1,基础部分
1),配置网卡
1. 修改网卡配置注意事项
1).ubuntu从17.10开始,已放弃在/etc/network/interfaces里固定IP的配置,
即使配置也不会生效,而是改成netplan方式。
2).配置写在/etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml或者类似名称的yaml文件里。
3).修改配置以后不用重启,执行 netplan apply 命令可以让配置直接生效。
2. 修改命令如下: "注意缩进格式"
root@lss:~# cat /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml
# This is the network config written by 'subiquity'
network:
ethernets:
ens33:
addresses: [10.0.0.230/24]
gateway4: 10.0.0.254
nameservers:
addresses: [223.5.5.5]
version: 2
2).SSH配置
1). 默认Ubuntu不允许root远程登录,必须通过修改SSH配置文件才可以使用root
远程登录。
sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
PermitRootLogin yes
2). 修改后记得重启sshd进程
sudo systemctl restart sshd
3).root用户管理
1. 切换root账户
sudo su -
2. 修改root 密码
sudo passwd root
4).配置apt源(相当于yum 源)
1. ubuntu下的软件源可以在阿里源或者清华源上找到相应的配置方法: "找到相对应的版本"
https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/ubuntu/
2. 配置命令:
sudo cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.bak #先备份默认文件
sudo vim /etc/apt/sources.list
# 默认注释了源码镜像以提高 apt update 速度,如有需要可自行取消注释
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
# 预发布软件源,不建议启用
# deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
更新缓存:
sudo apt update
2.Ubuntu软件包管理工具使用
1.apt-get和apt命令介绍
1.apt等同于Centos7的yum命令
2.apt-get是第一代的包管理工具,最稳定
3.apt是改进的包管理工具,比apt-get要先进,官方推荐使用apt来管理软件
2.Ubuntu和CentOS7包管理工具区别
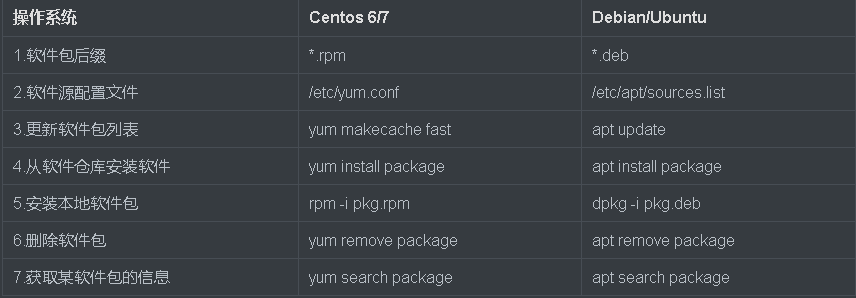
3.ubantu系统安装nginx
1,直接apt 安装
sudo apt-get install nginx
配置文档路径:
1. 主配置文件: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
lss@lss:/var/www/html$ cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user www;
worker_processes auto;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 768;
# multi_accept on;
}
http {
##
# Basic Settings
##
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
# server_tokens off;
# server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
# server_name_in_redirect off;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
##
# SSL Settings
##
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; # Dropping SSLv3, ref: POODLE
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
##
# Logging Settings
##
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
##
# Gzip Settings
##
gzip on;
# gzip_vary on;
# gzip_proxied any;
# gzip_comp_level 6;
# gzip_buffers 16 8k;
# gzip_http_version 1.1;
# gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
##
# Virtual Host Configs
##
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; ### 注意###
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*; ### 注意###
}
#mail {
# # See sample authentication script at:
# # http://wiki.nginx.org/ImapAuthenticateWithApachePhpScript
#
# # auth_http localhost/auth.php;
# # pop3_capabilities "TOP" "USER";
# # imap_capabilities "IMAP4rev1" "UIDPLUS";
#
# server {
# listen localhost:110;
# protocol pop3;
# proxy on;
# }
#
# server {
# listen localhost:143;
# protocol imap;
# proxy on;
# }
#}
2. include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
lss@lss:/var/www/html$ ll /etc/nginx/conf.d/
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 8 15:22 ./
drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 4096 Jan 8 15:23 ../
3. include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
lss@lss:/var/www/html$ ll /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 8 14:56 ./
drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 4096 Jan 8 15:23 ../
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 34 Jan 8 14:56 default -> /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
lss@lss:/var/www/html$ sudo cat /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
##
# You should look at the following URL's in order to grasp a solid understanding
# of Nginx configuration files in order to fully unleash the power of Nginx.
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/tutorials/config_pitfalls/
# https://wiki.debian.org/Nginx/DirectoryStructure
#
# In most cases, administrators will remove this file from sites-enabled/ and
# leave it as reference inside of sites-available where it will continue to be
# updated by the nginx packaging team.
#
# This file will automatically load configuration files provided by other
# applications, such as Drupal or Wordpress. These applications will be made
# available underneath a path with that package name, such as /drupal8.
#
# Please see /usr/share/doc/nginx-doc/examples/ for more detailed examples.
##
# Default server configuration
#
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
# SSL configuration
#
# listen 443 ssl default_server;
# listen [::]:443 ssl default_server;
#
# Note: You should disable gzip for SSL traffic.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/773332
#
# Read up on ssl_ciphers to ensure a secure configuration.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/765782
#
# Self signed certs generated by the ssl-cert package
# Don't use them in a production server!
#
# include snippets/snakeoil.conf;
root /var/www/html;
# Add index.php to the list if you are using PHP
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name _;
location / {
# First attempt to serve request as file, then
# as directory, then fall back to displaying a 404.
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
# pass PHP scripts to FastCGI server
#
#location ~ .php$ {
# include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
#
# # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets):
# fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
# # With php-cgi (or other tcp sockets):
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# Virtual Host configuration for example.com
#
# You can move that to a different file under sites-available/ and symlink that
# to sites-enabled/ to enable it.
#
#server {
# listen 80;
# listen [::]:80;
#
# server_name example.com;
#
# root /var/www/example.com; #站点目录
# index index.html;
#
# location / {
# try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
# }
#}
2).配置nginx
1. conf.d:用户自己定义的conf配置文件
2. sites-available:系统默认设置的配置文件
3. sites-enabled:由sites-available 中的配置文件转换生成
4. nginx.conf:汇总以上三个配置文件的内容,同时配置我们所需要的参数
在部署需要的web服务时,我们可以拷贝sites-enabled中的default 文件到conf.d并用修改名字为**.conf然后进行配置
lss@lss:/var/www/html$ sudo cat /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
server {
listen 80 default_server; #监听端口
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name www.oldboy.com; #域名名称
#以下为location 匹配规则
location / {
root /var/www/html; #站点目录
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html; #显示内容
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
# 以下为PHP 配置
#location ~ .php$ {
# include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
#
# # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets):
# fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
# # With php-cgi (or other tcp sockets):
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# Virtual Host configuration for example.com
#
# You can move that to a different file under sites-available/ and symlink that
# to sites-enabled/ to enable it.
#
#server {
# listen 80;
# listen [::]:80;
#
# server_name example.com;
#
# root /var/www/example.com;
# index index.html;
#
# location / {
# try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
# }
#}
3.)查看是否启动
root@lss:/var/www/html# sudo netstat -lntup |grep 80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 68915/nginx: master
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.53:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 802/systemd-resolve
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6012 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 68008/sshd: root@pt
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 68915/nginx: master
tcp6 0 0 ::1:6012 :::* LISTEN 68008/sshd: root@pt
udp 0 0 127.0.0.53:53 0.0.0.0:* 802/systemd-resolve
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo systemctl reload nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx
