所有子类的父类
object类的主要方法
(1)toString();
(2)equals();
(3) hashCode()
再通过题目了解到了接口的概念:接口是一种特殊的类,里面全部是由全局变量和公共的抽象方法组成。
注意:抽象方法必须定义成public访问权限。
接口的使用和抽象类一样都是需要通过子类来实现,而子类通过implements关键字来实现接口(可实现多个接口)。
实现接口的格式