1、split命令用于分离文件
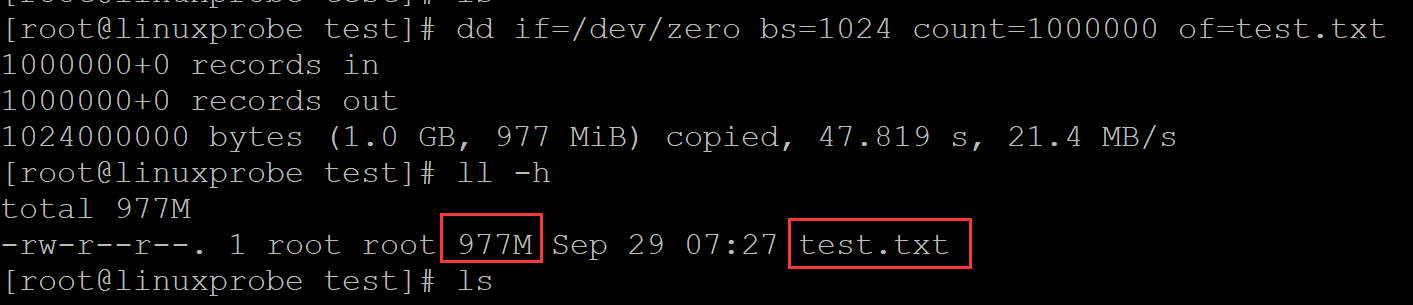
创建测试文件:
[root@linuxprobe test]# dd if=/dev/zero bs=1024 count=1000000 of=test.txt
1000000+0 records in
1000000+0 records out
1024000000 bytes (1.0 GB, 977 MiB) copied, 47.819 s, 21.4 MB/s
[root@linuxprobe test]# ll -h
total 977M
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 977M Sep 29 07:27 test.txt
[root@linuxprobe test]#
2、基本用法
依据文件大小拆分文件:
split -b 200M test.txt ## -b参数指定文件大小,可以是K、M、G、T等

默认生成了以x开头的文件。
3、指定输出文件的前缀,直接在分离文件后加前缀
split -b 200M test.txt result ##直接加前缀result

4、把ab后缀该为数字后缀,直接加 -d:
split -b 200M test.txt result -d ##直接加-d

5、把拆分后的数据合并并校验
[root@linuxprobe test]# cat result00 result01 result02 result03 result04 > result ## 合并
[root@linuxprobe test]# md5sum result test.txt ##校验

6、依据行进行拆分
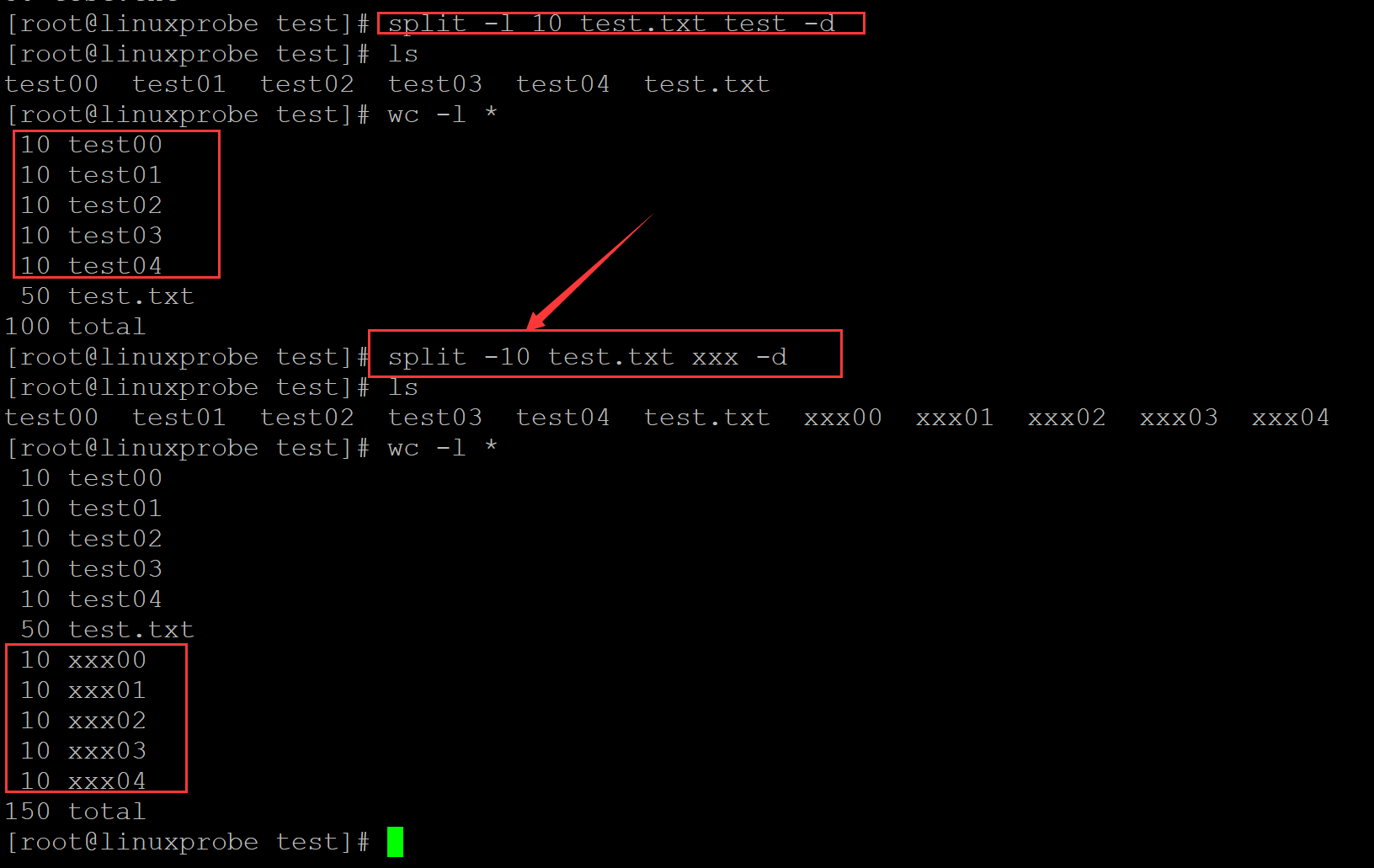
创建测试数据并拆分:
[root@linuxprobe test]# rm -f *
[root@linuxprobe test]# seq 50 > test.txt ##测试数据
[root@linuxprobe test]# wc -l test.txt
50 test.txt
[root@linuxprobe test]# split -l 10 test.txt test -d ## test为前缀; -d 这只为数字 ,-l 按照每10行进行拆分,l可以省略,直接 -10也没问题
[root@linuxprobe test]# ls
test00 test01 test02 test03 test04 test.txt
[root@linuxprobe test]# wc -l *
10 test00
10 test01
10 test02
10 test03
10 test04
50 test.txt
100 total
参考:http://c.biancheng.net/linux/split.html