---恢复内容开始---
命名规则:
1、类名使用 UpperCamelCase 风格,必须遵从驼峰形式,但以下情形例外:(领域模型 的相关命名)DO / BO / DTO / VO 等。
2、方法名、参数名、成员变量、局部变量都统一使用 lowerCamelCase 风格,必须遵从 驼峰形式。
正例: localValue / getHttpMessage() / inputUserId
3、常量命名全部大写,单词间用下划线隔开,力求语义表达完整清楚,不要嫌名字长。
正例: MAX_STOCK_COUNT 反例: MAX_COUNT
4、抽象类命名使用 Abstract 或 Base 开头;异常类命名使用 Exception 结尾;测试类 命名以它要测试的类的名称开始,以 Test 结尾。
Java 流式输入输出
java中的数据的输入/输出操作以流(stream)方式进行;
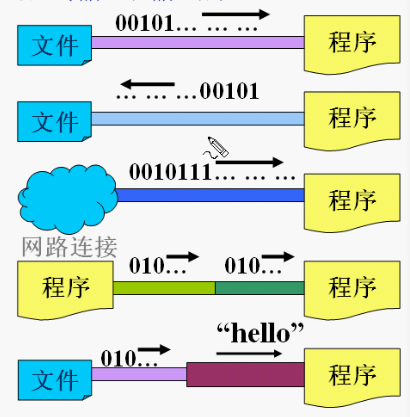
java.io(输入输出站在程序的角度看)
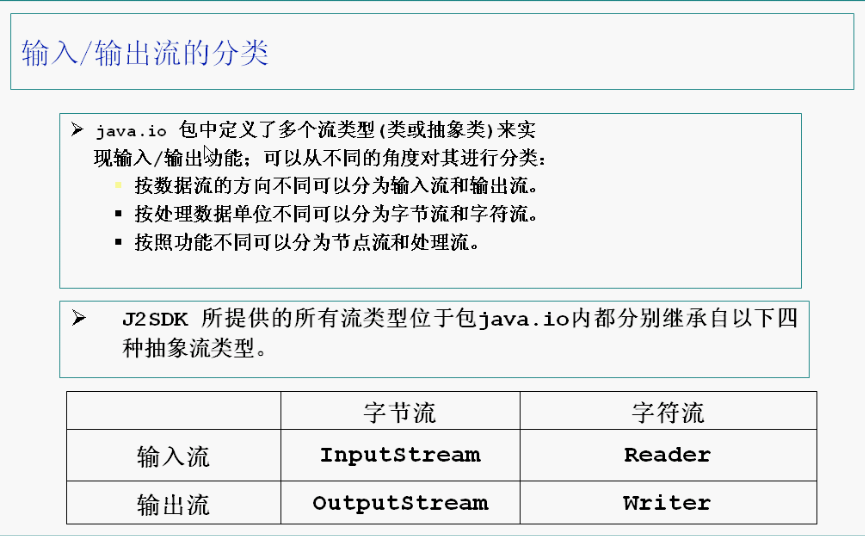
字节流:InputStream OutputStream
字符流: Reader Writer (2字节-UTF16)
节点流和处理流
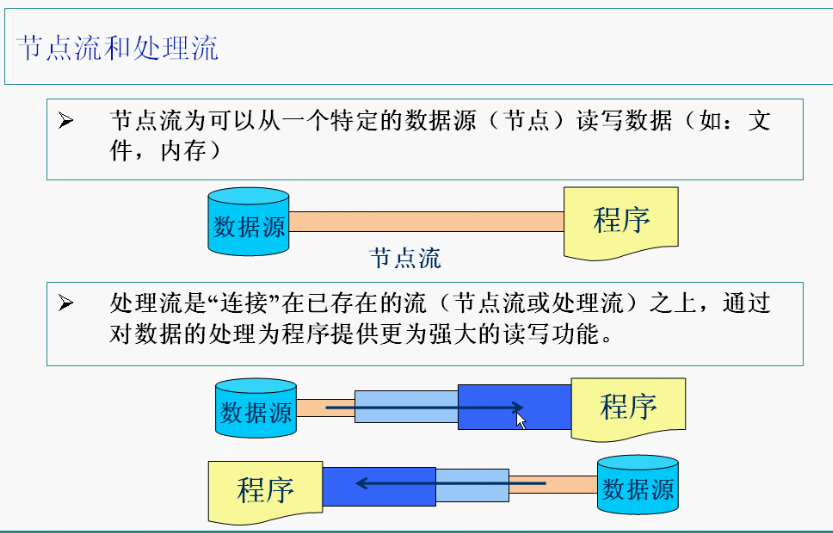
节点流:
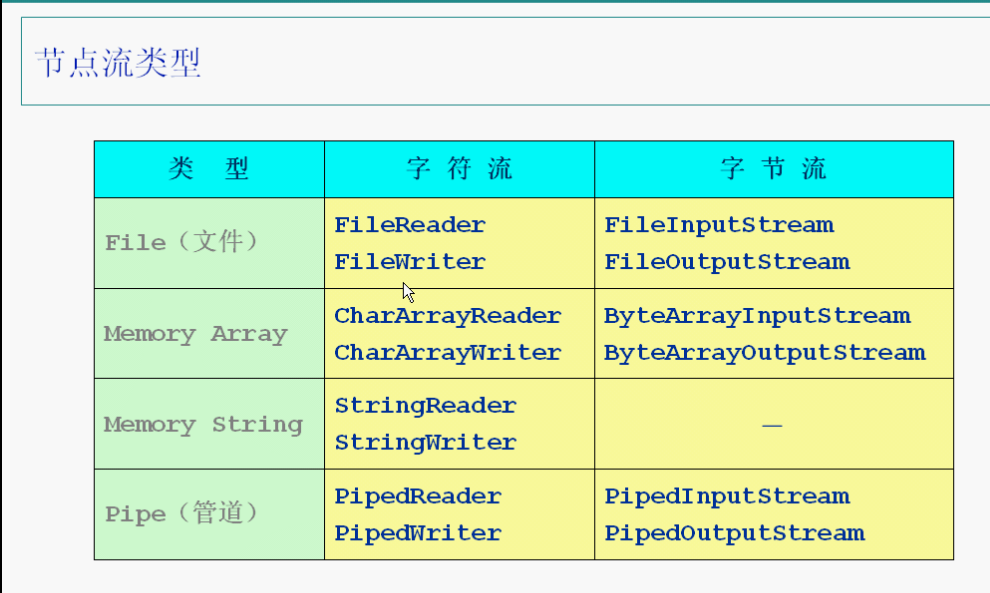
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
FileDescriptor 是“文件描述符”。
FileDescriptor 可以被用来表示开放文件、开放套接字等。
以FileDescriptor表示文件来说:当FileDescriptor表示某文件时,我们可以通俗的将FileDescriptor看成是该文件。但是,我们不能直接通过FileDescriptor对该文件进行操作;若需要通过FileDescriptor对该文件进行操作,则需要新创建FileDescriptor对应的FileOutputStream,再对文件进行操作。
java文件路径,注意与windows系统进行区别
windows文件系统: D:workspace
java程序设计: D:\workspace\hello.txt或者 D:/workspace/hello.txt
---java路径分隔符,一般为"/"或者"\"
使用FileReader或BufferedReader从文件中读取字符或文本数据,并总是指定字符编码;使用FileInputStream从Java中文件或套接字中读取原始字节流。
import java.io.*; public class TestInputStream { public static void main(String[] args){ int b = 0; FileInputStream in = null;//create a FileInputStream Object try { in = new FileInputStream("D:/workspace/helloworld.txt"); //opening a connection to an actual file } catch(FileNotFoundException e) { // exception System.out.println("找不到指定文件"); System.exit(-1);//捕获到异常,就退出程序。exit(a):a=0代表正常退出,a != 0代表非正常退出。 } try { long num = 0; while (( b = in.read()) != -1) { //Reads a byte of data from this input stream System.out.println((char)b); // return -1 if the end of the file is reached. num++; } in.close(); //Closes this file input stream and releases any system resources associated with the stream. System.out.println(); System.out.println("共读取了"+num+"个字节"); } catch(IOException e) { System.out.println("文件读取错误"); System.exit(-1); } } }
FileReader 和 FileWrite
import java.io.*; public class HelloFileReader { public static void main(String[] args){ FileReader fr = null; int c =0; try { fr = new FileReader("D:/workspace/helloworld.txt"); int ln = 0; while ((c = fr.read()) != -1){ System.out.println((char)c); } fr.close(); } catch(FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("找不到指定文件"); } catch (IOException e){ System.out.println("文件读取错误"); } } }
FileReader
import java.io.*; public class TestFileWrite { public static void main(String[] args){ FileWriter fw = null; try { fw = new FileWriter("D:/workspace/hello.bat"); for (int c = 0;c <= 50000;c++){ fw.write(c); } fw.close(); } catch(IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("无法找到文件"); System.exit(1);//终止JVM } } }
BufferedInputStream示例
import java.io.*; public class TestBufferStream1 { public static void main(String[] args){ try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:/workspace/helloworld.txt"); BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); int c = 0; System.out.println((char)bis.read()); System.out.println((char)bis.read()); bis.mark(100);//直接从第100个开始读 for (int i = 0;i < 10&&(c = bis.read()) != -1;i++){ System.out.println((char) c+""); } System.out.println();//打印空行 bis.reset();//回到第100个的标记 for (int i = 0;i < 10&&(c = bis.read()) != -1;i++){ System.out.println((char) c+""); } bis.close(); } catch(IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
BufferedWriter示例
import java.io.*; public class TestBufferedWritee { public static void main(String[] args){ try { BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:/workspace/world.txt")); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("D:/workspace/world.txt"));//throw 的IllegalArgumentException 属于RuntimeException可以不做处理 String s = null; for (int i = 1;i <= 100;i++){ s = String.valueOf(Math.random());//random() 随机产生0.0~1.0的双精度浮点型数据 bw.write(s);//Writes a single character. bw.newLine();//行分隔符 } bw.flush();//Flushes this buffered output stream.输出时,bufferter需要flush while ((s = br.readLine()) != null){ System.out.println(s); } bw.close(); br.close(); } catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }