1. 简述
栈(stack) 是一个先入后出(FILO-First In Last Out)的有序列表,是限制线性表中元素的插入和删除只能在线性表的同一端进行的一种特殊线性表。允许插入和删除的一端,为变化的一端,称为栈顶(Top),另一端为固定的一端,称为栈底(Bottom)。根据栈的定义可知,最先放入栈中元素在栈底,最后放入的元素在栈顶,而删除元素刚好相反,最后放入的元素最先删除,最先放入的元素最后删除。
出栈(pop)、入栈(push) 示意图

2. 应用场景
- 计算器
- 子程序的调用:在跳往子程序前,会先将下个指令的地址存到堆栈中,直到子程序执行完后再将地址取出,以回到原来的程序中
- 处理递归调用:和子程序的调用类似,只是除了储存下一个指令的地址外,也将参数、区域变量等数据存入堆栈中
- 表达式的转换:[中缀表达式→后缀表达式] 与 求值(实际解决)
- 二叉树的遍历
- 图形的深度优先(depth一first)搜索法
3. 栈结构实现
3.1 数组实现
/**
* 使用 [数组] 来模拟栈
* 入栈:stack[++top] = data;
* 出栈:value = stack[top--];
*/
public class ArrayStack {
private int maxSize;
private int[] stack;
private int top = -1;
public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {
super();
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
// 栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize-1;
}
// 空栈
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
// 入栈
public void push(int value) {
// 判断栈是否满
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
stack[++top] = value;
}
// 出栈
public int pop() {
// 判断栈是否空
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("空栈");
return stack[top--];
}
// 遍历栈 (栈顶→栈底)
public void showStack() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空, 没有数据");
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--)
System.out.printf("stack[%d] = %d", i, stack[i]);
}
}
3.2 链表实现
public class LinkedListStack {
private int maxSize;
private Node head;
private Node top;
public LinkedListStack(int maxSize) {
super();
this.maxSize = maxSize;
head = new Node();
top = head;
}
// 栈满
public boolean isFull() {
int count = 0;
Node temp = head.next;
while (temp != null) {
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return count == maxSize;
}
// 空栈
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == head;
}
// 入栈
public void push(int val) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
Node n = new Node();
n.data = val;
top.next = n;
top = n;
}
// 出栈
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("空栈");
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != top) temp = temp.next;
int val = top.data;
top = temp;
return val;
}
// 遍历栈
public void showStack() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空, 没有数据");
return;
}
Node reHead = new Node();
Node cur = head.next;
Node next;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = reHead.next;
reHead.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
cur = reHead.next;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.println(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [data=" + data + "]";
}
}
4. 使用栈结构计算表达式
4.1 思路分析
通过一个 index(索引),逐个字符的遍历表达式:

使用栈来计算如下表达式:
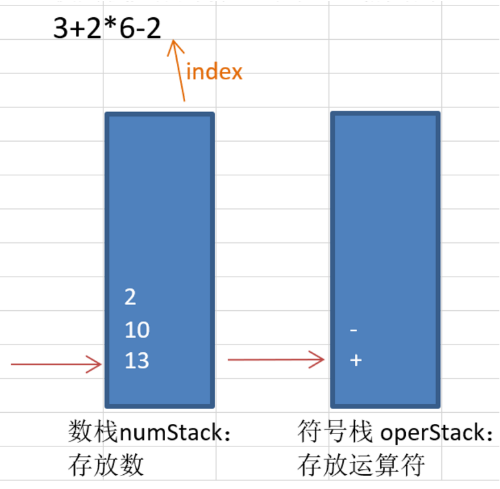
4.2 代码实现
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 算式
String expression = "17*2*2-123+1-5+3-4";
char[] expressionArr = expression.toCharArray();
// 创建 [数栈] 和 [符号栈]
CalcStack numStack = new CalcStack(10);
CalcStack operStack = new CalcStack(10);
// 定义相关变量
// -- 用于扫描的索引
int index = 0;
// -- 用于拼接多位数字构成的数据
String keepNum = "";
int num1, num2, oper, result;
// -- 将每次扫描得到的char保存到此
char ch = ' ';
// 扫描表达式
while (index != expressionArr.length) {
// 依次得到每一个字符
ch = expressionArr[index];
if (operStack.isOper(ch)) { // ch 是符号
// ∵ 是符号 ∴ 要判断 当前符号栈是否为空
if (!operStack.isEmpty()) {
if (operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peekTop())) {
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
result = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
// 运算结果入 [数栈]
numStack.push(result);
// 当前操作符入 [符号栈]
operStack.push(ch);
} else { // 当前操作符的优先级 > 栈顶的操作符的优先级
operStack.push(ch);
}
} else {
operStack.push(ch);
}
} else { // ch 是数字
/*
* numStack.push(ch); X
* ∵ 在 ASCII 码表中, '1' —— 49 ∴这么写是错误的
* numStack.push(ch - 48); X
* ∵ 无法处理单个数据是多位数的情况, 如 24, 123
* ∴ 当处理数字时, 不能直接入栈, 应判断该数据是否还有余下的位数
* 1. 定义一个字符串变量, 用于拼接数字
* 2. 得到首位数字后, 追加进字符串
* 3. 向 index 指向位置之后再看一眼
* 3.1 是数字, 再次追加
* 3.2 是符号, 则将字符串入栈, 注意清空字符串以便下次使用
*/
keepNum += ch;
// 如果 ch 已经是算式的末位, 就直接入栈
if (index == expressionArr.length-1) {
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
} else {
if (operStack.isOper(expressionArr[index+1])) {
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
// 记得清空!!!
keepNum = "";
}
}
}
index++;
}
// 从 [数栈] 和 [符号栈] 中 pop 出相应的数据和符号,进行运算
// 若符号栈为空, 则数栈中肯定只剩一个数字, 其就是算式结果
while (!operStack.isEmpty()) {
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
result = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
numStack.push(result);
}
System.out.printf("%s = %d", expression, numStack.peekTop());
}
}
class CalcStack {
private int maxSize;
private int[] stack;
private int top = -1;
public CalcStack(int maxSize) {
super();
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
// 栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize-1;
}
// 空栈
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
// 入栈
public void push(int value) {
// 判断栈是否满
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
stack[++top] = value;
}
// 出栈
public int pop() {
// 判断栈是否空
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("空栈");
return stack[top--];
}
public int peekTop() {
return stack[top];
}
// 遍历栈 (栈顶→栈底)
public void showStack() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空, 没有数据");
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--)
System.out.printf("stack[%d] = %d", i, stack[i]);
}
// 返回运算符优先级(拟定为:优先级使用数字表示, 数字越大, 则优先级越高)
public int priority(int oper) {
if (oper == '*' || oper == '/')
return 1;
else if (oper == '+' || oper == '-')
return 0;
else
return -1; // 目前算式只包含加减乘除
}
// 判断是否为一个运算符
public boolean isOper(char val) {
return val == '+' || val == '-' || val == '*' || val == '/';
}
// 计算
public int cal(int num1, int num2, int oper) {
int result = 0;
switch (oper) {
case '+':
result = num2 + num1;
break;
case '-':
result = num2 - num1;
break;
case '*':
result = num2 * num1;
break;
case '/':
result = num2 / num1;
break;
}
return result;
}
}