一、maven是什么?
maven是项目管理工具
二、maven为什么要用?
在做开发的时候常常会用到外部的工具包(jar包),这就需要你一个一个的去他们的官网下工具包,然后在项目里依赖他们,比较的麻烦。
maven有一个远程仓库,里面存了几乎所有要用到的工具包,只需在项目里配置maven要用到的pom.xml文件,项目首先自动会将这些工具包下载到本地仓库,然后项目就可以依赖到这些工具包,比较方便。
三、maven怎么用?
1、maven项目结构
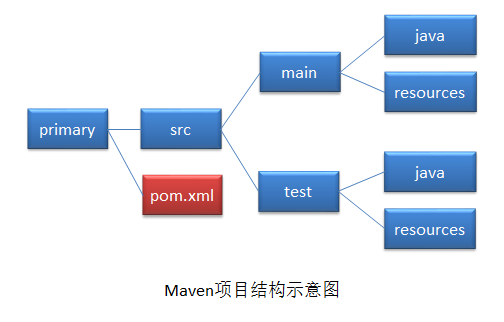
2、maven项目构建命令(命令运行与pom文件在同一目录)
mvn clean;【清理】 mvn clean compile/test/package/install;【编译/测试/打包/安装】 * 执行后面的命令,前面的命令也会执行 * 由<packaging>pom/jar/war</packaging>决定打包类型
3、传递(<dependency></dependency>标签下)
<scope></scope>常用取值 compile:向下传递,其为默认值,大多数都为此值; test:不向下传递,测试类的包为此值; runtime:向下传递,jdbc驱动包为此值; provided:不向下传递,servlet-api包为此值; 不向下传递:gav下加 <optional>true</optional> 不接收传递:gav下加 <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> 依赖优先级: 直接依赖后者高于前者,直接依赖高于间接依赖,间接依赖前者高于后者
4、maven继承
直接继承: 父工程: <packaging>pom</packaging> 子工程:工程的gav不需要g和v <parent> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> <version></version> <relativePath>../父工程</relativePath> </parent> 可选继承: 1、父工程: <packaging>pom</packaging> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> <version></version> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> 2、子工程:子工程可选继承多个父工程,依赖的gav不需要v <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> <version></version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> <version></version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>
四、父子工程三种启动方式
父工程:mvn tomcat:run
子工程:mvn tomcat:run,需要先安装其他子工程,可由父工程mvn install
本地:本地tomcat运行
五、示例
1、父工程
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> <version></version> <packaging>pom</packaging> <parent> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> <version></version> </parent> <modules> <module></module> </modules> <properties></properties> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> <version></version> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> </project>
2、子工程
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId></artifactId> <parent> <artifactId></artifactId> <groupId></groupId> <version></version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>