Description
An array of positive integers a1, a2, ..., an is given. Let us consider its arbitrary subarray al, al + 1..., ar, where 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n. For every positive integer s denote by Ks the number of occurrences of s into the subarray. We call the power of the subarray the sum of products Ks·Ks·s for every positive integer s. The sum contains only finite number of nonzero summands as the number of different values in the array is indeed finite.
You should calculate the power of t given subarrays.
First line contains two integers n and t (1 ≤ n, t ≤ 200000) — the array length and the number of queries correspondingly.
Second line contains n positive integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 106) — the elements of the array.
Next t lines contain two positive integers l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n) each — the indices of the left and the right ends of the corresponding subarray.
Output t lines, the i-th line of the output should contain single positive integer — the power of the i-th query subarray.
Please, do not use %lld specificator to read or write 64-bit integers in C++. It is preferred to use cout stream (also you may use %I64d).
3 2
1 2 1
1 2
1 3
3
6
8 3
1 1 2 2 1 3 1 1
2 7
1 6
2 7
20
20
20
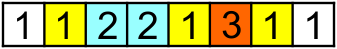
Consider the following array (see the second sample) and its [2, 7] subarray (elements of the subarray are colored):
1 //It is made by jump~ 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <cstdio> 6 #include <cmath> 7 #include <algorithm> 8 #include <ctime> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <queue> 11 #include <map> 12 #include <set> 13 #ifdef WIN32 14 #define OT "%I64d" 15 #else 16 #define OT "%lld" 17 #endif 18 using namespace std; 19 typedef long long LL; 20 const int MAXN = 200011; 21 const int size = 1000011; 22 int n,m,a[MAXN]; 23 int cnt[size]; 24 int kuai; 25 int nowl,nowr; 26 LL ans; 27 LL out[MAXN]; 28 29 struct wen{ 30 int l,r,id,belong; 31 }q[MAXN]; 32 33 inline int getint() 34 { 35 int w=0,q=0; 36 char c=getchar(); 37 while((c<'0' || c>'9') && c!='-') c=getchar(); 38 if (c=='-') q=1, c=getchar(); 39 while (c>='0' && c<='9') w=w*10+c-'0', c=getchar(); 40 return q ? -w : w; 41 } 42 43 inline bool cmp(wen p,wen pp){ if(pp.belong==p.belong) return p.r<pp.r; return p.belong<pp.belong; } 44 45 inline bool ccmp(wen p,wen pp){ return p.id<pp.id; } 46 47 inline void add(int x,int type){ 48 if(type==1) { 49 ans+=(LL)(cnt[a[x]]*2+1)*a[x]; 50 cnt[a[x]]++; 51 } 52 else{ 53 cnt[a[x]]--; 54 ans-=(LL)(cnt[a[x]]*2+1)*a[x]; 55 } 56 } 57 58 inline void work(){ 59 n=getint(); m=getint(); kuai=sqrt(n); 60 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) a[i]=getint(); 61 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) q[i].l=getint(),q[i].r=getint(),q[i].id=i,q[i].belong=(q[i].l-1)/kuai+1; 62 sort(q+1,q+m+1,cmp); 63 nowl=q[1].l; nowr=q[1].r; 64 for(int i=q[1].l;i<=q[1].r;i++) { 65 //ans-=(LL)cnt[a[i]]*cnt[a[i]]*a[i]; 66 ans+=(LL)(cnt[a[i]]*2+1)*a[i];//简化 67 cnt[a[i]]++; 68 //ans+=(LL)cnt[a[i]]*cnt[a[i]]*a[i]; 69 } 70 out[q[1].id]=ans; 71 //注意nowl、nowr是当前位置,处理完毕的状态 72 for(int i=2;i<=m;i++) { 73 while(nowl<q[i].l) add(nowl,-1),nowl++; 74 while(nowl>q[i].l) add(nowl-1,1),nowl--;//nowl已经插入,需要插入nowl-1 75 while(nowr<q[i].r) add(nowr+1,1),nowr++; 76 while(nowr>q[i].r) add(nowr,-1),nowr--; 77 out[q[i].id]=ans; 78 } 79 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) cout<<out[i]<<endl; 80 } 81 82 int main() 83 { 84 work(); 85 return 0; 86 }