菜鸟学python第十六天
1.re模块(正则表达式)
-
-
正则表达式是一个由特殊字符组成的序列,他能帮助对字符串的某种对应模式进行查找。
在python中,re 模块使其拥有全部的正则表达式功能。
-
-
re模块的使用
re正则表达式的运行机制: 一个一个进行比对
-
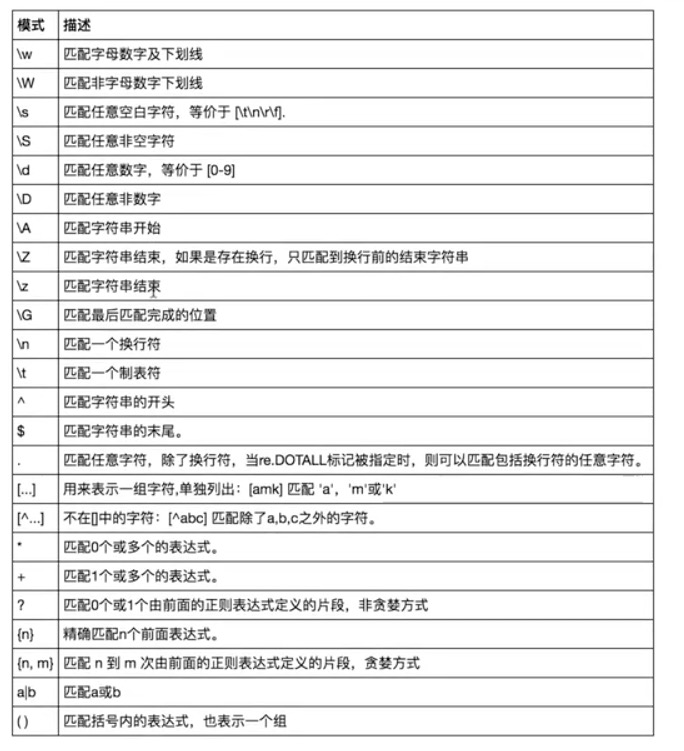
re.findall()
import re # w, 匹配字母数字下划线 print(re.findall('w', 'Aah123 +-_')) # w, ['A', 'a', 'h', '1', '2', '3', '_'] print(re.findall('ww', 'Aah123 +-_')) # ww, ['Aa', 'h1', '23'] print(re.findall('w9w', 'Aa9h123 +-_ aaa9--')) # w9w ,['a9h'] # W :匹配非字母数字下划线 print(re.findall('W', 'hshk _=fh**#_ ')) # W,[' ', '=', '*', '*', '#', ' ', ' '] # s : 匹配任意空白字符( s 都包含在内) print(re.findall('s', 'dhfgk gds g_jflkds ')) # [' ', ' ', ' ', ' '] # ^str: 从头开始匹配 print(re.findall('^alex', 'hahahaha alex is alex is dsb')) # d第一位没查找到返回空 # $: 从尾开始匹配 print(re.findall('Jason$', 'hello Jason')) # ['Jason'] # .:可以匹配除换行符之外的任意字符,当re.DOTALL被指定时,则可匹配包含换行符在内的所有字符 print(re.findall('a.c', 'a alc aaac a c asffgf a c')) # ['alc', 'aac', 'a c'] print(re.findall('a.c', 'a alc aaac a c asffgf a c', re.DOTALL)) # ['alc', 'aac', 'a c', 'a c'] # [] : 代表匹配一个字符,这一个字符是来自于我们自定义的范围 print(re.findall('[1-9]', 's3jl5j6j33j6l')) # ['3', '5', '6', '3', '3', '6'] print(re.findall('[a-z]', 's3jl5j6j33j6l')) # ['s', 'j', 'l', 'j', 'j', 'j', 'l'] print(re.findall('5[a-z]6', 's3jl5j6j33j6l')) # ['5j6'] # 重复匹配 # ? : 代表左边那一个字符出现0次或1次(可有一个或没有的情况) print(re.findall('ab?', 'a ab aab a123b a123bbbbb')) # ['a', 'ab', 'a', 'ab', 'a', 'a'] # *:代表左边那一个字符出现0次到无穷次(可有可没有的情况) print(re.findall('ab*', 'a ab abbbb a1243b a123bbb')) # ['a', 'ab', 'abbbb', 'a', 'a'] # +:代表左边那个字符出现一次到无穷次(必须要出现一次以上,否则失败) print(re.findall('ab+', 'a jab a12b abbbbb ab')) # ['ab', 'abbbbb', 'ab'] # {n,m} : 代表左边那个字符出现n次到m次 print(re.findall('ab{1,3}', 'ab abb abbb aab aaab a b b a')) # ['ab', 'abb', 'abbb', 'ab', 'ab'] print(re.findall('ab{1,}', 'ab abb abbbb aab aaab a b')) # ['ab', 'abb', 'abbbb', 'ab', 'ab'] print(re.findall('ab{3}','a ab abb abbbb a123b a123bbbb')) # ['abbb'] # .*:匹配任意0个到无穷个字符,贪婪匹配(到右边字符最后一次出现时结束) print(re.findall('a.*b', 'aghfhkdsnb-9=-0b')) # ['aghfhkdsnb-9=-0b'] print(re.findall('href="(.*)"','<p>动感视频</p><a href="https://www.douniwan.com/1.mp4">逗你玩呢 </a><a href="https://www.xxx.com/2.mp4">葫芦娃</a>')) # ['https://www.douniwan.com/1.mp4">逗你玩呢</a><a href="https://www.xxx.com/2.mp4'] # .*?:匹配任意0个到无穷个字符,非贪婪匹配(到右边字符第一次出现时结束) print(re.findall('a.*?b', 'aghfhkdsnb-9=-0b')) # ['aghfhkdsnb'] print(re.findall('href="(.*?)"','<p>动感视频</p><a href="https://www.douniwan.com/1.mp4">逗你玩呢 </a><a href="https://www.xxx.com/2.mp4">葫芦娃</a>')) # ['https://www.douniwan.com/1.mp4', 'https://www.xxx.com/2.mp4'] # |:或者 print(re.findall('ab|ac', 'ab bb ac cc abb acc')) # ['ab', 'ac', 'ab', 'ac'] # ():分组 print(re.findall('a(?:ab|c)', 'aab ac ac ab abbb aaaab')) # ['aab', 'ac', 'ac', 'aab'] print(re.findall('a(ab|c)', 'aab ac ac ab abbb aaaab')) # ['ab', 'c', 'c', 'ab'] # : 转意 print(re.findall('a\\c', 'ac aac')) # \\转以后相当于\ print(re.findall(r'a\c', 'ac aac')) # r表示原生代码,指定python语法不要去识别它 # re.I : 忽略大小写 print(re.findall('alex', 'my name s alex Alex is dsb aLex AleX', re.I)) # ['alex', 'Alex', 'aLex', 'AleX'] # re.M :区分换行符 msg = """ my name is egon ghkhdsgdskhf egon hgkshd1243 egon""" print(re.findall('egon$', msg, re.M)) # $表示从后开始找,re.M表示识别多行 # ['egon', 'egon', 'egon']
-
-
-
re模块其他方法
-
re.search(): 返回查找到的第一个内容,查找不到返回none
res=re.search('(href)="(.*?)"','<p>动感视频</p><a href="https://www.douniwan.com/1.mp4">逗你玩呢</a><a href="https://www.xxx.com/2.mp4">葫芦娃</a>') print(res) # 匹配成功第一个返回属性及内容,匹配不成功返回none print(res.group(0)) # 匹配成功返回第一个内容,group将其转换为字符串 print(res.group(1)) # 匹配成功返回分组的第一个内容(href) print(res.group(2)) # 匹配成功返回分组的第二个内容 输出结果: <_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(14, 51), match='href="https://www.douniwan.com/1.mp4"'> href="https://www.douniwan.com/1.mp4" href https://www.douniwan.com/1.mp4
-
re.match():从开头查找,开头是则返回该值,不是则返回none
res=re.match('abc','123abc') ## res=re.search('^abc','123abc') print(res) 输出结果: None
-
re.compile():将要匹配的字符准备好
pattern=re.compile('alex') print(pattern.findall('alex is alex is alex')) print(pattern.search('alex is alex is alex')) print(pattern.match('alex is alex is alex'))
-
-
-
练习
# 提取算式中的数字,包含负数,减号除外 msg = "1-2*(60+(-40.35/5)-(-40*3))" print(re.findall('D?(-?d+.?d*)', msg)) 输出结果: ['1', '2', '60', '-40.35', '5', '-40', '3']
2. hashlib 模块
-
hash:一种算法,用来对数据进行运算校验,返回hash值。
-
hash三大特性: 1. 只要传入的内容是一样的那返回的hash值一定一样。
2.只要采用的hash算法固定,无论传入多长内容hash值长度不变
3.hash值不可逆,就是不能通过hash值逆推出文件内容
-
为何要用hash:
1.文件完整性校验(特性1、2)
原理:下载前拿到文件的hash值,下载完成后在目标设备上在进行校验,比对两者是否一致,从而判断文件完整性
方法:将文件以行的形式一行一行读到内存中,加以hash运算最后得到hash值(不能将文件一次性全读到内存中,会导致内存溢出),但是一行行验证当文件行数过多时,效率太低,故我们可以选择几个特征区域加以hash,验证即可。
import hashlib m=hashlib.md5() # md5 默认hash值为32位 m.update('你好'.encode('utf-8')) m.update('hello'.encode('utf-8')) # 与m.update('你好hello'encode('utf-8'))de hash值一致 print(m.hexdigest()) # 对以上update文件进行校验返回其hash值 输出结果: 65c83c71cb3b2e2882f99358430679c3 # hash值长度之与算法有关,与文件大小无关 m2=hashlib.sha512() # sha512算法hash值长度为128 m2.update(b'asdfassssssssssssssssssssssssssss') # print(m2.hexdigest()) print(len(m2.hexdigest())) 输出结果: 128 # 文件验证 with open(r'D:xxxxxxfile.txt',mode='rb') as f: m=hashlib.md5() for line in f: m.update(line) print(m.hexdigest())
2.用来对数据加密(特性3)
原理:在数据的某些位置添加设定数据,将其数据复杂化
# 数据加密 pwd=input('password>>> ').strip() m=hashlib.md5() m.update('加密数据'.encode('utf-8')) # 在密码前加密,也可在其他任意位置加密,增加破解难度 m.update(pwd.encode('utf-8')) # 原密码数据 m.update('加密数据'.encode('utf-8')) # 在密码后加密,也可是其他位置 print(m.hexdigest())