一、字符串
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 void main(){ 5 char str[50]="notepad"; 6 printf("%x ",str); 7 printf("%c,%d ",'�','�'); 8 printf("%c,%d ",0,0); 9 printf("%c,%d ",'0','0'); 10 system("pause"); 11 }

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 void main(){ 5 char str[4]={'c','a','l','c'}; 6 printf("%s ",str); 7 system("pause"); 8 }
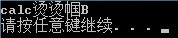
字符串之后没有结束符'�',直到遇到为止
二、指针
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 void main(){ 5 char *p= "tasklist"; 6 printf("%d,%d ",sizeof(p),sizeof("tasklist")); 7 printf("%x ",&p); 8 system(p);//本质上就是字符串的首地址 9 system("pause"); 10 }

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 void main(){ 5 char *p= "tasklist"; 6 p = p + 4;//只打印list 7 while (*p)//*p==0跳出循环,*p=='�' 8 { 9 printf("%c,%x ", *p,p); 10 p++; 11 } 12 13 system("pause"); 14 }

三、字符串数组
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 void main() { 5 //字符串数组 6 char str[4][10] = { { "notepad" }, 7 { "calc" }, 8 { "tasklist" }, 9 { "ipconfig" } }; 10 char(*p)[10] = str; //指向二维数组的指针, 11 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)//循环四次 12 { 13 system(p[i]); //字符串元素首地址 14 } 15 16 system("pause"); 17 }
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 //字符串修改字符 4 void main() { 5 char str[10] = "taskoist"; 6 char *p = str; 7 p = p + 4; 8 *p = 'l'; 9 system(str); 10 system("pause"); 11 }
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 //字符串修改字符 4 void main() { 5 char *p= "taskoist";//"taskoist"常量不可修改 6 char *ps = p; 7 ps += 4; 8 //*ps = 'l';//运行时出错 9 system(p); 10 system("pause"); 11 }
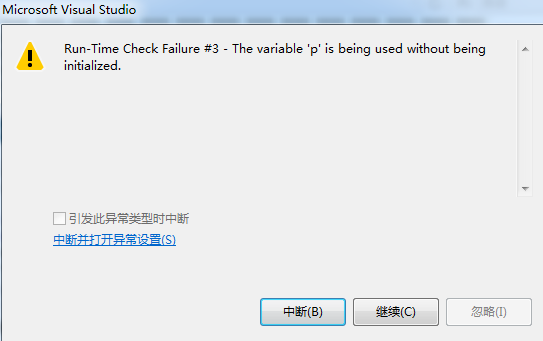
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 void main() { 5 char *p; 6 scanf("%s",p);//使用了未初始化的局部变量“p” 7 printf("%s",p); 8 system(p); 9 10 system("pause"); 11 }
解决方法一
char str[20];
char *p=str;
解决方法二
char *p=(char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*20);//指针必须指向一片内存
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 void main() { 5 char str[50]; 6 char str1[20]; 7 char str2[20]; 8 //gets(str1);//获取字符串初始化 9 gets_s(str1);//VS2015使用的是新C标准,也就是C11,而VC6.0用的是老标准。 在新标准中,应该是用gets_s代替gets 10 scanf("%s", str2); //获取字符串初始化 11 printf("%s %s", str1, str2); 12 sprintf(str, "%s %s", str1, str2); //字符相加 13 fprintf(stdout,"hello world"); 14 15 system("pause"); 16 }
四、求字符串长度
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 int getLen(const char *p) {//传入的字符串不允许被随意修改 5 int i = 0; 6 if (p == NULL) return -1; 7 else 8 { 9 while (*p) { 10 i++; 11 p++; 12 } 13 } 14 return i; 15 } 16 17 void main() { 18 char str[] = "calc"; 19 printf("%d ",getLen(str)); 20 system("pause"); 21 }

五、获取CMD输出
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<string.h> 5 6 void execmd(char *in,char *out) { 7 FILE *pipe = _popen(in,"r");//read 读取 8 if (!pipe) return ; //判断管道是否为空 9 char buffer[128] = {0}; 10 while (!feof(pipe)) { //判断文件是否结束 11 if (fgets(buffer, 128, pipe))//获取每一行的数据 12 { 13 strcat(out, buffer);//连接字符串 14 } 15 } 16 _pclose(pipe);//关闭管道 17 //return 1; 18 } 19 20 void main() { 21 //注意:字符串需要初始化 22 char CMDin[50] = { 0 };//输入的指令 23 char CMDout[4096] = {0};//输出的语句 24 scanf("%s",CMDin);//扫描输入 25 execmd(CMDin,CMDout);//获取结果 26 printf("打印的输出:%s",CMDout);//打印结果 27 printf("%x",CMDout); 28 //system(CMDin); 29 30 system("pause"); 31 }
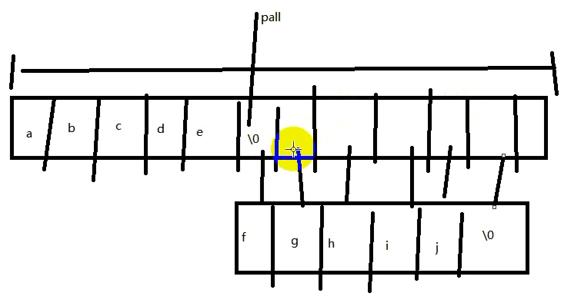
六、字符串拼接
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<string.h>//字符串处理函数 5 6 int getlen(char *str) { 7 int num = 0; 8 while (*str) {//取出内容,0就是�字符 9 num++;//计数一次 10 str++;//指针移动一次 11 } 12 return num; 13 } 14 15 void mystrcat(char *all, char *add) { 16 int all_len = getlen(all); 17 int add_len = getlen(add); 18 char *pall = all; 19 char *padd = add; 20 pall += all_len;//指针移动到/0 21 while (*padd) { 22 *pall = *padd; 23 padd++; 24 pall++; 25 } 26 *(pall + 1) = '�'; 27 } 28 29 void main() { 30 char str[30]="tracert";//遍历路由 31 char web[50]; 32 scanf("%s",web); 33 34 //方法一 35 /*char cmd[100]; 36 sprintf(cmd, "%s %s", str, web); 37 system(cmd);*/ 38 39 //方法二 40 /*strcat(str, " "); 41 strcat(str,web); 42 system(str);*/ 43 44 //方法三 45 mystrcat(str, " "); 46 mystrcat(str, web); 47 system(str); 48 }

七、字符串检索
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 5 int getlen(char *str) { 6 int num = 0; 7 while (*str) {//取出内容,0就是�字符 8 num++;//计数一次 9 str++;//指针移动一次 10 } 11 return num; 12 } 13 14 char * findstr(char *all, char *str) { 15 char *p = NULL; 16 int all_len = getlen(all); 17 int str_len = getlen(str); 18 for (int i = 0; i < all_len-str_len; i++) 19 { 20 int flag = 1;//假定字符串相等 21 for (int j = 0; j < str_len; j++) 22 { 23 if (all[i + j] != str[j]) {//判定字符是否相等 24 flag = 0; 25 break; 26 } 27 } 28 if (flag == 1) //如果为1,就是相等 29 { 30 p = &all[i]; 31 break; 32 } 33 } 34 return p; 35 } 36 37 void main() { 38 char all[200] = "i love china i love cpp i love c"; 39 //char str[30] = "i love cp"; 40 char str[30] = "i love cp0"; 41 //char *p = strstr(all, str); 42 char *p = findstr(all, str); 43 if (p == NULL) printf("can not find!"); 44 else 45 { 46 printf("find! "); 47 printf("*p=%c ",*p);//字符串检索的位置 48 } 49 system("pause"); 50 }

八、字符串查找(指针查找)
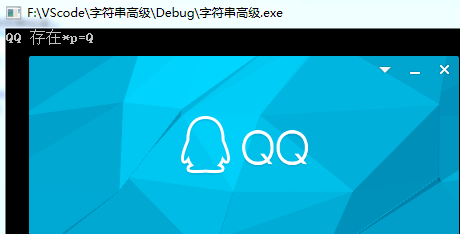
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<string.h> 5 6 int execmd(char *in, char *out) 7 { 8 char buffer[128] = { 0 }; 9 FILE *pipe = _popen(in, "r");//读取 10 if (!pipe) //管道创建为空,返回0 11 { 12 return 0; 13 } 14 while (!feof(pipe)) //判断文件是否结束 15 { 16 if (fgets(buffer, 128, pipe)) //获取每一行的数据 17 { 18 strcat(out,buffer);//连接字符串 19 } 20 } 21 _pclose(pipe);//关闭管道 22 return 1; 23 } 24 25 void main() 26 { 27 char CMDin[30] = "tasklist";//查看所有的进程 28 char CMDout[8192] = { 0 }; //输出的语句 29 execmd(CMDin, CMDout); //获取结果 30 char *p = strstr(CMDout, "QQ.exe"); 31 if (p == NULL) 32 { 33 printf("QQ不存在"); 34 } 35 else 36 { 37 printf("QQ 存在"); 38 printf("*p=%c", *p); 39 } 40 getchar(); 41 }