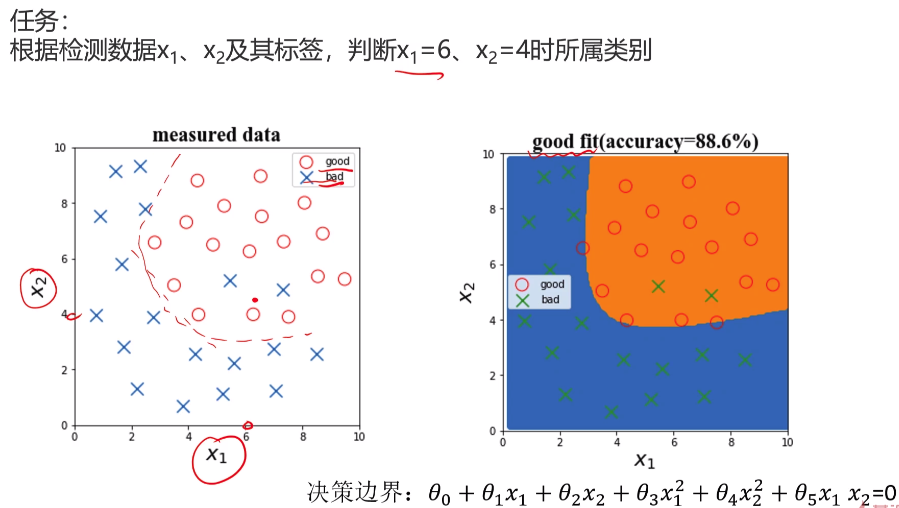
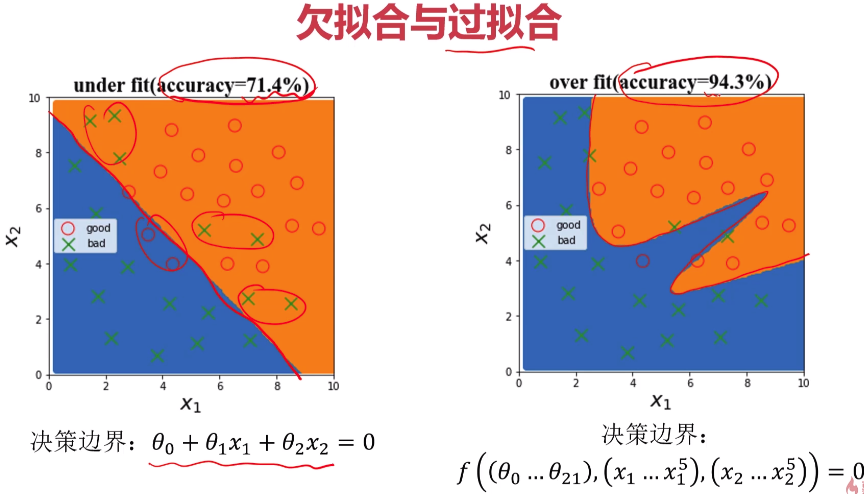
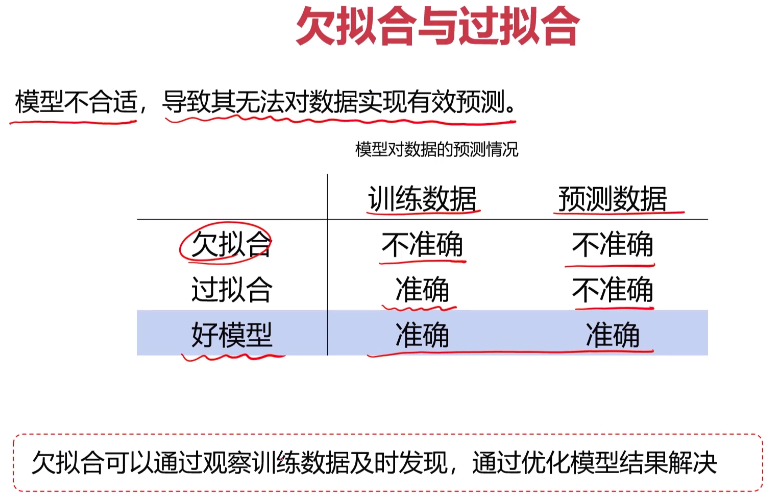
- 过拟合和欠拟合









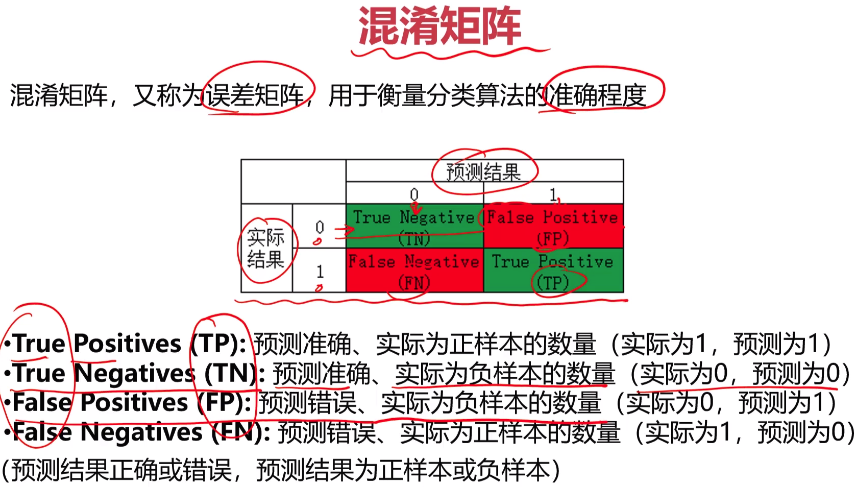
- 数据分离与混淆矩阵

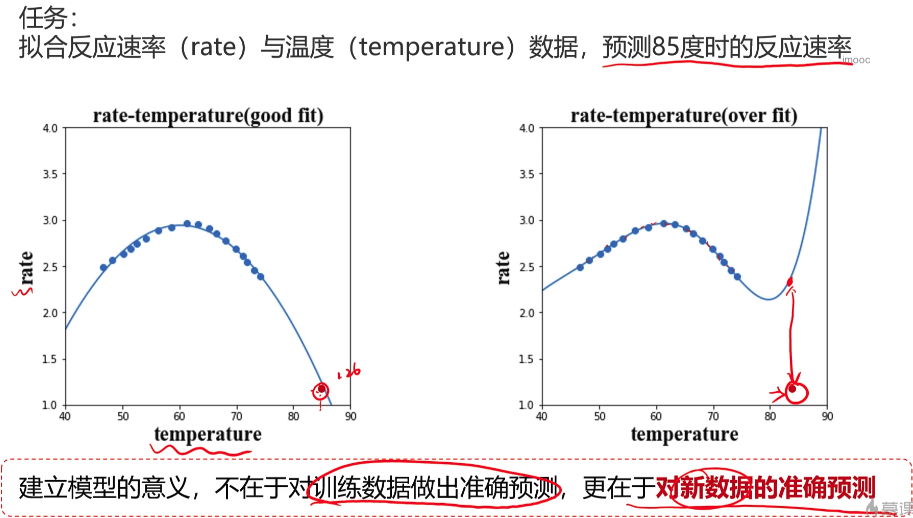

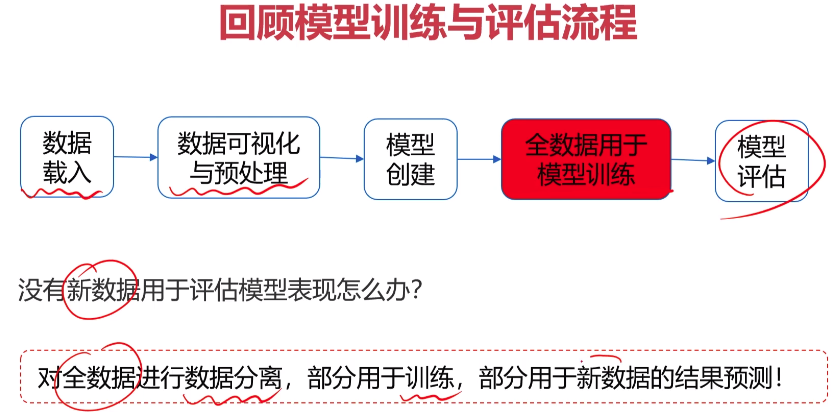
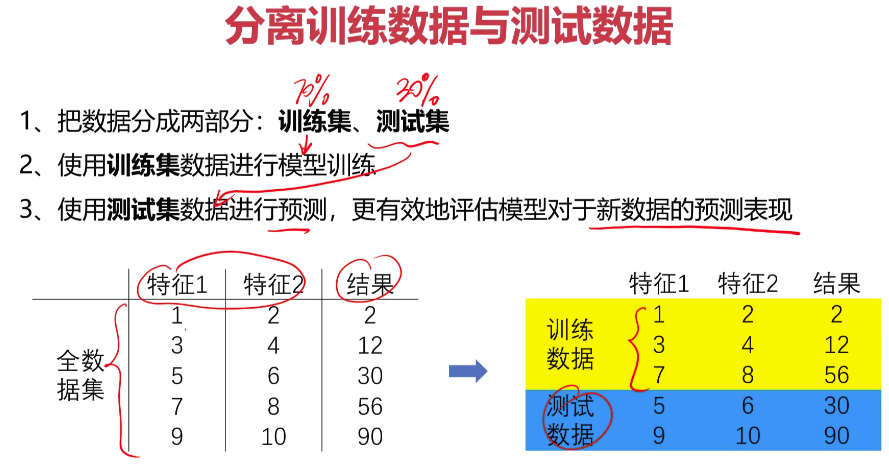


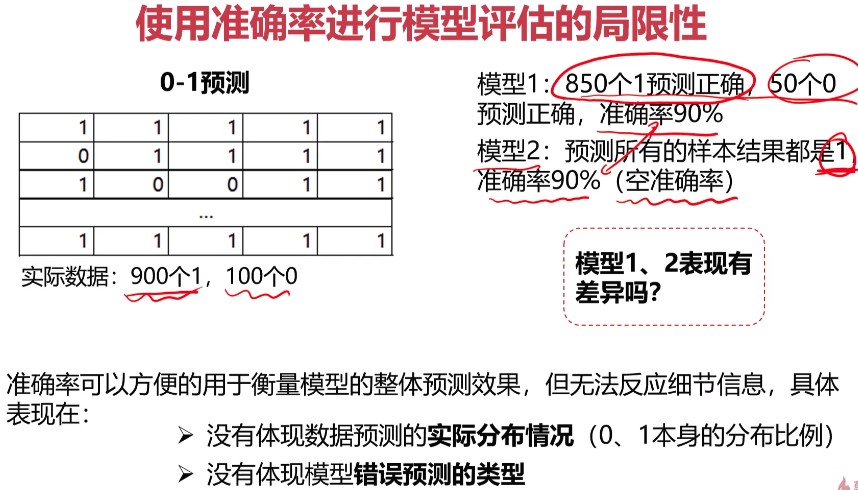





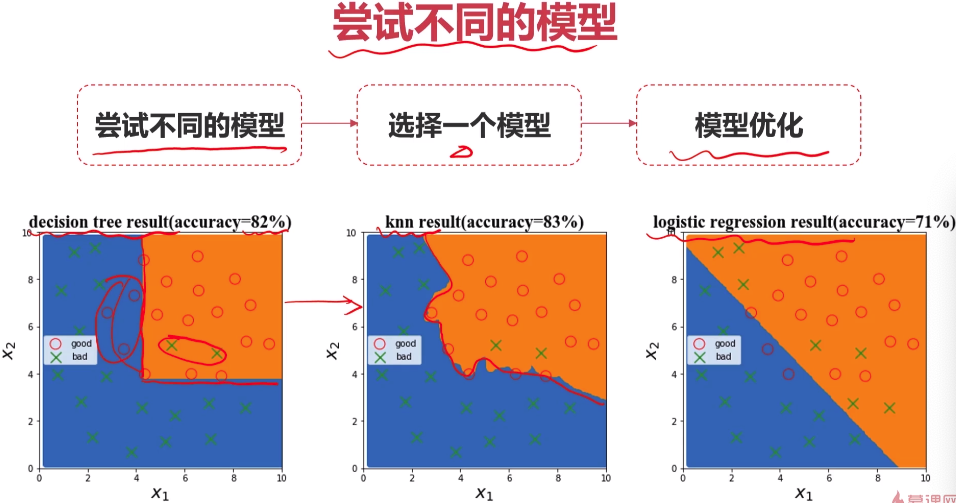
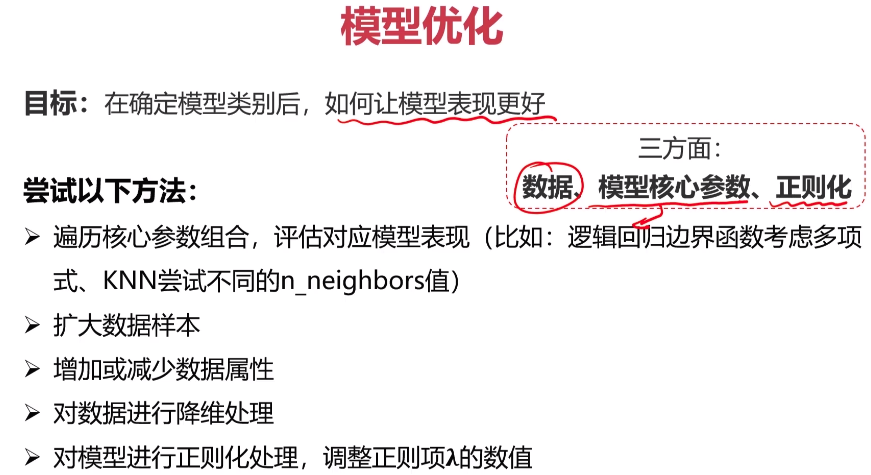
- 模型优化









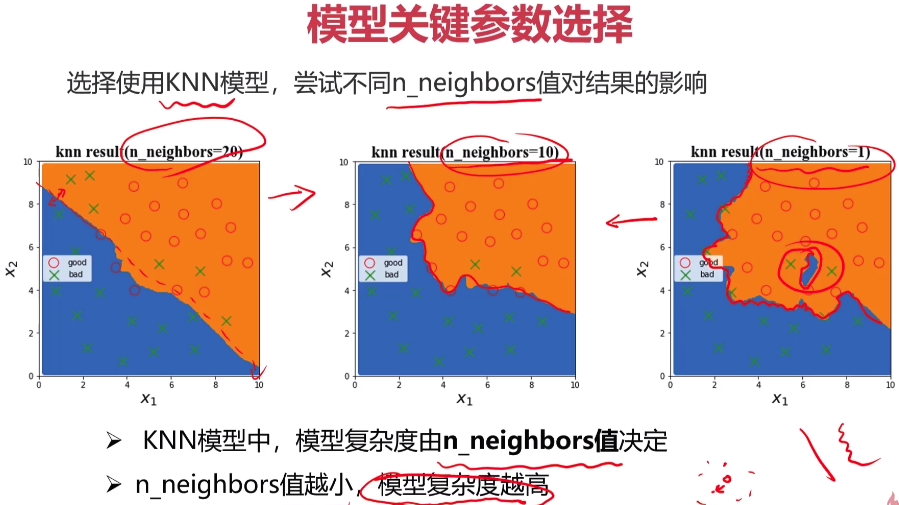

- 实战准备

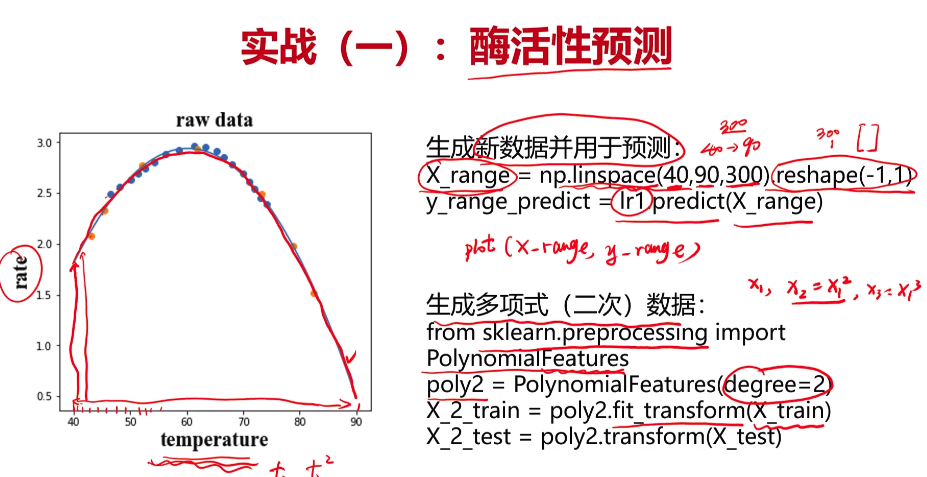



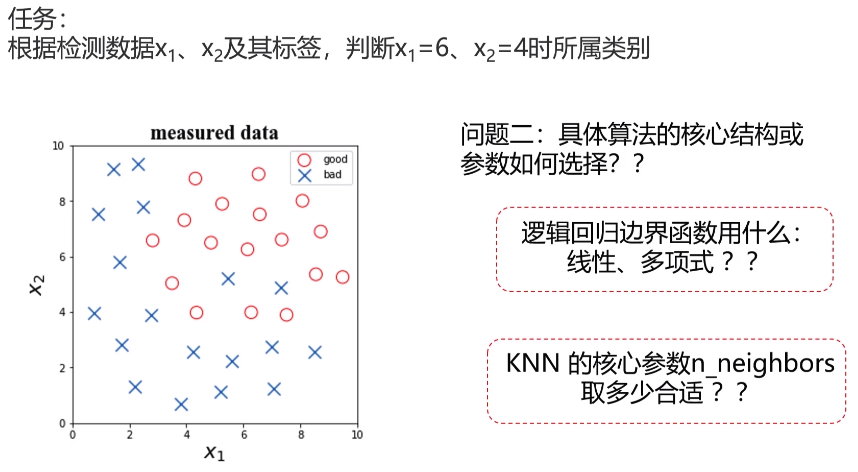
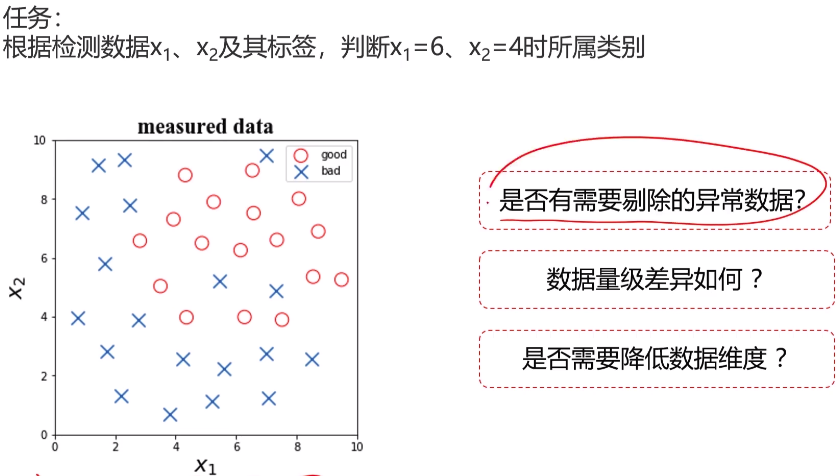
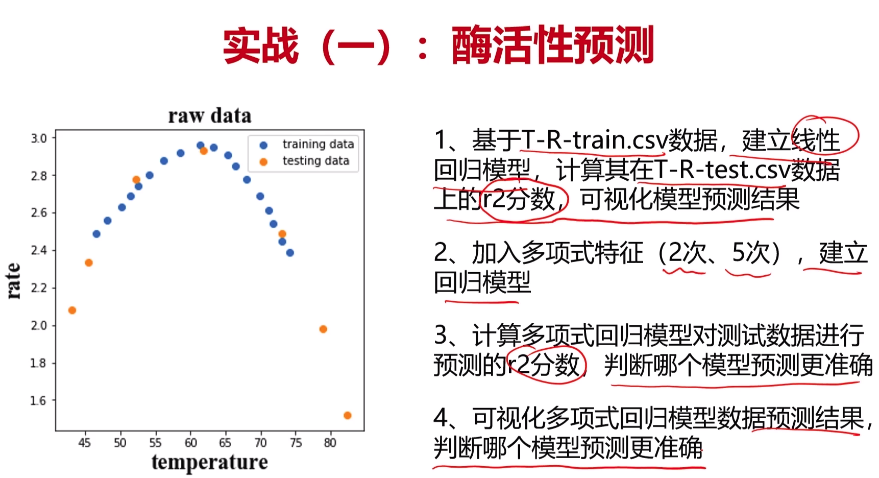
- 实战一





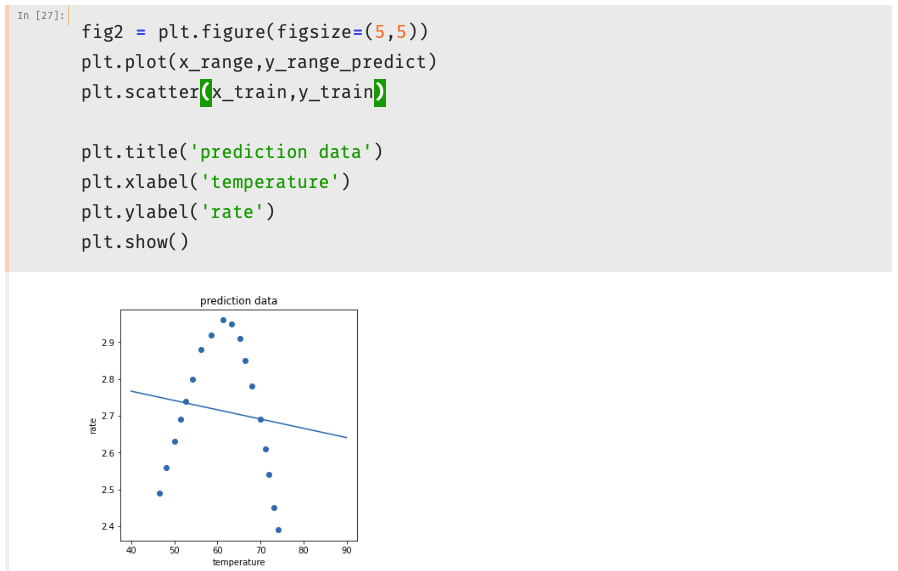


1 #generate new data 建立新数据 2 x_2_range = np.linspace(40,90,300).reshape(-1,1)#最小值40,最大值90,产生300个点;转成300行一列的数组 3 x_2_range = poly2.transform(x_2_range) 4 y_2_range_predict = lr2.predict(x_2_range) 5 6 x_5_range = np.linspace(40,90,300).reshape(-1,1)#最小值40,最大值90,产生300个点;转成300行一列的数组 7 x_5_range = poly5.transform(x_5_range) 8 y_5_range_predict = lr5.predict(x_5_range)


- 实战二

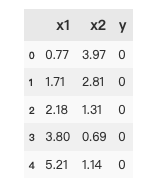
1 #load the data 2 import pandas as pd 3 import numpy as np 4 data = pd.read_csv('data_class_raw.csv') 5 data.head()
1 #define x and y 2 x = data.drop(['y'],axis=1) 3 y = data.loc[:,'y'] 4 print(x.shape,y.shape)
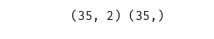
1 #visualize the data 2 %matplotlib inline 3 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 4 fig1 = plt.figure(figsize=(5,5)) 5 bad = plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==0],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==0]) 6 good = plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==1],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==1]) 7 plt.legend((good,bad),('good','bad')) 8 plt.title('raw data') 9 plt.xlabel('x1') 10 plt.ylabel('x2') 11 plt.show()
1 #anomaly detextion 异常点检测 2 from sklearn.covariance import EllipticEnvelope 3 ad_model = EllipticEnvelope(contamination=0.02) 4 ad_model.fit(x[y==0]) 5 y_predict_bad = ad_model.predict(x[y==0]) 6 print(y_predict_bad)
[ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 -1]
1 #visualize the data 2 %matplotlib inline 3 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 4 fig1 = plt.figure(figsize=(5,5)) 5 bad = plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==0],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==0]) 6 good = plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==1],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==1]) 7 plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==0][y_predict_bad==-1],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==0][y_predict_bad==-1],marker='x',s=150) 8 plt.legend((good,bad),('good','bad')) 9 plt.title('raw data') 10 plt.xlabel('x1') 11 plt.ylabel('x2') 12 plt.show()

1 data = pd.read_csv('data_class_processed.csv') 2 data.head() 3 #define x and y 4 x = data.drop(['y'],axis=1) 5 y = data.loc[:,'y']
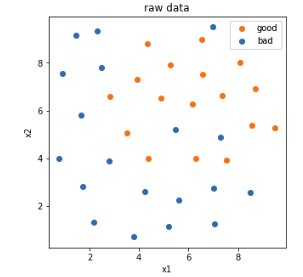
1 #pca 2 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 3 from sklearn.decomposition import PCA 4 x_norm = StandardScaler().fit_transform(x)#标准化处理数据 5 pca = PCA(n_components=2) 6 x_reduced = pca.fit_transform(x_norm) 7 var_ratio = pca.explained_variance_ratio_ 8 print(var_ratio) 9 fig4 = plt.figure(figsize=(5,5)) 10 plt.bar([1,2],var_ratio) 11 plt.show()
1 #train and test split:random_state=4,test_size=0.4 数据分离 2 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 3 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,random_state=4,test_size=0.4) 4 print(x_train.shape,x_test.shape,x.shape)
1 #knn model 2 from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier 3 knn_10 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=10) 4 knn_10.fit(x_train,y_train) 5 y_train_predict = knn_10.predict(x_train) 6 y_test_predict = knn_10.predict(x_test) 7 #calculate the accuracy 8 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score 9 accuracy_train = accuracy_score(y_train,y_train_predict) 10 accuracy_test = accuracy_score(y_test,y_test_predict) 11 print('training accuracy:',accuracy_train) 12 print('testing accuracy:',accuracy_test)
training accuracy: 0.9047619047619048 testing accuracy: 0.6428571428571429
1 #visualize the knn result and boundary 2 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0,10,0.05),np.arange(0,10,0.05)) 3 print(yy.shape)
(200, 200)
1 x_range = np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()] 2 print(x_range.shape)
(40000, 2)
1 y_range_predict = knn_10.predict(x_range)
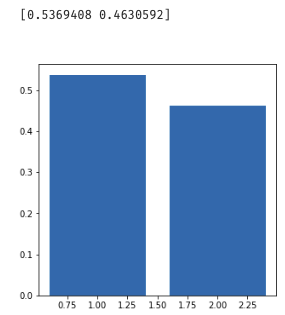
1 fig4 = plt.figure(figsize=(5,5)) 2 knn_bad = plt.scatter(x_range[:,0][y_range_predict==0],x_range[:,1][y_range_predict==0]) 3 knn_good = plt.scatter(x_range[:,0][y_range_predict==1],x_range[:,1][y_range_predict==1]) 4 5 bad = plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==0],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==0]) 6 good = plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==1],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==1]) 7 plt.legend((good,bad,knn_good,knn_bad),('good','bad','knn_good','knn_bad')) 8 plt.title('raw data') 9 plt.xlabel('x1') 10 plt.ylabel('x2') 11 plt.show()
1 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix 2 cm = confusion_matrix(y_test,y_test_predict) 3 print(cm)
[[4 2] [3 5]]
1 TP = cm[1,1] 2 TN = cm[0,0] 3 FP = cm[0,1] 4 FN = cm[1,0] 5 print(TP,TN,FP,FN)
5 4 2 3
1 accuracy =(TP+TN)/(TP+TN+FP+FN)#准确率:整体样本中正确样本数的比例 2 recall = TP/(TP+FP)#Sensitivity 灵敏度(召回率):正样本中,预测正确的比例 3 specificity = TN/(TN+FP)#特异度:负样本中,预测正确的比例 4 precision = TP/(TP+FP)#精确率:预测结果为正样本中,预测正确的比例 5 f1 = 2*precision*recall/(precision + recall)#F1 Score:综合Precision和Recall的喝一喝判断指标 6 print('准确率:',accuracy) 7 print('灵敏度:',recall) 8 print('特异度:',specificity) 9 print('精确率:',precision) 10 print('F1 Score:',f1)
准确率: 0.6428571428571429 灵敏度: 0.7142857142857143 特异度: 0.6666666666666666 精确率: 0.7142857142857143 F1 Score: 0.7142857142857143
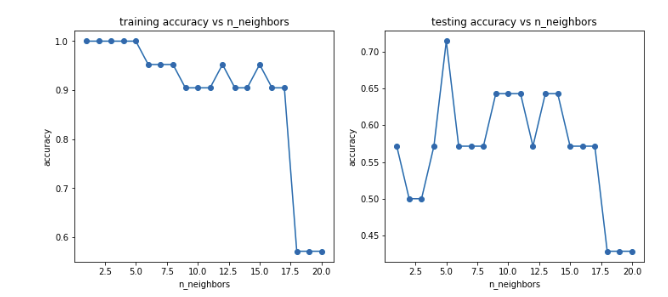
1 #try different k and calcualte the accuracy for each 2 n = [i for i in range(1,21)] 3 accuracy_train = [] 4 accuracy_test = [] 5 for i in n: 6 knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=i) 7 knn.fit(x_train,y_train) 8 y_train_predict = knn.predict(x_train) 9 y_test_predict = knn.predict(x_test) 10 accuracy_train_i = accuracy_score(y_train,y_train_predict) 11 accuracy_test_i = accuracy_score(y_test,y_test_predict) 12 accuracy_train.append(accuracy_train_i) 13 accuracy_test.append(accuracy_test_i) 14 print(accuracy_train,accuracy_test)
[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.9523809523809523, 0.9523809523809523, 0.9523809523809523, 0.9047619047619048, 0.9047619047619048, 0.9047619047619048, 0.9523809523809523, 0.9047619047619048, 0.9047619047619048, 0.9523809523809523, 0.9047619047619048, 0.9047619047619048, 0.5714285714285714, 0.5714285714285714, 0.5714285714285714]
[0.5714285714285714, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5714285714285714, 0.7142857142857143, 0.5714285714285714, 0.5714285714285714, 0.5714285714285714, 0.6428571428571429, 0.6428571428571429, 0.6428571428571429, 0.5714285714285714, 0.6428571428571429, 0.6428571428571429, 0.5714285714285714, 0.5714285714285714, 0.5714285714285714, 0.42857142857142855, 0.42857142857142855, 0.42857142857142855]
1 fig5 = plt.figure(figsize=(12,5)) 2 plt.subplot(121) 3 plt.plot(n,accuracy_train,marker='o') 4 plt.title('training accuracy vs n_neighbors') 5 plt.xlabel('n_neighbors') 6 plt.ylabel('accuracy') 7 8 plt.subplot(122) 9 plt.plot(n,accuracy_test,marker='o') 10 plt.title('testing accuracy vs n_neighbors') 11 plt.xlabel('n_neighbors') 12 plt.ylabel('accuracy') 13 plt.show()