IPC : Inter-Process Communication, 进程间通信
A进程把数据原原本本的发给B,这就是IPC
RPC : Remote Procedure Call, 远程过程调用
A进程如果想调用其无权限调用的led_open函数,而B进程可以调用:A进程封装数据发送给B;B进程取出数据调用led_open函数,这个过程就是RPC,其中A进程发数据给B的过程也是IPC,即RPC利用IPC来完成
进程间通信其实质也是需要三要素:源、目的、数据,这里源是进程A,目的怎么确定呢,进程B向ServiceManager注册服务,进程A向ServiceManager查询服务得到Handler,这个Handler指向进程B;数据就是个buf
android系统中的binder设计四个要素:client(进程A)、server(进程B)、ServiceManager(让A知道向谁发数据)、binder驱动(给前三者提供获取数据的接口)

RPC远程过程调用可以简单的理解为进程A想调用进程B的函数,那么
(1)调用哪一个函数
对server的函数编号,client编号给server
(2)传给它什么参数
再放在协商好的buf中,通过IPC传输
(3)返回值
B进程通过IPC发送返回值给进程A
ServiceManager所做的事情:
(1)open驱动
(2)告诉驱动,他是“ServiceManager”,建立server和client与ServiceManager的通讯
(3)while(1)
{
读驱动获取数据,没数据的时候休眠
解析数据
(根据获得的数据调用,比如server注册服务的时候提供的注册数据、client获取服务的数据信息)
1、注册服务,在链表中记录服务名
2、查询链表中是否有所需的服务,返回“server进程”的handle
}
server所做的事情:
(1)open驱动
(2)注册服务:向ServiceManager发送服务名(数据是发给驱动程序,驱动程序才知道是发给ServiceManager)
(3)while(1)
{
读驱动获得client发送的数据,没有数据则休眠
解析数据
调用对应的函数
}
client所做的事情:
(1)open驱动
(2)获取服务:向ServiceManager查询服务,获得一个handle,(这个过程是client把数据发给驱动程序)
(3)向handle发数据
frameworks
ativecmdsservicemanager //系统自带用C语言实现的binder应用程序
service_manager.c :
a. binder_open
b. binder_become_context_manager //告诉驱动,我是ServiceManager
c. binder_loop(bs, svcmgr_handler); //循环处理
c.1 res = ioctl(bs->fd, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr);//读数据
c.2 binder_parse
// 解析
// 处理 : svcmgr_handler,根据不同的ID执行不同的动作,下面这些宏定义就是ID
SVC_MGR_GET_SERVICE/SVC_MGR_CHECK_SERVICE : 获取服务
SVC_MGR_ADD_SERVICE : 注册服务
// 回复信息
bctest.c //半成品
(1)注册服务的过程:
a. binder_open
b. binder_call(bs, &msg, &reply, target, SVC_MGR_ADD_SERVICE)//在svcmgr_publish函数中被调用,target就是数据发送给谁,这里是ServiceManager,把数据组织好了给binder驱动,驱动发给ServiceManager
// msg含有服务的名字
// reply它会含有servicemanager回复的数据
// target:0表示servicemanager
// SVC_MGR_ADD_SERVICE:code: 表示要调用servicemanager中的"addservice函数"
(2)获取服务的过程:
a. binder_open
b. binder_call(bs, &msg, &reply, target, SVC_MGR_CHECK_SERVICE)//在svcmgr_lookup函数中被调用
// 含有服务的名字
// 它会含有servicemanager回复的数据, 表示提供服务的进程
// 0表示servicemanager
// code: 表示要调用servicemanager中的"getservice函数"
binder.c (封装好的C函数)
binder_call分析(远程调用):binder_call(struct binder_state *bs,struct binder_io *msg, struct binder_io *reply,uint32_t target, uint32_t code)
(1)向谁发数据(target)
(2)调用哪个函数(code)
(3)提供什么参数(msg)
(4)返回值(reply)
怎么用?
(1)构造参数:放到buf中,用结构体binder_io来描述数据格式
(2)调用ioctl发送数据:
ioctl(bs->fd, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr);//把binder_io结构体、target、code组织为binder_write_read结构体bwr,并使用ioctl发出去
(3)ioctl发送数据后其也会接受binder_write_read结构体bwr数据,需要把他转换成binder_io结构体
怎么写APP?
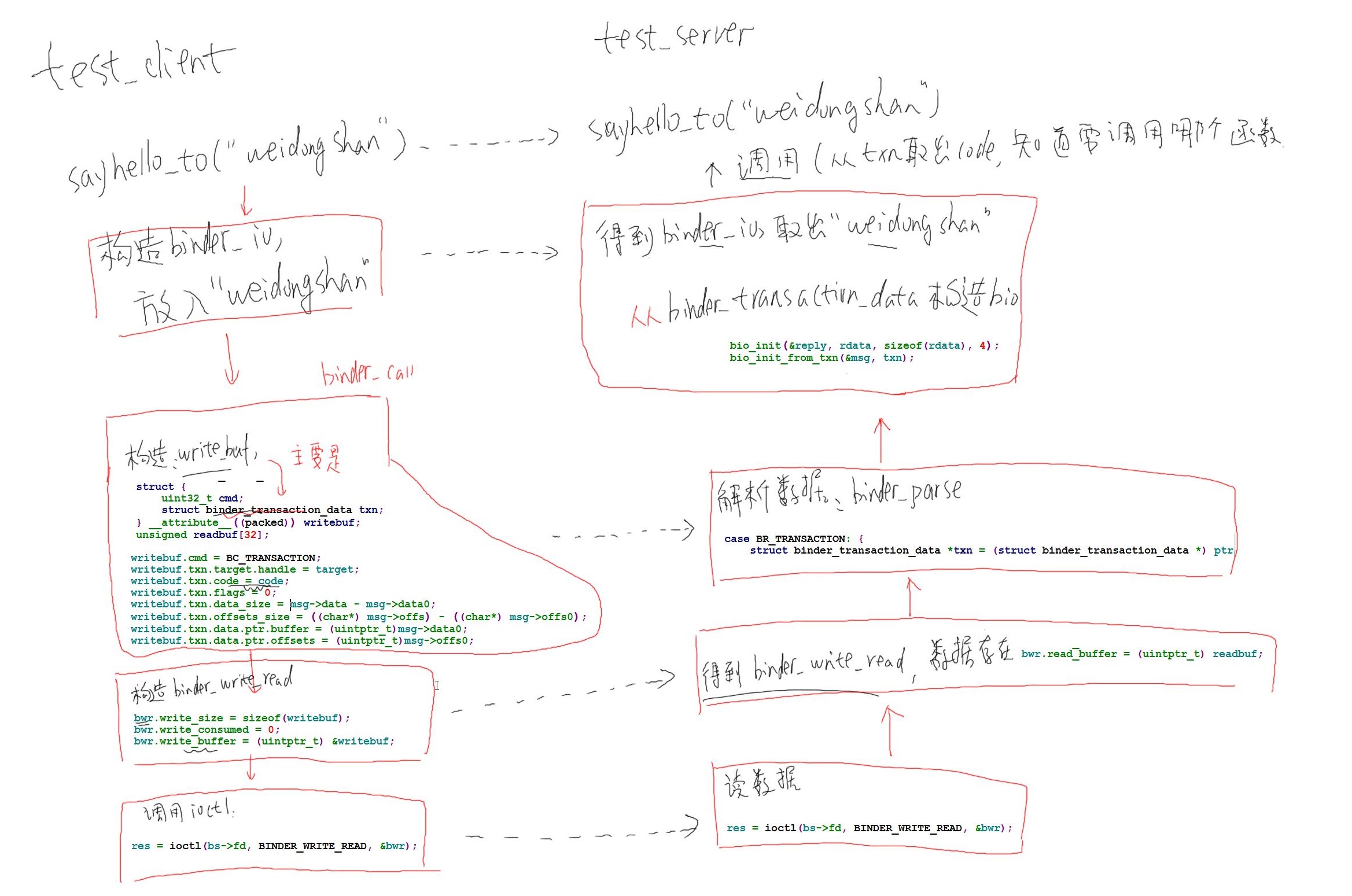
(1)client:A、binder_open;B、获得服务:handle;C、构造参数binder_io;D、调用binder_call;E、binder_call会返回一个binder_io,分析它取出返回值;
(2)server:A、binder_open;B、注册服务;C、ioctl()读数据 ;D、解析binder_write_read结构体数据E、根据code决定调用哪个函数,从binder_io取出参数;F、处理完后把返回值转换为binder_io,发给client
应用编写:
test_server.h
1 #ifndef _TEST_SERVER_H 2 #define _TEST_SERVER_H 3 4 #define HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO 1 5 #define HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO_TO 2 6 7 #endif // _TEST_SERVER_H
test_server.c
其提供“hello”服务,有两个函数:1、void sayhello(void);2、int sayhello_to(char * name);
int svcmgr_publish(struct binder_state *bs, uint32_t target, const char *name, void *ptr)
{
int status;
unsigned iodata[512/4];
struct binder_io msg, reply;
bio_init(&msg, iodata, sizeof(iodata), 4);
bio_put_uint32(&msg, 0); // strict mode header
bio_put_string16_x(&msg, SVC_MGR_NAME);
bio_put_string16_x(&msg, name);
bio_put_obj(&msg, ptr);
if (binder_call(bs, &msg, &reply, target, SVC_MGR_ADD_SERVICE))
return -1;
status = bio_get_uint32(&reply);
binder_done(bs, &msg, &reply);
return status;
}
void sayhello(void)
{
static int cnt = 0;
fprintf(stderr, "say hello : %d
", ++cnt);
}
int sayhello_to(char *name)
{
static int cnt = 0;
fprintf(stderr, "say hello to %s : %d
", name, ++cnt);
return cnt;
}
int hello_service_handler(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_transaction_data *txn,
struct binder_io *msg,
struct binder_io *reply)
{
/*根据txn->code知道要调用哪个函数,如果需要参数,可以从msg取出,如果返回结果,可以把结果放入reply*/
uint16_t *s;
char name[512];
size_t len;
uint32_t handle;
uint32_t strict_policy;
int i;
strict_policy = bio_get_uint32(msg);
switch(txn->code) {
case HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO:
sayhello();
bio_put_uint32(reply, 0); //先获得0,后面接得才是数据,因为client端是这么组织bio的
return 0;
case HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO_TO:
s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len); //"IHelloService"
s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len); // name
if (s == NULL) {
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)//取出来的是16位的数据,需要转换为8位的
name[i] = s[i];
name[i] = '�';
//处理
i = sayhello_to(name);
//把返回结果放入reply
bio_put_uint32(reply, 0); /* no exception */
bio_put_uint32(reply, i);
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr, "unknown code %d
", txn->code);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int test_server_handler(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_transaction_data *txn,
struct binder_io *msg,
struct binder_io *reply)
{
int (*handler)(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_transaction_data *txn,
struct binder_io *msg,
struct binder_io *reply);
handler = (int (*)(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_transaction_data *txn,
struct binder_io *msg,
struct binder_io *reply))txn->target.ptr;
return handler(bs, txn, msg, reply);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
struct binder_state *bs;
uint32_t svcmgr = BINDER_SERVICE_MANAGER;
uint32_t handle;
int ret;
bs = binder_open(128*1024);
if (!bs) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to open binder driver
");
return -1;
}
/* add service */
ret = svcmgr_publish(bs, svcmgr, "hello", hello_service_handler);
//可能有多个svcmgr_publish(bs, svcmgr, "hello1", hello1_service_handler);
//ret = svcmgr_publish(bs, svcmgr, "hello", (void *)123);方法1!
if (ret) { fprintf(stderr, "failed to publish hello service "); return -1; } binder_set_maxthreads(bs, 10);
//binder_loop(bs,hello_service_handler);//方法1
binder_loop(bs, test_server_handler);//test_server_handler是受到消息后怎么处理的处理函数,在test_server_handler里面可以根据svcmgr_publish函数的最后一个函数指针调用其,因为可能存在多个svcmgr_publish来注册多个服务,所有这种方式是最好的,上面那种直接使用hello_service_handler的情况仅针对只有一个服务的情况
return 0;
}
test_client.c
uint32_t svcmgr_lookup(struct binder_state *bs, uint32_t target, const char *name)
{
uint32_t handle;
unsigned iodata[512/4];
struct binder_io msg, reply;
bio_init(&msg, iodata, sizeof(iodata), 4);
bio_put_uint32(&msg, 0); // strict mode header
bio_put_string16_x(&msg, SVC_MGR_NAME);
bio_put_string16_x(&msg, name);
if (binder_call(bs, &msg, &reply, target, SVC_MGR_CHECK_SERVICE))
return 0;
handle = bio_get_ref(&reply);
if (handle)
binder_acquire(bs, handle);
binder_done(bs, &msg, &reply);
return handle;
}
struct binder_state *g_bs;
uint32_t g_hello_handle;
uint32_t g_goodbye_handle;
void sayhello(void)
{
unsigned iodata[512/4];
struct binder_io msg, reply;
bio_init(&msg, iodata, sizeof(iodata), 4);
bio_put_uint32(&msg, 0); // strict mode header,先放入一个0,后面接得就是数据
bio_put_string16_x(&msg, "IHelloService");
if (binder_call(g_bs, &msg, &reply, g_hello_handle, HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO))
return ;
//sayhello函数是void返回,不需要解析reply
binder_done(g_bs, &msg, &reply);
}
int sayhello_to(char *name)
{
unsigned iodata[512/4];
struct binder_io msg, reply;
int ret;
int exception;
bio_init(&msg, iodata, sizeof(iodata), 4);
bio_put_uint32(&msg, 0); // strict mode header
bio_put_string16_x(&msg, "IHelloService");
bio_put_string16_x(&msg, name);
if (binder_call(g_bs, &msg, &reply, g_hello_handle, HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO_TO))
return 0;
exception = bio_get_uint32(&reply);
if (exception)
ret = -1;
else
ret = bio_get_uint32(&reply);
binder_done(g_bs, &msg, &reply);
return ret;
}
/* ./test_client hello
* ./test_client hello <name>
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
struct binder_state *bs;
uint32_t svcmgr = BINDER_SERVICE_MANAGER;
uint32_t handle;
int ret;
if (argc < 2){
fprintf(stderr, "Usage:
");
fprintf(stderr, "%s hello
", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "%s hello <name>
", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
bs = binder_open(128*1024);
if (!bs) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to open binder driver
");
return -1;
}
g_bs = bs;
/* get service */
handle = svcmgr_lookup(bs, svcmgr, "hello");
g_hello_handle = handle;
/* send data to server */
if (argc == 2) {
sayhello();
} else if (argc == 3) {
ret = sayhello_to(argv[2]);
fprintf(stderr, "get ret of sayhello_to = %d
", ret);
}
binder_release(bs, handle);
return 0;
}
上机测试:
a. 烧写非android系统, 比如QT(因为android系统上电会运行其只带的service_manager,这里借助QT系统)
b. 重新编译内核让它支持NFS, 更新板上内核,可以通过nfs挂载
make menuconfig
File systems --->
[*] Network File Systems --->
<*> NFS client support
[*] NFS client support for NFS version 3
[*] NFS client support for the NFSv3 ACL protocol extension
[*] NFS client support for NFS version 4
[*] NFS client support for NFSv4.1 (EXPERIMENTAL)
[*] Root file system on NFS
[*] Use the legacy NFS DNS resolver
[*] Use the new idmapper upcall routine
make zImage
c. mount nfs, 运行service_manager, test_server, test_client
mount -t nfs -o nolock 192.168.1.123:/work /mnt
./service_manager &
./test_server &
./test_client hello
./test_client hello weidongshan