1.FastDFS
1.1. 什么是FastDFS?
FastDFS是用c语言编写的一款开源的分布式文件系统。FastDFS为互联网量身定制,充分考虑了冗余备份、负载均衡、线性扩容等机制,并注重高可用、高性能等指标,使用FastDFS很容易搭建一套高性能的文件服务器集群提供文件上传、下载等服务。
1.2. FastDFS架构
FastDFS架构包括 Tracker server和Storage server。客户端请求Tracker server进行文件上传、下载,通过Tracker server调度最终由Storage server完成文件上传和下载。
Tracker server作用是负载均衡和调度,通过Tracker server在文件上传时可以根据一些策略找到Storage server提供文件上传服务。可以将tracker称为追踪服务器或调度服务器。
Storage server作用是文件存储,客户端上传的文件最终存储在Storage服务器上,Storage server没有实现自己的文件系统而是利用操作系统 的文件系统来管理文件。可以将storage称为存储服务器。

服务端两个角色:
Tracker:管理集群,tracker也可以实现集群。每个tracker节点地位平等。
收集Storage集群的状态。
Storage:实际保存文件
Storage分为多个组,每个组之间保存的文件是不同的。每个组内部可以有多个成员,组成员内部保存的内容是一样的,组成员的地位是一致的,没有主从的概念。
1.3. 文件上传的流程
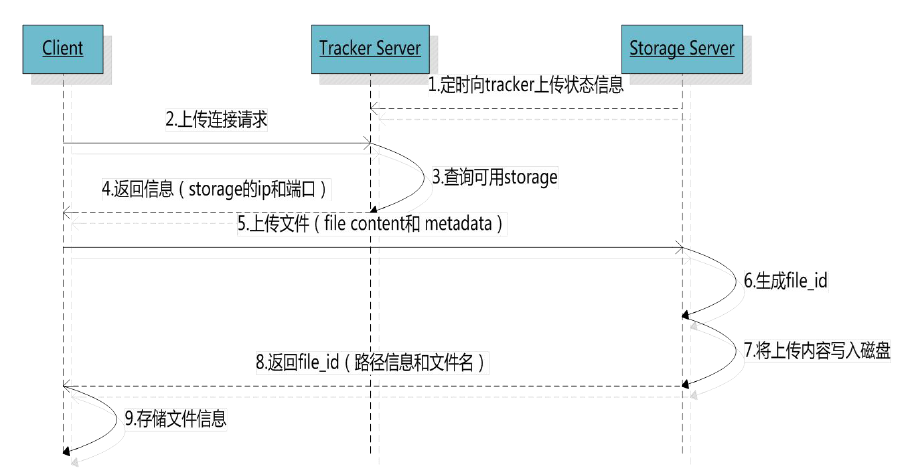
客户端上传文件后存储服务器将文件ID返回给客户端,此文件ID用于以后访问该文件的索引信息。文件索引信息包括:组名,虚拟磁盘路径,数据两级目录,文件名。

n 组名:文件上传后所在的storage组名称,在文件上传成功后有storage服务器返回,需要客户端自行保存。
n 虚拟磁盘路径:storage配置的虚拟路径,与磁盘选项store_path*对应。如果配置了store_path0则是M00,如果配置了store_path1则是M01,以此类推。
n 数据两级目录:storage服务器在每个虚拟磁盘路径下创建的两级目录,用于存储数据文件。
n 文件名:与文件上传时不同。是由存储服务器根据特定信息生成,文件名包含:源存储服务器IP地址、文件创建时间戳、文件大小、随机数和文件拓展名等信息。
1.4. 文件下载

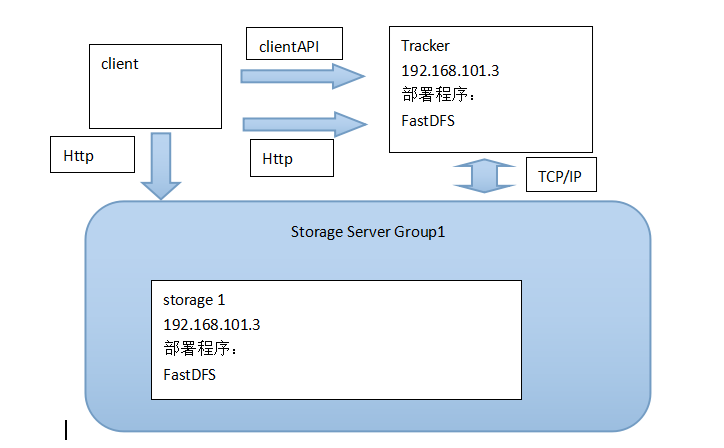
1.5. 最简单的FastDFS架构
2. 图片服务器安装方法
2.1. 安装步骤
第一步:把图片服务器解压缩。
第二步:把图片服务器添加到Vmware中。
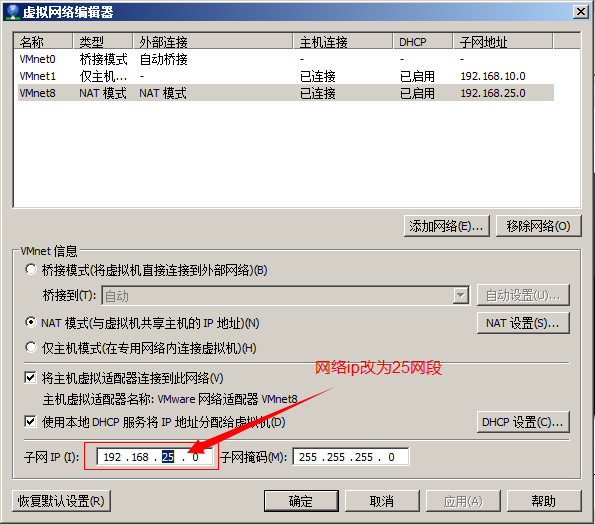
第三步:Vmware的网络配置。
第四步:开机
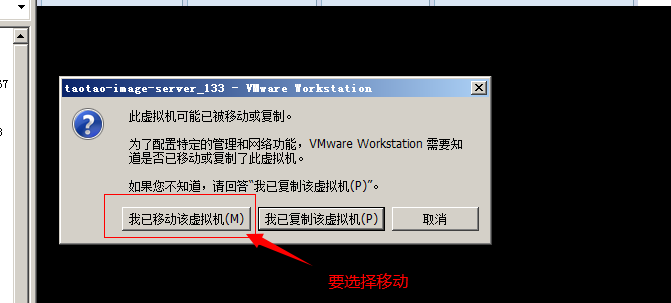
移动:网络配置不发生变化。要使用图片服务器,需要保证网络配置不变。
复制:重新生成一块网卡mac地址是新地址。
Ip地址:192.168.25.133
用户名root、itcast
密码:itcast
3. 图片服务器使用
3.1. Java客户端:
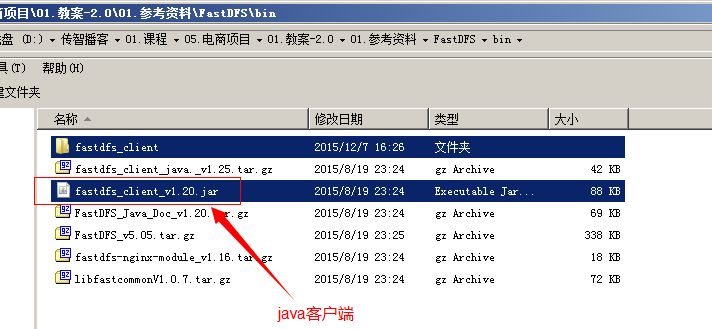
Maven环境:
3.2. 上传图片
3.2.1. 上传步骤
1、加载配置文件,配置文件中的内容就是tracker服务的地址。
配置文件内容:tracker_server=192.168.25.133:22122
2、创建一个TrackerClient对象。直接new一个。
3、使用TrackerClient对象创建连接,获得一个TrackerServer对象。
4、创建一个StorageServer的引用,值为null
5、创建一个StorageClient对象,需要两个参数TrackerServer对象、StorageServer的引用
6、使用StorageClient对象上传图片。
7、返回数组。包含组名和图片的路径。
3.2.2. 代码
public class FastDFSTest {
@Test
public void testFileUpload() throws Exception {
// 1、加载配置文件,配置文件中的内容就是tracker服务的地址。
ClientGlobal.init("D:/workspaces-itcast/e3-manager-web/src/main/resources/resource/client.conf");
// 2、创建一个TrackerClient对象。直接new一个。
TrackerClient trackerClient = new TrackerClient();
// 3、使用TrackerClient对象创建连接,获得一个TrackerServer对象。
TrackerServer trackerServer = trackerClient.getConnection();
// 4、创建一个StorageServer的引用,值为null
StorageServer storageServer = null;
// 5、创建一个StorageClient对象,需要两个参数TrackerServer对象、StorageServer的引用
StorageClient storageClient = new StorageClient(trackerServer, storageServer);
// 6、使用StorageClient对象上传图片。
//扩展名不带“.”
String[] strings = storageClient.upload_file("D:/Documents/Pictures/images/200811281555127886.jpg", "jpg", null);
// 7、返回数组。包含组名和图片的路径。
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}
3.3. 使用工具类上传
封装好的FastDFSClient 工具类
package cn.kmily.fastdfs.cliennt;
import org.csource.common.NameValuePair;
import org.csource.fastdfs.ClientGlobal;
import org.csource.fastdfs.StorageClient1;
import org.csource.fastdfs.StorageServer;
import org.csource.fastdfs.TrackerClient;
import org.csource.fastdfs.TrackerServer;
public class FastDFSClient {
private TrackerClient trackerClient = null;
private TrackerServer trackerServer = null;
private StorageServer storageServer = null;
private StorageClient1 storageClient = null;
public FastDFSClient(String conf) throws Exception {
if (conf.contains("classpath:")) {
conf = conf.replace("classpath:", this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath());
}
ClientGlobal.init(conf);
trackerClient = new TrackerClient();
trackerServer = trackerClient.getConnection();
storageServer = null;
storageClient = new StorageClient1(trackerServer, storageServer);
}
/**
* 上传文件方法
* <p>Title: uploadFile</p>
* <p>Description: </p>
* @param fileName 文件全路径
* @param extName 文件扩展名,不包含(.)
* @param metas 文件扩展信息
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public String uploadFile(String fileName, String extName, NameValuePair[] metas) throws Exception {
String result = storageClient.upload_file1(fileName, extName, metas);
return result;
}
public String uploadFile(String fileName) throws Exception {
return uploadFile(fileName, null, null);
}
public String uploadFile(String fileName, String extName) throws Exception {
return uploadFile(fileName, extName, null);
}
/**
* 上传文件方法
* <p>Title: uploadFile</p>
* <p>Description: </p>
* @param fileContent 文件的内容,字节数组
* @param extName 文件扩展名
* @param metas 文件扩展信息
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public String uploadFile(byte[] fileContent, String extName, NameValuePair[] metas) throws Exception {
String result = storageClient.upload_file1(fileContent, extName, metas);
return result;
}
public String uploadFile(byte[] fileContent) throws Exception {
return uploadFile(fileContent, null, null);
}
public String uploadFile(byte[] fileContent, String extName) throws Exception {
return uploadFile(fileContent, extName, null);
}
}
@Test
public void testFastDfsClient() throws Exception {
FastDFSClient fastDFSClient = new FastDFSClient("D:/workspaces-itcast/e3-manager-web/src/main/resources/resource/client.conf");
String file = fastDFSClient.uploadFile("D:/Documents/Pictures/images/2f2eb938943d.jpg");
System.out.println(file);
}