随笔记录方便自己和同路人查阅。
#------------------------------------------------我是可耻的分割线-------------------------------------------
Beautiful Soup 是一个模块,用于从 HTML 页面中提取信息(用于这个目的时,它比正则表达式好很多)。BeautifulSoup 模块的名称是 bs4(表示 Beautiful Soup,第 4 版)。要安装它,需要在命令行中运行 pip install beautifulsoup4。虽然安装时使用的名字是 beautifulsoup4,但要导入它,就使用 import bs4。
新建一个txt文档,把下面内容复制到文档,并吧文档后缀改为.html
<!-- This is the example.html example file. -->
<html><head><title>The Website Title</title></head>
<body>
<p>Browse my <strong>博乐园</strong> website from <a href="https://www.cnblogs.com/lirongyang/">my website</a>.</p>
<p class="slogan">Learn Python the easy way!</p>
<p>By <span id="author">Li Rong Yang</span></p>
</body></html>
你可以看到,既使一个简单的 HTML 文件,也包含许多不同的标签和属性。对于复杂的网站,事情很快就变得令人困惑。好在,Beautiful Soup 让处理 HTML 变得容易很多。
#------------------------------------------------我是可耻的分割线-------------------------------------------
1、从HTML创建一个BeautifulSoup对象
bs4.BeautifulSoup()方法,示例代码:
#! python 3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Autor: Li Rong Yang
import requests,bs4
#取得Response 对象
res = requests.get('https://www.cnblogs.com/lirongyang/')
try:
res.raise_for_status()
except Exception as exc:
print('There was a problem: %s' % (exc))
#使用bs4.BeautifulSoup()方法,解析Response 对象
noStarchSoup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(res.text,"html.parser")
print(noStarchSoup)
运行结果:

2、用select()方法寻找元素
针对你要寻找的元素,调用 method()方法,传入一个字符串作为 CSS“选择器”,这样就可以取得 Web 页面元素。选择器就像正则表达式:它们指定了要寻找的模
式,在这个例子中,是在 HTML 页面中寻找,而不是普通的文本字符串。
CSS 选择器的例子
soup.select('div')所有名为<div>的元素
soup.select('#author')#带有 id 属性为 author 的元素
soup.select('.notice')#所有使用 CSS class 属性名为 notice 的元素
soup.select('div span')#所有在<div>元素之内的<span>元素
soup.select('div > span')#所有直接在<div>元素之内的<span>元素,中间没有其他元素
soup.select('input[name]')#所有名为<input>,并有一个 name 属性,其值无所谓的元素
soup.select('input[type="button"]')#所有名为<input>,并有一个 type 属性,其值为 button 的元素
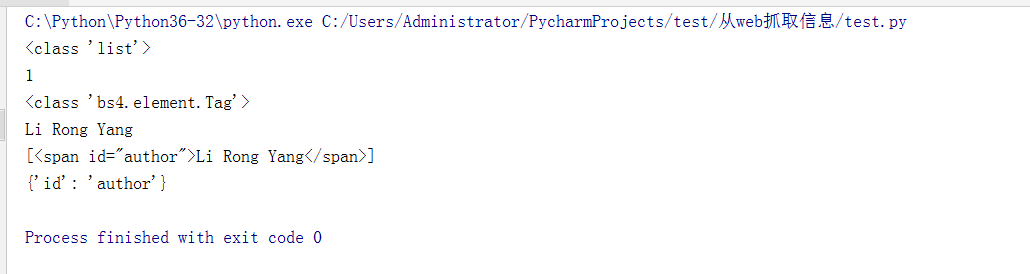
soup.select('#author')方式示例代码:
#! python 3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Autor: Li Rong Yang
import requests,bs4
exampleFile = open('d:\example.html')
exampleSoup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(exampleFile.read(),"html.parser")
#select('#author')返回一个列表,其中包含所有带有 id="author"的元素
elems = exampleSoup.select('#author')
#查看select()方法,返回的类型
print(type(elems))
#查看select()方法,告诉我们列表中有几个 Tag 对象
print(len(elems))
#查看select()方法,返回的长度
print(type(elems[0]))
#查看select()方法, getText()方法,返回该元素的文本
print(elems[0].getText())
#查看select()方法,将返回一个字符串,其中包含开始和结束标签,以及该元素的文本
print(str(elems))
#查看select()方法,attrs是一个字典,包含该元素的属性'id',以及id属性的值'author'
print(elems[0].attrs)
运行结果:
3、通过元素的属性获取数据,我们以本地保存的html为例子
#! python 3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Autor: Li Rong Yang
import requests,bs4
exampleSoup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(open('d:\example.html'),"html.parser")
elems = exampleSoup.select('a')[0]
#以字符串形式显示查找的内容
print(str(elems))
print(elems.get('id'))
elems = exampleSoup.select('span')[0]
#以字符串形式显示查找的内容
print(str(elems))
#查找id相符的内容
print(elems.get('id'))
#将属性名'id'传递给 get(),返回该属性的值'author'
print(elems.attrs)
运行结果:
