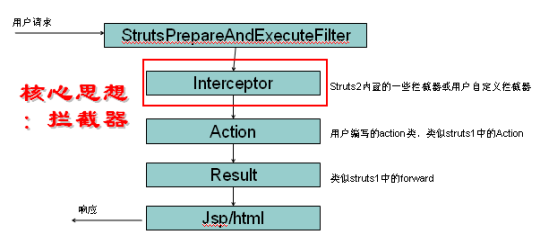
4.Struts2的处理流程
以下是struts-defautl.xml中的拦截器
建议通过这个struts-default的副本查看,更形象

它实现了很多的功能,其中包括国际化,文件上传,类型转换,表单验证,都是在跳转到Action类处理之前就做好了,所有我们只需要在Action类中使用就可以了,大大方便了我们的开发
下面通过使用eclipse的断点调试,看看拦截器的执行过程。我们分别在一下三个拦截器中设置断点,在我们的三个拦截器类中(invocation.invoke()所在函数中断点)中设置断点,然后根据流程查看拦截器执行顺序.

@Override public String doIntercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { Object action = invocation.getAction(); if (action instanceof Preparable) { try { String[] prefixes; if (firstCallPrepareDo) { prefixes = new String[] {ALT_PREPARE_PREFIX, PREPARE_PREFIX}; } else { prefixes = new String[] {PREPARE_PREFIX, ALT_PREPARE_PREFIX}; } PrefixMethodInvocationUtil.invokePrefixMethod(invocation, prefixes); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { /* * The invoked method threw an exception and reflection wrapped it * in an InvocationTargetException. * If possible re-throw the original exception so that normal * exception handling will take place. */ Throwable cause = e.getCause(); if (cause instanceof Exception) { throw (Exception) cause; } else if(cause instanceof Error) { throw (Error) cause; } else { /* * The cause is not an Exception or Error (must be Throwable) so * just re-throw the wrapped exception. */ throw e; } } if (alwaysInvokePrepare) { ((Preparable) action).prepare(); } } return invocation.invoke(); }
可见简写成下面,容易理解
PrepareInterceptor @Override public String doIntercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { //invoke()表示放行,跳转到Action类(在跳转到Action类之前,先将所有的拦截器先执行完成) //invoke()方法的返回值,返回Action类方法的返回值 System.out.println("PrepareInterceptor的being方法"); String value = invocation.invoke(); System.out.println("PrepareInterceptor的end方法"); return value }
ChainingInterceptor @Override public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { ValueStack stack = invocation.getStack(); CompoundRoot root = stack.getRoot(); if (shouldCopyStack(invocation, root)) { copyStack(invocation, root); } //invoke()表示放行,跳转到Action类(在跳转到Action类之前,先将所有的拦截器先执行完成) //invoke()方法的返回值,返回Action类方法的返回值 System.out.println("ChainingInterceptorbeing的begin方法"); String value = invocation.invoke(); System.out.println("ChainingInterceptor的end方法"); return value
ParametersInterceptor @Override public String doIntercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { //invoke()表示放行,跳转到Action类(在跳转到Action类之前,先将所有的拦截器先执行完成) //invoke()方法的返回值,返回Action类方法的返回值 System.out.println("ParametersInterceptor的begin方法"); String value = invocation.invoke(); System.out.println("ParametersInterceptor的end方法"); return value }
public class HelloWorldAction extends ActionSupport{ @Override public String execute() throws Exception { System.out.println("欢迎访问HelloWorldAction中的execute方法!"); return "success"; } //自定义add方法 public String add(){ System.out.println("欢迎访问HelloWorldAction中的add的方法!"); return "success"; } }
这里注意:当执行每个拦截器时,调用拦截器中的invocation.invoke();方法前的内容,此时会陆续继续执行拦截器,执行拦截器的顺序是prepare、chain、params。那么执行完Action的方法后,即调用invocation.invoke(); 方法,会继续执行params、chain、prepare拦截器中invocation.invoke();后的内容,所以我们看到顺序会是后又3,2,1.

注意上面只是为了方便理解,所以简化了源码并在源码中添加输出语句,实际源码不能改变,具体可以自己打断点,看一下流程运转;