字符串的内容用不可变
三种常见方式+1:
- 直接创建:
三种常见方式:
pulic String() 创建一个空白字符串,不含任何内容
public String(char[] array) 根据字符数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串。
public String(byte[] array) 根据字节数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串。
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个空白字符串
String s = new String();
System.out.println("第一个字符串:" + s);
// 创建字符数组字符串
char[] ch = {'A', 'B', 'C'};
String s1 = new String(ch);
System.out.println("第二个字符串:" + s1);
// 创建字节数组字符串
byte[] by = {97, 98, 99};
String s2 = new String(by);
System.out.println("第三个字符串:" + s2);
// 直接创建字符串
String s4 = "你好";
}
}

字符串的常量池:
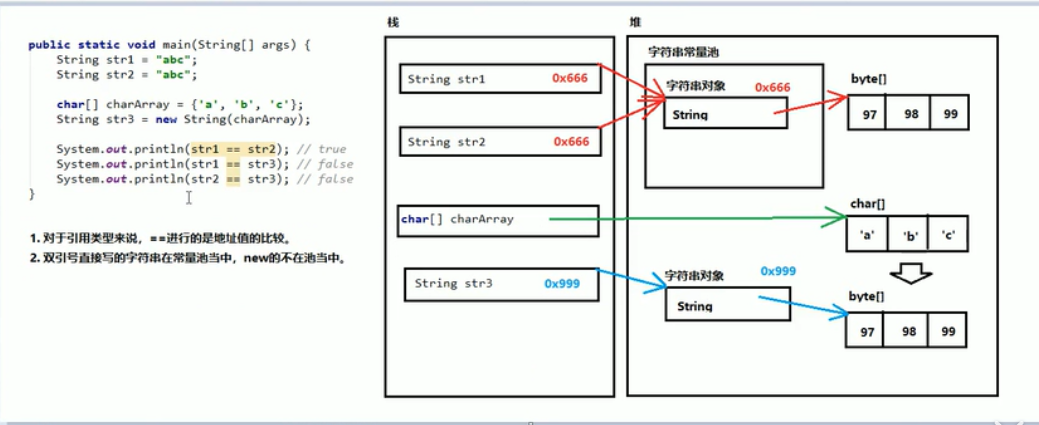
== 号是进行对象的地址值比较,如果需要字符串的内容值进行比较

注意事项:
- 任何对象都能用Object进行接收
- equals方法具有对称性,也就是a.equals(b)和b.equals(a)效果一样。
- 如果比较双方一个常量一个变量,推荐把常量字符串写在前面,因为变量有可能为空,为空调用equals方法
会报空指针异常。
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) 将此 String 与另一个 String 比较,不考虑大小写。如果两个字符串的长度相同,并且其中的相应字符都相等(忽略大小写),则认为这两个字符串是相等的。
public class equalsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "abc";
char[] ch = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str3 = new String(ch);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); //true
System.out.println(str1.equals(str3)); //true
System.out.println(str2.equals(str3)); //true
String str5 = null;
System.out.println("c".equals(str5)); //推荐写法
//System.out.println(str5.equals("c")); //不推荐,会报空指针异常 //java.lang.NullPointerException
// 不区分大小写进行比较
String str4 = "abc";
String str6 = "ABC";
System.out.println(str4.equalsIgnoreCase(str6)); //true
}
}
字符串中常用方法:
concat(String str)
将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾。
charAt(int index)
返回指定索引处的 char 值。
indexOf(String str)
返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
length()
返回此字符串的长度。
substring(int beginIndex)
返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。
substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。
getBytes()
使用平台的默认字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。
char[] toCharArray()
将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组。
replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement)
使用指定的字面值替换序列替换此字符串所有匹配字面值目标序列的子字符串。
字符串拼接的用法:
/*
定义一个方法,把数组{1,2,3}按照指定格式拼接成一个字符串[word1#word2#word3]
*/
public class Demo06StringPractise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arra = {1,2,3};
String s = returnDeom(arra);
System.out.println(s);
}
public static String returnDeom(int[] array){
String s = "[";
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if(i == array.length-1){
s += "word"+ array[i] + "]";
}else {
s += "word" + array[i];
}
}
return s;
}
}
tocharArray的用法:
/*
键盘输入一个字符串,并且统计其中各个字符串出现的次数。
*/
public class DemoString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串");
String input = sc.next();
int countUpper = 0;
int countlower = 0;
int countNums = 0;
int countOther = 0;
// 将字符串转为字符数组进行bianl
char[] chars = input.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if ('A' < chars[i] && chars[i] < 'Z'){
countUpper += 1;
}else if('a' < chars[i] && chars[i] < 'z'){
countlower += 1;
}else if('0' < chars[i] && chars[i] < '9'){
countNums += 1;
}else {
countOther += 1;
}
}
}
}