插件
简述
MyBatis 在四大对象的创建过程中,都会有插件进行介入。插件可以利用动态代理机制一层层的包装目标对象,而实现目标对象执行目标方法之前进行拦截效果。MyBatis 允许在已映射语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用。
public class Configuration {
// 创建的时候不是直接返回的,要经过插件的层层包装
public Xxx newXxx(...) {
Xxx xxx = new Xxx(...);
xxx = (Xxx) interceptorChain.pluginAll(xxx);
}
}
·················································
public class InterceptorChain {
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
// [插件机制] 用插件为 target(四大对象) 创建代理对象
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
}
默认情况下,MyBatis 允许插件来拦截的方法调用包括:
[Executor] update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed
[ParameterHandler] getParameterObject, setParameters
[ResultSetHandler] handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters
[StatementHandler] prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query
插件开发步骤
实现 Interceptor 接口
public interface Interceptor {
// 拦截目标对象的目标方法的执行
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 包装目标对象。包装:为目标对象创建代理对象
Object plugin(Object target);
// 将插件注册时的 <property> 属性设置进来
void setProperties(Properties properties);
}
为 target 创建动态代理
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
// 目标对象
private Object target;
// 包装目标对象的插件
private Interceptor interceptor;
// 插件签名(要拦截的方法)
private Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor
, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) { // 是插件签名声明的类型,返回其动态代理对象
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target; // 不是的,就直接返回目标对象
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
// 若调用 @Signature 声明的方法,则直接来到代理这儿
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ Step Into ↓↓↓↓↓ =====> #1.3[1]
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
// issue #251
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor "
+ interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, Set<Method>>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type());
if (methods == null) {
methods = new HashSet<Method>();
signatureMap.put(sig.type(), methods);
}
try {
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on "
+ sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type
, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
while (type != null) {
for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) {
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]);
}
}
编写插件签名
@Intercepts
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Intercepts {
Signature[] value();
}
@Signature
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Signature {
// 要拦截四大对象的哪一个
Class<?> type();
// 拦截哪个方法
String method();
// 方法的参数列表(有的方法可能会有方法重载)
Class<?>[] args();
}
注册插件
注册到全局配置文件中。
<configuration>
<!-- properties -->
<!-- 注册插件 -->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="cn.edu.nuist.plugins.MyFirstPlugin">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="shaw"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!-- ... -->
</configuration>
自定义插件
MyFirstPlugin
// 完成插件签名:告诉 MyBatis 该插件用来拦截哪个对象的哪个方法
@Intercepts({
@Signature(
type = StatementHandler.class,
method = "parameterize",
args = java.sql.Statement.class
)
})
public class MyFirstPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override // 拦截目标对象的目标方法
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("=====>[MyFirstPlugin] before intercept");
// ------------------------------------------------------------
编写插件功能
// ------------------------------------------------------------
// 执行目标方法
Object result = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("=====>[MyFirstPlugin] after intercept");
return result; // "放行"
}
@Override // 包装目标对象。包装:为目标对象创建代理对象
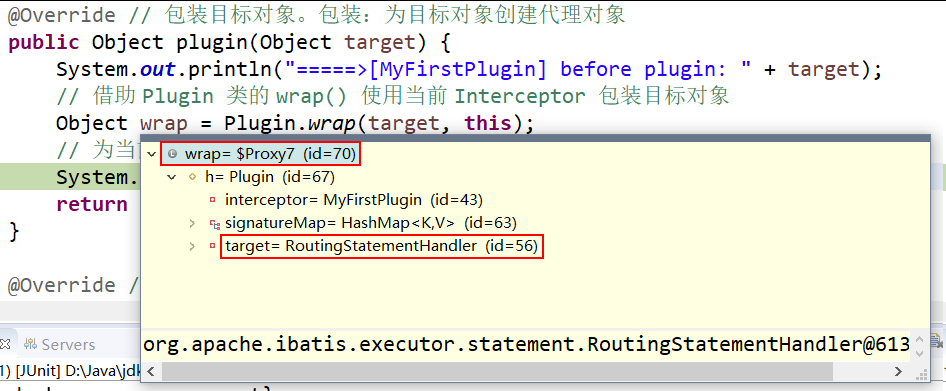
public Object plugin(Object target) {
System.out.println("=====>[MyFirstPlugin] before plugin: " + target);
// 借助 Plugin 类的 wrap() 使用当前 Interceptor 包装目标对象
// ===== ↓↓↓↓↓ Step Into ↓↓↓↓↓ =====> #1.2.2[2]
Object wrap = Plugin.wrap(target, this);
// 为当前 target 创建的动态代理
System.out.println("=====>[MyFirstPlugin] after plugin: " + wrap);
return wrap;
}
@Override // 将插件注册时的 <property> 属性设置进来
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
System.out.println("=====>[MyFirstPlugin] setProperties");
System.out.println(properties);
}
}
插件功能举例:动态的改变 SQL 运行的参数,如查询 1 号 teacher,则返回 3 号 teacher。
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 1. 拿到 target 元数据
MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(invocation.getTarget());
System.out.println("SQL 语句用的参数:"
+ metaObject.getValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject"));
// 2. 修改 SQL 参数
metaObject.setValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject", 3);
// 3. 执行目标方法
return invocation.proceed();
}
执行流程
单插件
以自定义插件 MyFirstPlugin 为例
打印控制台:
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] setProperties: {password=shaw, username=root}
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] before plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor@71c3b41
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] after plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor@71c3b41
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] before plugin:
org.apache.ibatis.scripting.defaults.DefaultParameterHandler@1f97cf0d
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] after plugin:
org.apache.ibatis.scripting.defaults.DefaultParameterHandler@1f97cf0d
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] before plugin:
org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.DefaultResultSetHandler@2e222612
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] after plugin:
org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.DefaultResultSetHandler@2e222612
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] before plugin:
org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler@61386958
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] after plugin:
org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler@61386958($Proxy7)
DEBUG 09-19 09:13:23,609 ==> Preparing: SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE tid = ?
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] before intercept
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] after intercept
DEBUG 09-19 09:53:34,568 ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
DEBUG 09-19 09:53:34,582 <== Total: 1
Teacher [...]
执行流程:
- 程序启动,加载 MyBatis 全局配置文件,载入插件,为插件属性赋值:
setProperties(...) - 调用 Mapper 查询方法,创建四大组件 → #1.1
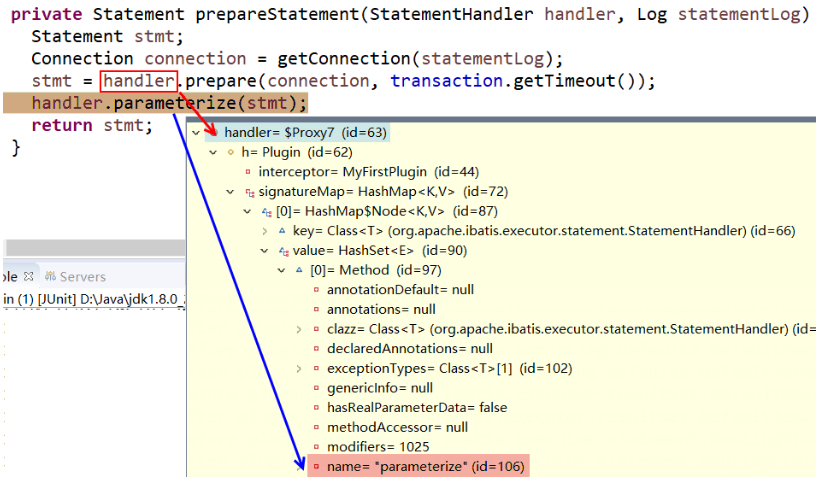
- 因为就配置了一个插件,所以现象就是 MyFirstPlugin 对四大组件挨个尝试 plugin → #1.3[2]
- 程序若调用了【插件签名】中声明的方法,则直接进入 #1.2.2[3]:proxy.invoke()
多插件
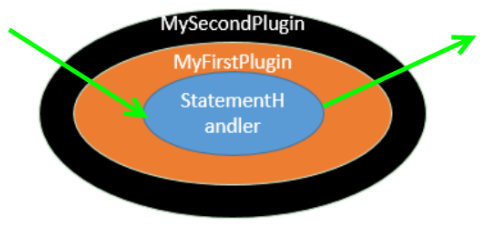
MySecondPlugin 与 MyFirstPlugin 拦截同一个方法。
配置顺序如下:
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="cn.edu.nuist.plugins.MyFirstPlugin">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="shaw"/>
</plugin>
<plugin interceptor="cn.edu.nuist.plugins.MySecondPlugin"></plugin>
</plugins>
打印控制台:
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] setProperties: {password=shaw, username=root}
=====>[MySecondPlugin] setProperties: {}
=====>[MyFirstPlugin]
before plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor@6b09bb57
=====>[MyFirstPlugin]
after plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor@6b09bb57
=====>[MySecondPlugin]
before plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor@6b09bb57
=====>[MySecondPlugin]
after plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor@6b09bb57
=====>[MyFirstPlugin]
before plugin: org.apache.ibatis.scripting.defaults.DefaultParameterHandler@49fc609f
=====>[MyFirstPlugin]
after plugin: org.apache.ibatis.scripting.defaults.DefaultParameterHandler@49fc609f
=====>[MySecondPlugin]
before plugin: org.apache.ibatis.scripting.defaults.DefaultParameterHandler@49fc609f
=====>[MySecondPlugin]
after plugin: org.apache.ibatis.scripting.defaults.DefaultParameterHandler@49fc609f
=====>[MyFirstPlugin]
before plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.DefaultResultSetHandler@22a67b4
=====>[MyFirstPlugin]
after plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.DefaultResultSetHandler@22a67b4
=====>[MySecondPlugin]
before plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.DefaultResultSetHandler@22a67b4
=====>[MySecondPlugin]
after plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.DefaultResultSetHandler@22a67b4
=====>[MyFirstPlugin]
before plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler@3b084709
=====>[MyFirstPlugin]
after plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler@3b084709
=====>[MySecondPlugin]
before plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler@3b084709
=====>[MySecondPlugin]
after plugin: org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler@3b084709
DEBUG ==> Preparing: SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE tid = ?
=====>[MySecondPlugin] before intercept
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] before intercept
=====>[MyFirstPlugin] after intercept
=====>[MySecondPlugin] after intercept
DEBUG ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
DEBUG <== Total: 1
Teacher [...]
执行流程:

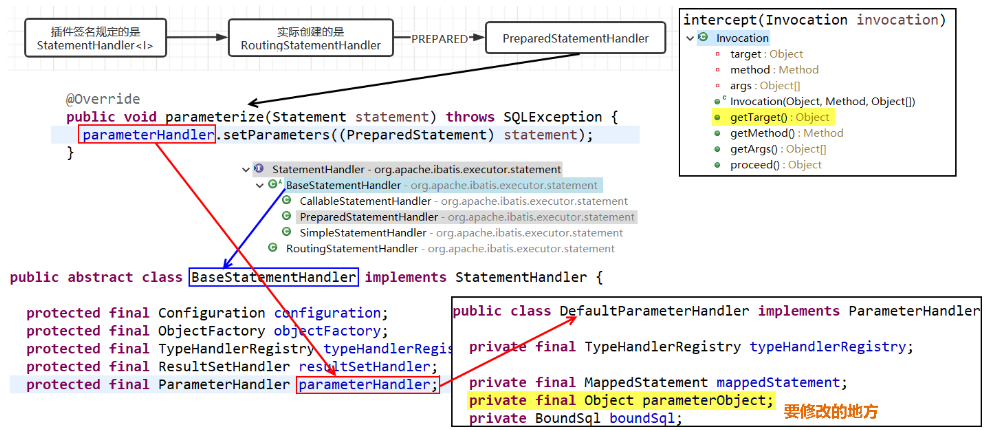
handler.parameterize(stmt) → Plugin.invoke() → return interceptor.intercept(...)- Step Into 会进入 MySecondPlugin 的 interceptor 方法,在方法体中调用
invocation.proceed() - Step Into 会进入 MyFirstPlugin 的 interceptor 方法,此时,再在方法体中调用
invocation.proceed(),才是真正进入目标对象的目标方法
分页插件 PageHelper
PageHelper 是 MyBatis 中非常方便的第三方分页插件。
- 导入相关包 pagehelper-x.x.x.jar 和 jsqlparser-0.9.5.jar
- 在 MyBatis 全局配置文件中配置分页插件
<plugins> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin> </plugins> - 使用 PageHelper 提供的方法进行分页
@RequestMapping("/getAllTeachers") public String getAllTeachers(Model model , @RequestParam(value="pageNum", defaultValue = "1")Integer pageNum) { // 获取第 pageNum 页,默认每页 10 条 PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, 10); // 这个查询就是一个分页查询! List<Teacher> list = teacherService.getAllTeachers(); // 用 PageInfo 对结果集进行包装 PageInfo<Teacher> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(list, 5); // 构造器param2: 连续显示多少页 2 3 4 5 6 // int[] nums = pageInfo.getNavigatepageNums(); model.addAttribute("pageInfo", pageInfo); return "success"; } - 可以使用更强大的 PageInfo 封装返回结果
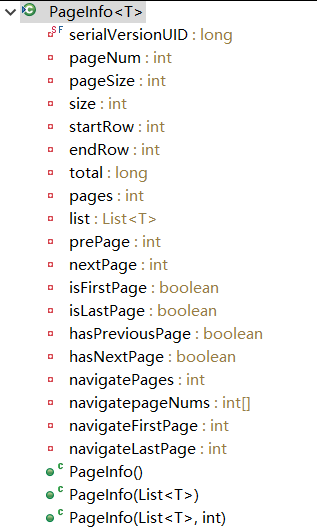
- peek 源码
public abstract class PageMethod { protected static final ThreadLocal<Page> LOCAL_PAGE = new ThreadLocal<Page>(); /** * 设置 Page 参数 * * @param page */ protected static void setLocalPage(Page page) { LOCAL_PAGE.set(page); } /** * 开始分页 * * @param pageNum 页码 * @param pageSize 每页显示数量 * @param count 是否进行count查询 */ public static <E> Page<E> startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize, boolean count) { Page<E> page = new Page<E>(pageNum, pageSize, count); setLocalPage(page); return page; } // ... }
批量操作

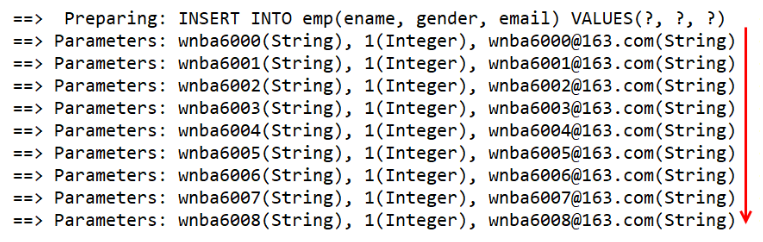
@Test
public void testBatchInsertEmp() {
// 什么时候需要批量操作,就获取可批量操作的 SqlSession;没必要在配置文件中修改
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH);
EmployeeDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeDao.class);
for(int i = 5000; i < 5050; i++) {
String s = "wnba"+i;
mapper.insertEmp(new Employee(s, s+"@163.com", 1));
}
sqlSession.commit();
}
批量:预编译 SQL → 设置参数 * 10000 times → 执行
非批量:[预编译 SQL → 设置参数 → 执行] * 10000 times
与 Spring 整合
-
在 applicationContext.xml 中配置
<!-- 配置一个可以批量操作的 SqlSession --> <bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate"> <constructor-arg name="sqlSessionFactoryBean" ref="sqlSessionFactoryBean"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="executorType" value="BATCH"></constructor-arg> </bean> -
在 Service 中自动注入该 SqlSession
@Service public class TeacherService { @Autowired private SqlSession batchSqlSession; public void batchInsertTeachers() { TeacherMapper mapper = batchSqlSession.getMapper(TeacherMapper.class); // ... } }
调用存储过程
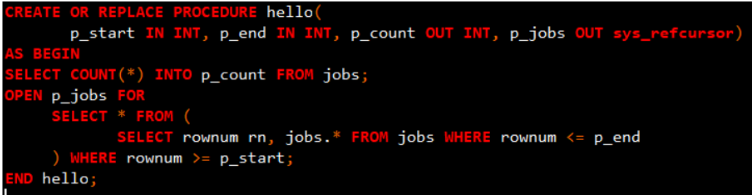
<mapper namespace="cn.edu.nuist.dao.JobDao">
<!-- void InjectPageJobsByProcedure()
1. 使用 <select> 定义调用存储过程
2. statementType="CALLABLE"
-->
<select id="InjectPageJobsByProcedure" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call hello(#{start, mode=IN, jdbcType=INTEGER}
, #{end, mode=IN, jdbcType=INTEGER}
, #{count, mode=OUT, jdbcType=INTEGER}
, #{jobs, mode=OUT, jdbcType=CURSOR, javaType=ResultSet, resultMap=pageJob})
}
</select>
<resultMap type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Job" id="pageJob">
<result property="jobId" column="job_id"/>
<result property="jobTitle" column="job_title"/>
<result property="minSalary" column="min_salary"/>
<result property="maxSalary" column="max_salary"/>
</resultMap>
</mapper>
@Test
public void testBatchInsertEmp() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
JobDao jobDao = sqlSession.getMapper(JobDao.class);
Page page = new Page();
page.setStart(1);
page.setEnd(5);
jobDao.InjectPageJobsByProcedure(page);
System.out.println(page.getCount());
System.out.println(page.getJobs());
}
自定义类型处理器
通过自定义 TypeHandler 的形式来在设置参数或者取出结果集的时候自定义参数封装策略。
TypeHandler
实现 TypeHandler<I> 或者继承 BaseTypeHandler。
public interface TypeHandler<T> {
void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i
, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
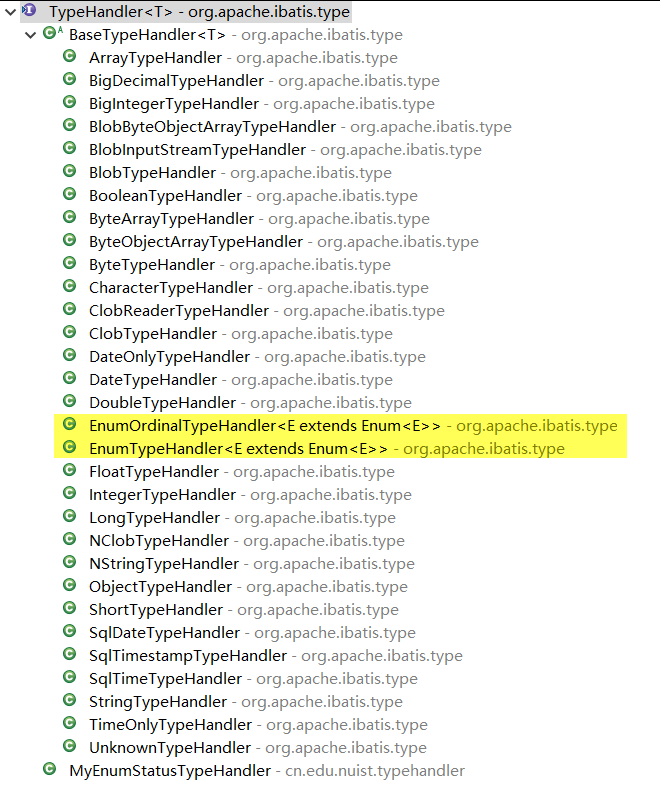
自定义处理枚举类型
- EnumTypeHandler:
ps.setString(i, parameter.name()); - EnumOrdinalTypeHandler:
ps.setInt(i, parameter.ordinal()); - 【需求】希望 DB 保存的是 code,而不是索引或者枚举名
public class MyEnumStatusTypeHandler implements TypeHandler<EmpStatus> {
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i
, EmpStatus parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(i, parameter.getCode().toString());
}
@Override
public EmpStatus getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
int code = rs.getInt(columnName);
System.out.println("GET empStatus FROM DB: " + code);
EmpStatus status = EmpStatus.getEmpStatusByCode(code);
return status;
}
@Override
public EmpStatus getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
int code = rs.getInt(columnIndex);
System.out.println("GET empStatus FROM DB: " + code);
EmpStatus status = EmpStatus.getEmpStatusByCode(code);
return status;
}
@Override
public EmpStatus getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
// ...
}
}
配置
- 在全局配置该 TypeHandler 要处理的 javaType
<typeHandlers> <typeHandler javaType="cn.edu.nuist.bean.EmpStatus" handler="cn.edu.nuist.typehandler.MyEnumStatusTypeHandler"/> </typeHandlers> - 在自定义结果集标签的时候指定 typeHandler
<resultMap type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee" id="empMap"> <id column="eid" property="eid"/> <!-- ... --> <result column="empStatus" property="empStatus" typeHandler="cn.edu.nuist.typehandler.MyEnumStatusTypeHandler"/> </resultMap> - 插入标签做参数处理的时候指定 typeHandler
<insert id="insertEmpWithStatus" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="eid"> INSERT INTO emp(ename, gender, email, empStatus) VALUES(#{ename}, #{gender}, #{email}, #{empStatus, typeHandler=cn.edu.nuist.typehandler.MyEnumStatusTypeHandler}) </insert>