在开发中,频繁的创建和销毁一个线程,是很耗资源的,为此找出了一个可以循环利用已经存在的线程来达到自己的目的,线程池顾名思义,也就是线程池的集合,通过线程池执行的线程任务,可以很有效的去规划线程的使用。
1.ThreadPoolExecutor介绍
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1,2,0,TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3));
第1个参数corePoolSize:核心线程数
第2个参数maximumpoolSize:最大线程数
第3个参数keepAliveTime:等待时间,当任务量大于队列长度需要创建线程的时侯,新创建的线程如果没有任务,时间一过就会自动销毁
第4个参数unit:时间单位
第5个参数BlockingQueue:阻塞队列,如果方法有参数,例如是3,表示队列长度为3.如果方法无参数,队列长度为Integer.MAX.VALUE
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor t = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1,2,0,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3));
t.execute(new TestThread());//第1个任务
t.execute(new TestThread());//第2个任务
t.execute(new TestThread());//第3个任务
t.execute(new TestThread());//第4个任务
t.execute(new TestThread());//第5个任务 开启第2个线程
t.execute(new TestThread());//第6个任务 最大线程为2,这里会报错
}
}
class TestThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
构造器如下:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
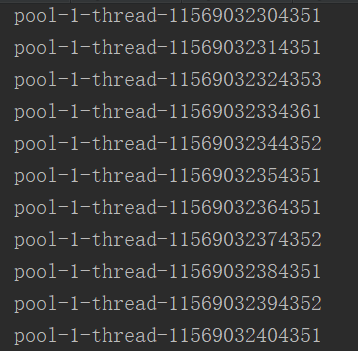
结果截图: 任务超过6个报错,最大线程数为2,实际需要3个线程执行
总结线程池的这些参数 core,maxPoolSize,keepalive
-
如果线程池工作线程数<=core,由核心线程执行
-
如果线程池工作线程数>core并且阻塞队列未满,将task插入阻塞队列,还是由核心线程执行
-
如果线程池工作流程数>core并且阻塞队列已满,且工作线程数<=maxPoolSize,创建新线程,由核心线程和新创建线程一起执行
-
如果线程池工作流程数>maxPoolSize并且阻塞队列已满,执行拒绝策略
- keepalive就是等待新创建的线程,如果新线程没有执行任务到了该时间,则销毁
2.newCachedThreadPool 可缓存线程池,线程可重复利用,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程
public class ExecutorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService e = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i =0; i<100; i++) {
e.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
}
构造器如下:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
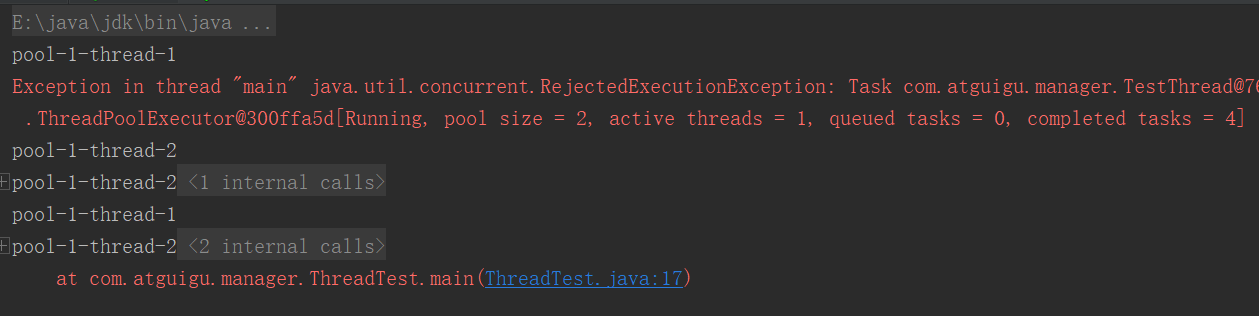
部分结果截图: 线程数量不定

3.newFixedThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池
public class ExecutorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService e = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for(int i =0; i<100; i++) {
e.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
}
构造器如下:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
部分结果截图: 只有固定5个线程再执行任务
4.newSingleThreadExecutor 创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行,可以控制线程的执行顺序
public class ExecutorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService e = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for(int i =0; i<100; i++) {
e.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
}
构造器如下:
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
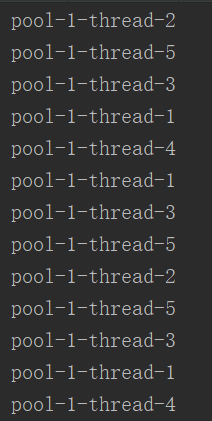
结果截图:只有1个线程执行
5.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor 创建一个单线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行,可以作一个定时器使用。
public class ScheduledExecutorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService s = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
s.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
},0,10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
构造器如下:
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService
(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1));
}
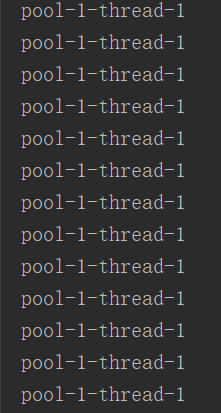
结果如下: 每隔10秒执行1次