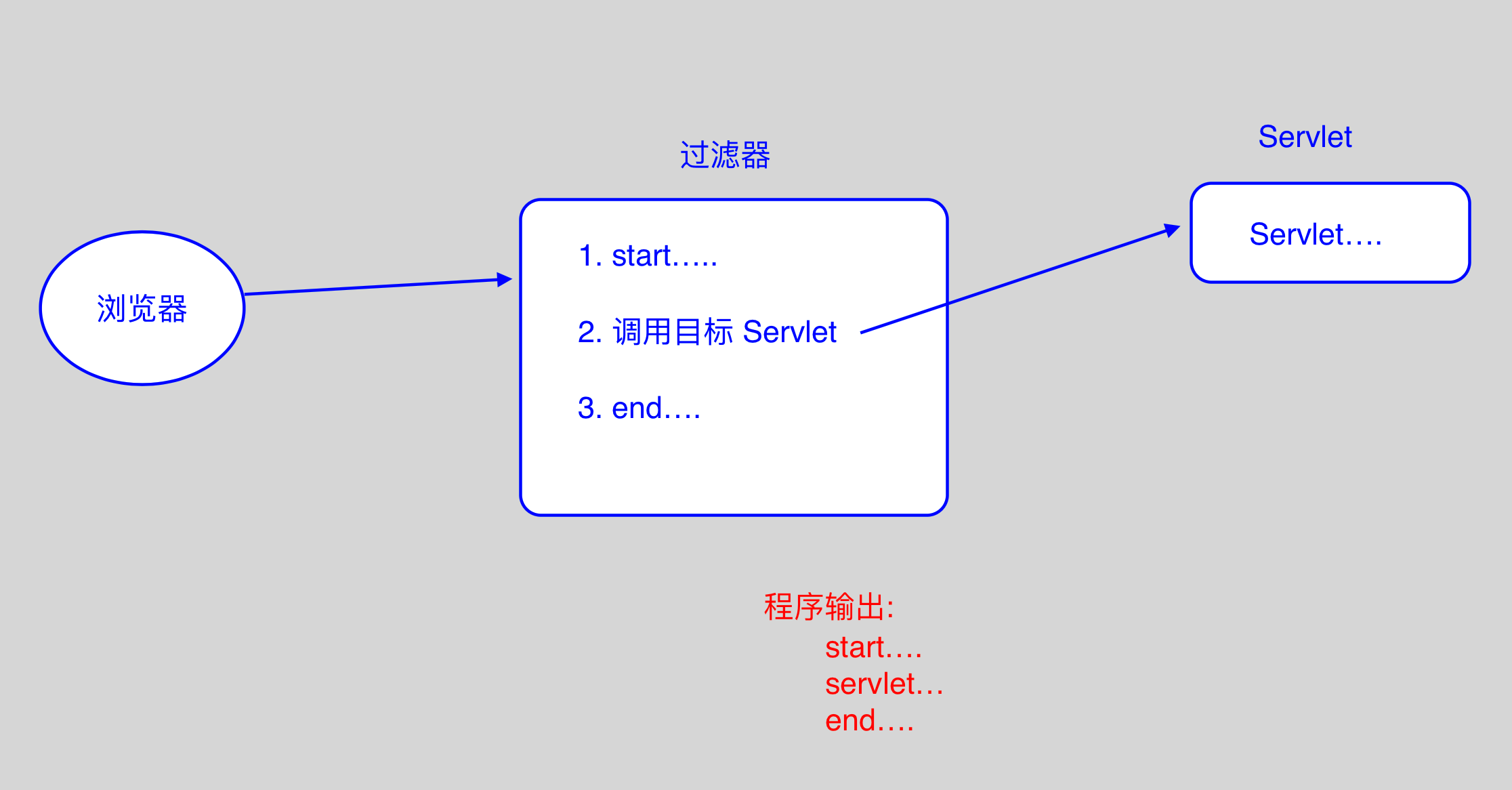
1. 什么是过滤器
- Servlet 是用来处理请求的, 过滤器是用来拦截请求的.
- 当用户请求某个 Servlet 时,会先执行部署在这个请求上的 Filter, 而 Filter 决定是否调用 Servlet.
当执行 Servlet 代码完成后, 还会执行 Filter 后面的代码!! - 它会在一组资源(jsp, servlet, css, html 等等)的前面执行.
- Filter 是单例的!!
2. 编写过滤器
2.1 步骤
- 写一个类实现 Filter 接口;
- 在 web.xml 中进行配置.
2.2 filter 接口的三个方法
void init(FilterConfig)- 创建之后,马上执行, Filter 会在服务器启动时创建!
void destroy()- 销毁之前执行. 在服务器关闭时,销毁!
void doFilter(ServletRequest, ServletResponse, FilterChain)- 每次过滤时,都会执行.
2.3 web.xml 中的配置
<filter>
<filter-name>xxx</filter-name>
<filter-class>cn.itcast.web.filter.AFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>xxx</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
2.4 Filter 相关的类型
-
FilterConfig, 与 ServletConfig 相似
- 获取初始化参数:
getInitParameter(); - 获取过滤器名称:
getFilterName(); - 获取 application:
getServletContext(); (较常用) - 获取所有初始化参数的名称:
Enumeration getInitParameterNames();
- 获取初始化参数:
-
FilterChain
- doFilter(ServletRequest, ServletResponse), 表示放行!
相当于调用了目标 Servlet 的 service() 方法.
- doFilter(ServletRequest, ServletResponse), 表示放行!
2.5 多过滤器
- FilterChain 的 doFilter() 方法: 执行目标资源, 或是执行下一个过滤器!
// 如果访问 AServlet, 需要经过AFilter 和 BFilter 两个过滤器,
AFilter#start...
BFilter#start...
AServlet...
BFilter#end...
AFilter#end...
3. 过滤器的四种拦截方式
- 拦截请求(默认拦截方式)
- 拦截转发
- 拦截包含
- 拦截错误
// <filter-mapping> 进行配置 <dispatcher> 元素
<filter>
<filter-name>AFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>cn.itcast.web.filter.AFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>AFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/AServlet</url-pattern>
<dispatcher>REQUEST</dispatcher> // 拦截请求
<dispatcher>FORWARD</dispatcher> // 拦截转发
<dispatcher>INCLUDE</dispatcher> // 拦截包含
<dispatcher>ERROR</dispatcher> // 拦截错误
</filter-mapping>
4. 多个过滤器的执行顺序
- <filter-mapping> 的配置顺序决定了过滤器的执行顺序!!
5. 过滤器的应用场景
- 执行目标资源之前做预处理工作, 例如设置编码,这种通常都会放行, 只是在目标资源执行之前做一些准备工作;
- 通过条件判断是否放行, 例如校验当前用户是否已经登录, 或者用户 IP 是否已经被禁用;
- 在目标资源执行后, 做一些后续的特殊处理工作, 例如对目标资源输出的数据进行处理;
// 示例一: 分 IP 统计访问次数
/*
* 分析:
* 1. 使用 Map<String, Integer> 来装载统计的数据;
* 2. 使用 ServletContextListener, 在服务器启动时完成创建;
* 3. Map 保存到 ServletContext 中;
* 因为 Map 需要在 Filter 中用来保存数据,
* 而页面需要打印 Map 中的数据.
*/
// AListener
public class AListener implements SerlvetContextListener {
// 在服务器启动时, 创建Map, 保存到 ServletContext中
public void contextInitialized(SerlvetContextEvent sce){
Map<String, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<String,Integer>();
// 得到 ServletContext
ServletContext application = sce.getServletContext();
// 把 map 保存到 application 中
application.setAttribute("map",map);
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce){
}
}
// AFilter
public class AFilter implements Filter{
private FilterConfig config;
public void destory(){
}
public void init(FilterConfig config) throws ServletException{
// 赋值
this.config = config;
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException{
// 得到 application 中的 map
ServletContext app = config.getServletContext();
Map<String,Integer> map = (Map<String,Integer>)app.getAttribute("map");
// 从 request 域中得到 ip 地址
String ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
// 查看 map 中是否存在这个 ip 对应的访问次数, 如果存在, 把次数加 1 再保存回去
// 如果不存在这个 ip, 那么设置这个 ip 的访问次数为 1
if(map.containsKey(ip)){
int cnt = map.get(ip);
map.put(ip,cnt+1);
}else{
map.put(ip,1);
}
// 把 map 放回到 application 中
app.setAttribute("map",map);
// 放行
chain.doFilter(request,response);
}
}
// 示例二: 解决全站字符乱码(POST 和 GET 中文乱码问题)
// index.jsp
<body>
<h1>主页</h1>
<%-- POST 请求 --%>
<form action="<c:url value='/AServlet'/>" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" value="张三"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
</form>
<%-- GET 请求, tomcat 8.0 以上版本,没有乱码问题 --%>
<a href="<c:url value='/AServlet?username=李四'"/>点击这里</a>
</body>
// EncodingFilter
// 处理 POST 请求编码问题
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 处理 GET 请求编码问题
// 需要调包 request:
// 写一个 request 的装饰类
// 在放行时,使用我们自己的 request
if(req.getMethod().equals("GET")){
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest)request;
EncodingRequest er = new EncodingRequest(req);
chain.doFilter(er,response);
}else if(req.getMethod().equals("POST")){
chain.doFilter(request,response);
}
// EncodingRequest 类, 即 request 的装饰类
// 装饰 request 的 getParameter(String name) 方法
public class EncodingRequest implements HttpServletRequest{
private HttpServletRequest request;
// 有参构造方法(是你,还有你)
public EncodingRequest(HttpServletRequest request){
this.request = request;
}
// 增强 request 的方法
public String getParameter(String name){
String value = request.getParameter(name);
// 处理编码问题
try{
value = new String(value.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"utf-8");
}catch(Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return value;
}
// 复写 request 其他方法 (一切拜托你)
....
}
// EncodingRequest 类的升级版
// EncodingRequest 类继承 HttpServletRequestWrapper 类即可
// HttpServletRequestWrapper 实现了 HttpServletRequest 中的所有方法
public class EncodingRequest extends HttpServletRequestWrapper{
private HttpServletRequest req;
// 构造方法
public EncodingRequest(HttpServletRequest request){
// 将 request 参数传递给父类 HtttpServletRequestWrapper
super(request);
this.req = request;
}
// 需要增强的方法
public String getParameter(String name){
String value = req.getParameter(name);
try{
value = new String(value.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"utf-8");
}catch(UnsupportedEncodingException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return value;
}
}
参考资料: