联结:
SQL最强大的功能之一:在数据查询中联结(join)多个存储不同信息的表。
最简单的例子:检索供应商的名字,产品的名字,产品的地址。
一:使用“where”子句:
select prod_name,vend_name,vend_address from vendors,products where vendors.vend_id=products.vend_id;
新手必须要记住的一点是,在联结两个表时,实际上做的是第一个表的每一行与第二个表中的每一行配对。所以where会只匹配那些给定条件的行。
不加“where”,不加联结条件会造成笛卡尔积。检索出的行数是第一个表中的行数乘以第二个表的行数。
二:使用“inner join on”
select prod_name,vend_name,vend_address from vendors INNER JOIN products on vendors.vend_id=products.vend_id;
这种方法与使用where子句的结果一样。
使用注意事项:
1.DBMS对于关联表的处理可能非常耗费资源。
例子:检索所有顾客以及每个顾客所以下的总订单数。
输入:
SELECT Customers.cust_id, COUNT(Orders.order_num) AS num_ord FROM Customers INNER JOIN Orders On Customers.cust_id=Orders.cust_id GROUP BY Customers.cust_id;
分析:
SELECT语句使用INNER JOIN 将 Customers和Orders表相关联。
然后GROUP BY按顾客分组数据,函数调用COUNT(Orders.order_num),计算出每个顾客的订单总数。
例子:检索订购产品RGAN01的顾客列表:
输入:
SELECT cust_name,cust_contact from Customers WHERE cust_id IN (SELECT cust_id FROM Orders WHERE order_num IN (SELECT order_num FROM OrderItems WHERE prod_id='RGAN01'));
使用联结后
select cust_name,cust_contact from Customers, Orders,OrderItems WHERE Customers.cust_id=Orders.cust_id and OrderItems.order_num=Orders.order_num and Orders.prod_id='RGAN01';
分析:
所以 WHERE IN的操作 一般可以使用联结替代
高级联结(自联结、外联结):
使用不同类型的联结:
自联结:
查询有过与‘Jim Jones’联系过的顾客,联系过其他人的情况。
第一种解决方案:
SELECT cust_id,cust_name,cust_contact FROM Customers WHERE cust_name=(SELECT cust_name FROM Customers WHERE cust_contact='Jim Jones' ) ;
这是因为一个Customers有多个cust_contact。所以 不仅仅是cust_contact='Jim Jones' 。

第二种解决方案:
由于我们说了where in相当于联结的操作。
使用inner join:
select b.cust_name,b.cust_address,b.cust_contact,b.cust_id from customers a JOIN customers b on a.cust_name=b.cust_name and a.cust_contact='Jim Jones'
使用where:
select b.cust_name,b.cust_address,b.cust_contact,b.cust_id from customers a,customers b where a.cust_name=b.cust_name and a.cust_contact='Jim Jones'

外联结:
有时候需要包含没有关联到的那些行
比如:对每个顾客下的订单进行计数,包括那些至今尚未下订单的顾客;
比如:列出所有产品以及订购数量,包括没有人订购的产品;
比如:计算平均销售规模,包括那些至今尚未下订单的顾客。
查看有些顾客没有订单:
select customers.cust_id,orders.order_num from customers left outer JOIN orders on customers.cust_id=orders.cust_id;

使用带聚集函数的联结:
输入:
SELECT Customers.cust_id, COUNT(Orders.order_num) AS num_ord FROM Customers LEFT OUTER JOIN Orders on Customers.cust_id=Orders.cust_id GROUP BY Customers.cust_id
输出:
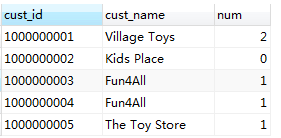
使用左连接,获得每个顾客的订单数量。