三、容器(图很重要)存储多个数据,想存多少存多少
3.1 简介
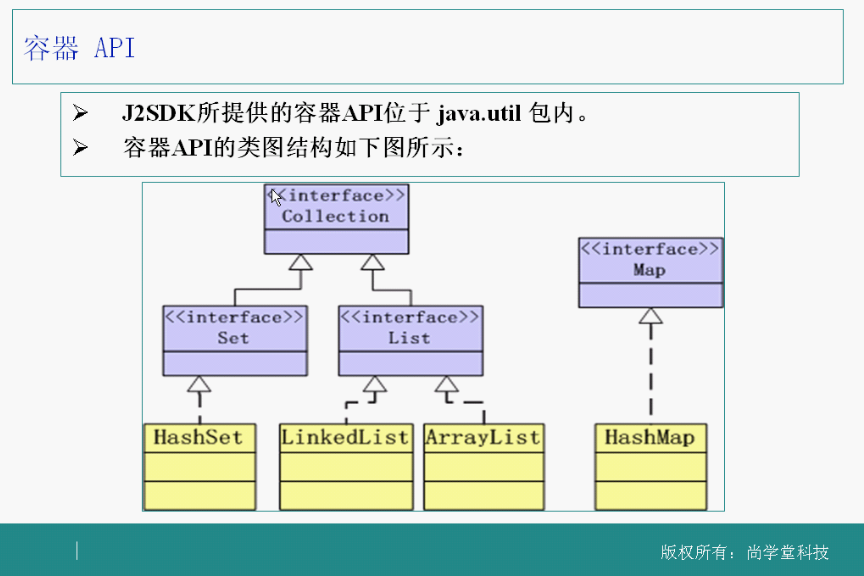
左边是一个一个往里装,右边map是一对一对往里装。collection接口是set和list接口的父类,set没有顺序,不可以重复;list有顺序,可以重复(可以equals)。Map定义了“键(key)-值(value)”存储,成对存储。
Collection类中,在调用remove、contains方法时,需要比较对象是否相等,这会涉及到object类中的equals方法和hashcode方法,对于自定义的类型,需要重写equals和hashcode方法以实现自定义对象的相等规则。例:

必学的六个接口:collection、set、list、map、iterator(遍历元素),comparable
3.2增强的for循环(JDK1.5以后)
缺点:
数组:不能方便的访问下标;
集合:与iterator相比,不能方便的删除集合中的内容。所以除了简单的遍历读数据外,一般不用。
import java.util.*;
public class EnhancedFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for(int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add(new String("aaa"));
c.add(new String("bbb"));
c.add(new String("ccc"));
for(Object o : c) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
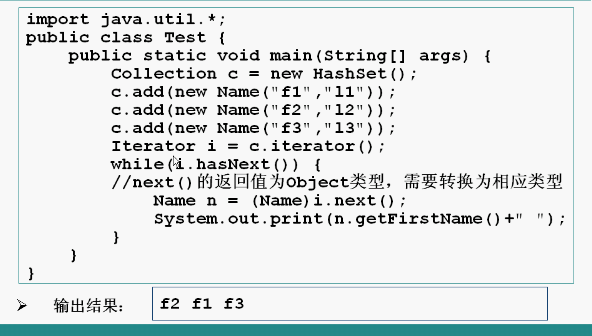
3.3Iterator接口(遍历一个collection的方式)
含有hasNext(),next(),remove()方法
3.4 Set接口
Set接口是collection的子接口,实现set的容器类中的元素没有顺序,而且不可能重复。Set类中有HashSet()和TreeSet()等
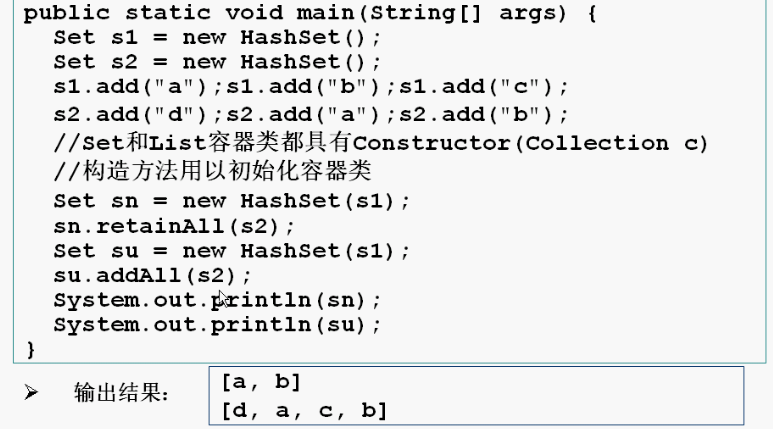
sn.retainAll(s1)//sn与s1求交集
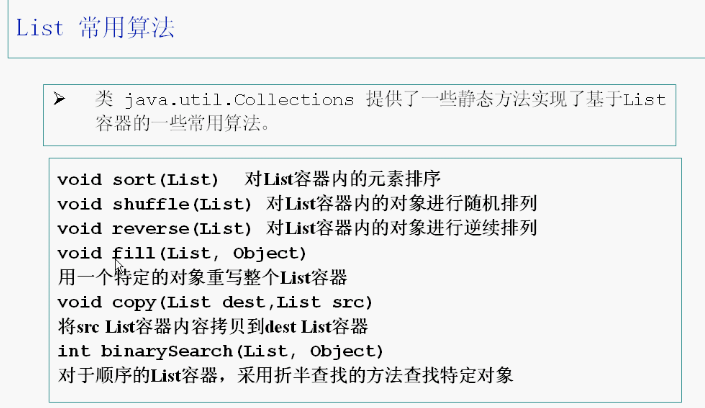
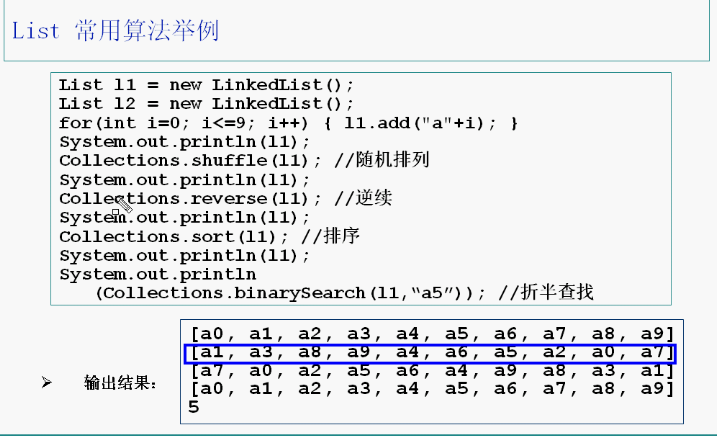
3.5 List接口
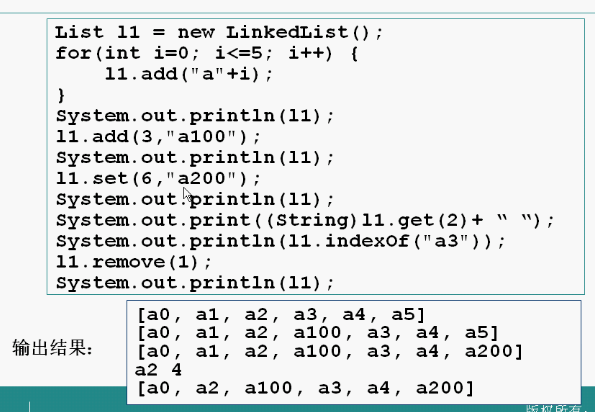
List接口也是collection的子接口,list接口的容器类中的元素是有顺序的,而且可以重复。arrayList(),linkedList()
Object set(int index,object element)//object返回值为以前的对象

3.6 comparable
import java.lang.cmparable 里面只有一个方法 public int compareTo(object obj)

3.7 Map接口
实现Map接口的类用来存储键-值对,键是用来做索引的,所以不能重复(指相互间间equals,因为equals效率较低,所以用hashcode比较,所以重写equals必须重写hashcode)
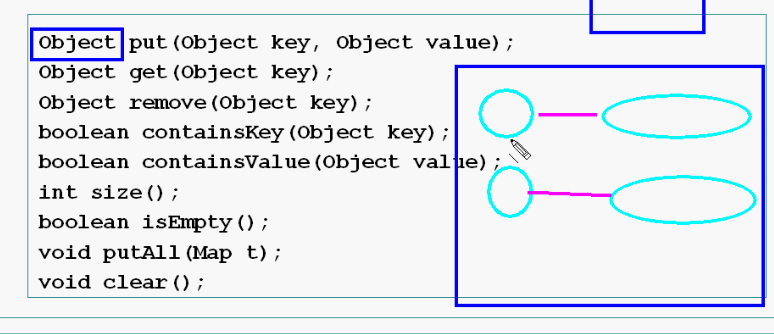
Map接口(JDK1.5之后满足下面的方法),本来map的方法必须是针对对象的,对于数据必须转换成对象,现在可以直接用1,这是因为JDK1.5支持自动将基础类型转换成对象(打包)和自动将对象转换成基础类型(解包)过程
3.8 泛型
List<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();//<String>只能装string类型(在API文档中,只要后面跟着<E>的都可以跟<>,这就叫泛型)
Map<String, Integer> m1 = new HashMap<String , Integer>();//Map里面装了一对东西,所以使用两个类型。
碰到集合时尽量用泛型,增强程序的可读性,即在定义集合时,定义集合中对象的类型。
3.9 List、Set、Map、数组之间的转换
3.9.1 List和Set转换
1、List->Set
Set set = new HashSet(new ArrayList())
2、Set->List
List list = new ArrayList(new HashSet())
3.9.2 List和数组转换
1、List->数组
List list = Arrays.asList(1,2) int [] res = (int[])list.toArray(new int[list.size()])
2、数组->List
List list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4)
3.9.3 Set和数组转换
1、Set->数组
Set set = new HashSet() List list = new ArrayList(set) int [] res = (int[])list.toArray(new int[list.size()])
2、数组->Set
Set set = new HashSet(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4)) //通过List过渡
3.9.4 Map的相关操作
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("1", "a");
map.put('2', 'b');
map.put('3', 'c');
System.out.println(map.keySet()); // 输出所有的key值
System.out.println(map.values()); // 输出所有的value
List list = new ArrayList(map.values()); // 将map的值转化为List
Set set = new HashSet(map.values()); // 将map的值转化为Set