下面是线程状态的变化图。
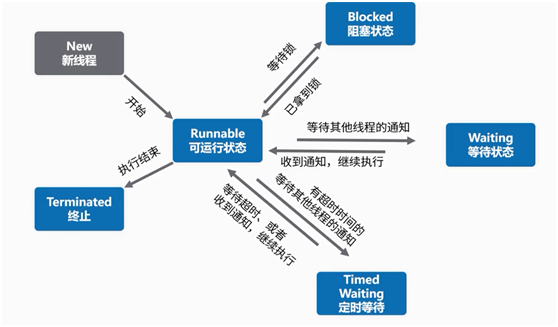
下面是6个状态都是什么。
让我们思考下面的问题。
sleep,wait,join,抢不到锁,等待IO时,线程到底处于什么状态。 话不多说,用代码说话。
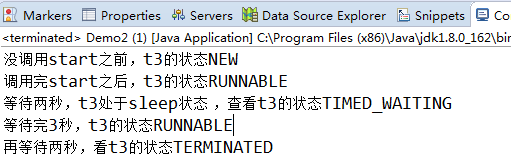
sleep时,处于TIMED_WAITING

public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //状态切换 新建-》运行-》等待-》运行-》终止 Thread t3=new Thread(()->{ try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("等待完3秒,t3的状态"+Thread.currentThread().getState()); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } }); System.out.println("没调用start之前,t3的状态"+t3.getState()); t3.start(); System.out.println("调用完start之后,t3的状态"+t3.getState()); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("等待两秒,t3处于sleep状态 ,查看t3的状态"+t3.getState()); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("再等待两秒,看t3的状态"+t3.getState()); } }
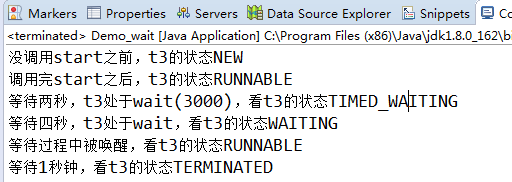
wait时 如果这么调用wait(3000),那么线程处于TIMED_WAITING,如果没有设置超时时间,那么线程处于WAITING
public class Demo_wait {
public static Object obj=new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//状态切换 新建-》运行-》wait-》运行-》终止
Thread t3=new Thread(()->{
try {
synchronized (obj) {
obj.wait(3000);
obj.wait();
System.out.println("等待过程中被唤醒,看t3的状态"+Thread.currentThread().getState());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println("没调用start之前,t3的状态"+t3.getState());
t3.start();
System.out.println("调用完start之后,t3的状态"+t3.getState());
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("等待两秒,t3处于wait(3000),看t3的状态"+t3.getState());
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println("等待四秒,t3处于wait,看t3的状态"+t3.getState());
synchronized (obj) {
obj.notifyAll();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("等待1秒钟,看t3的状态"+t3.getState());
}
}
View Code
join时,如果设置了超时时间,可以看到线程处于TIMED_WAITING,反之,线程处于WAITING

public class Demo_join { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread t1=new Thread(()->{ try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); Thread t2=new Thread(()->{ try { t1.join(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); System.out.println("没调用start之前,t2的状态"+t2.getState()); t1.start(); t2.start(); System.out.println("调用完start之后,t2的状态"+t2.getState()); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("等待两秒,t2处于join ,查看t3的状态"+t2.getState()); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("再等待两秒,看t2的状态"+t2.getState()); System.out.println("###########################################################"); Thread t3=new Thread(()->{ try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); Thread t4=new Thread(()->{ try { t3.join(1000); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); System.out.println("没调用start之前,t4的状态"+t4.getState()); t3.start(); t4.start(); System.out.println("调用完start之后,t4的状态"+t4.getState()); Thread.sleep(500); System.out.println("等待500毫秒,t4处于join ,查看t4的状态"+t4.getState()); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("再等待两秒,看t4的状态"+t2.getState()); } }

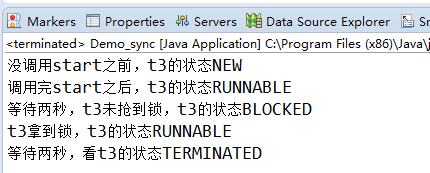
抢不到锁时,线程状态是BLOCKED

public class Demo_sync { public static Object obj=new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread t3=new Thread(()->{ try { synchronized (obj) { System.out.println("t3拿到锁,t3的状态"+Thread.currentThread().getState()); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); synchronized (obj) { System.out.println("没调用start之前,t3的状态"+t3.getState()); t3.start(); System.out.println("调用完start之后,t3的状态"+t3.getState()); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("等待两秒,t3未抢到锁,t3的状态"+t3.getState()); } Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("等待两秒,看t3的状态"+t3.getState()); } }
等待IO ,线程状态是RUNNABLE

public class Demo_IO { public static Object obj=new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread t3=new Thread(()->{ try { ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(8000); Socket accept = server.accept(); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(accept.getInputStream())); String buffer=""; while((buffer=br.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(buffer); } accept.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); System.out.println("没调用start之前,t3的状态"+t3.getState()); t3.start(); System.out.println("调用完start之后,t3的状态"+t3.getState()); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("等待两秒,看t3的状态"+t3.getState()); } }

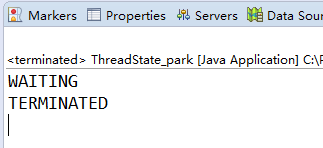
LockSupport.park 时, 线程状态是WAITING
public class ThreadState_park {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1=new Thread(()->{
LockSupport.park();
});
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(t1.getState());
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
System.out.println(t1.getState());
}
}
View Code