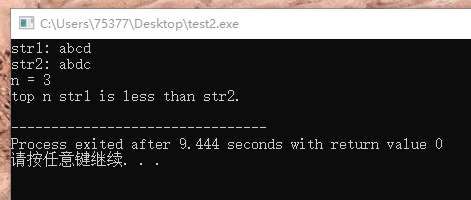
1、函数原型。
#include <stdio.h> int strncmp(const char *s1, const char *s2, size_t n) //函数返回int型,形参为两个指向char型的指针)和 unsigned 型n。 { while(n && *s1 && *s2) // 当n和*s1和*s2都不为0时,执行循环体 { if(*s1 != *s2) // 当循环体中*s1不等于*s2时,执行if判断语句。 return (unsigned char)*s1 - (unsigned char)*s2; s1++; //指针依次向后移动 s2++; n--; //字符个数依次减少 } //当while语句不成立,即n、*s1、*s2中任一一个为0,或者*s1和*s2同时为0, while循环条件不成立 if(!n) // 当n为0,即字符比较完毕,不存在 *s1 != *s2的情况,因此返回0. return 0; if(*s1) // 当*s1为正,n为正,*s2位0时,说明在前几个字符一致的情况下,字符串str1的长度大于str2的长度,str1大于str2 return 1; if(*s1 == *s2 ) //当*s1和*s2同时等于0,*s1和*s2相等。(这部分为个人增加的) return 0; return -1; // 当*s1为0,*s2为正时,str1小于str2. } int main(void) { char str1[128]; char str2[128]; printf("str1: "); scanf("%s", str1); printf("str2: "); scanf("%s", str2); unsigned n; printf("n = "); scanf("%u", &n); int tmp = strncmp(str1, str2, n); // 实参给与 字符串数组名 和 unsigned型整数。 if(tmp > 0) puts("top n str1 is greater than str2."); else if(tmp == 0) puts("top n str1 is equal to str2."); else puts("top n str1 is less than str2."); return 0; }
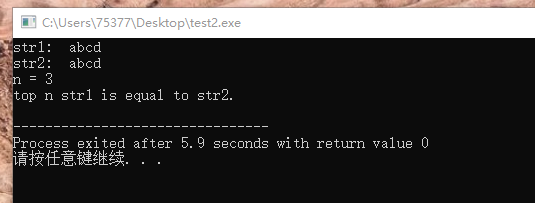
2、加载strncmp函数头文件,可以直接调用strncmp函数
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> // head file? It can run without loading!!!!; int main(void) { char str1[128]; char str2[128]; unsigned n; printf("str1: "); scanf("%s", str1); printf("str2: "); scanf("%s", str2); printf("n = "); scanf("%u", &n); int tmp = strncmp(str1, str2, n); // 函数实参为字符串数组名和 unsigned型整数 if(tmp > 0) puts("top n str1 is greater than str2."); else if(tmp == 0) puts("top n str1 is equal to str2."); else puts("top n str1 is less than str2."); return 0; }