来自Leetcode第146题LRU缓存机制
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。
获取数据 get(key) - 如果密钥 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取密钥的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果密钥不存在,则写入其数据值。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最近最少使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
示例:
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // 返回 1
cache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得密钥 2 作废
cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得密钥 1 作废
cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.get(4); // 返回 4
硬件实现的4路组相联 + LRU算法
参考组原实验mooc
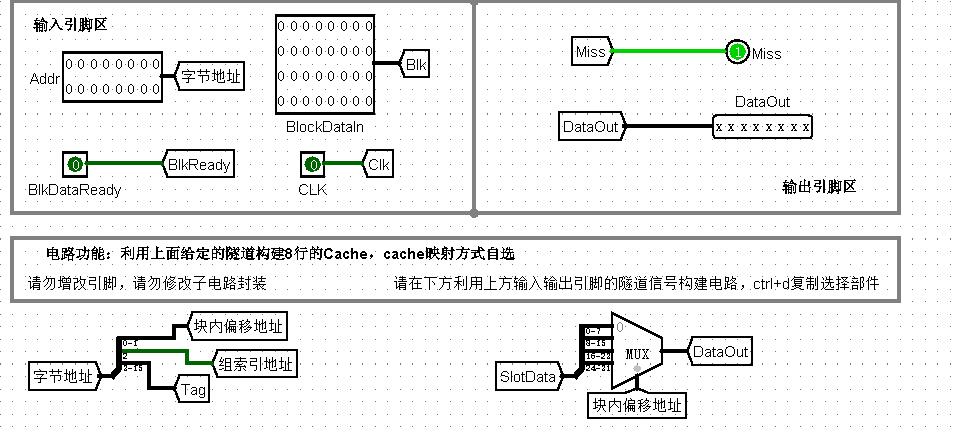
输入输出引脚图:
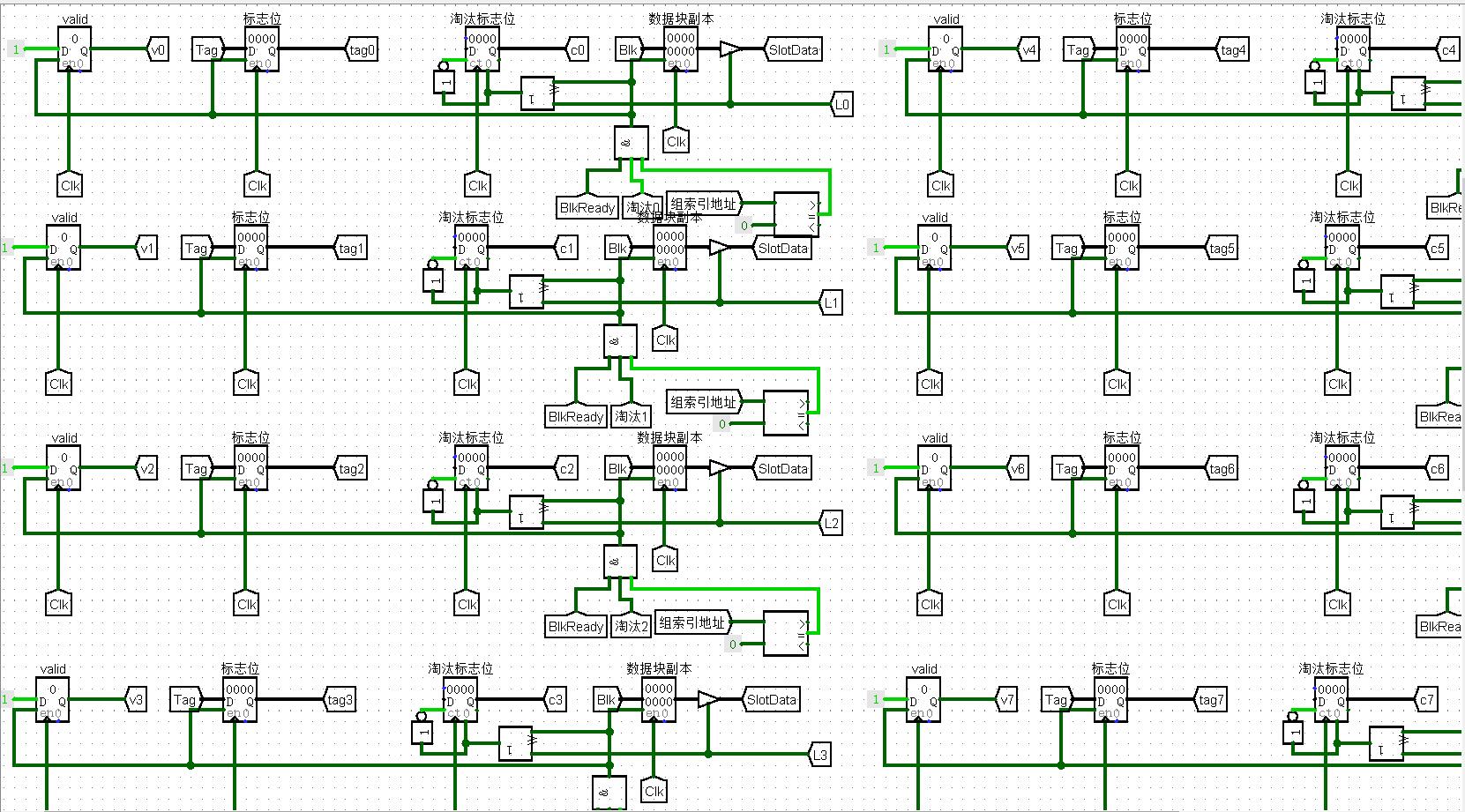
8个cache槽分2组4路:
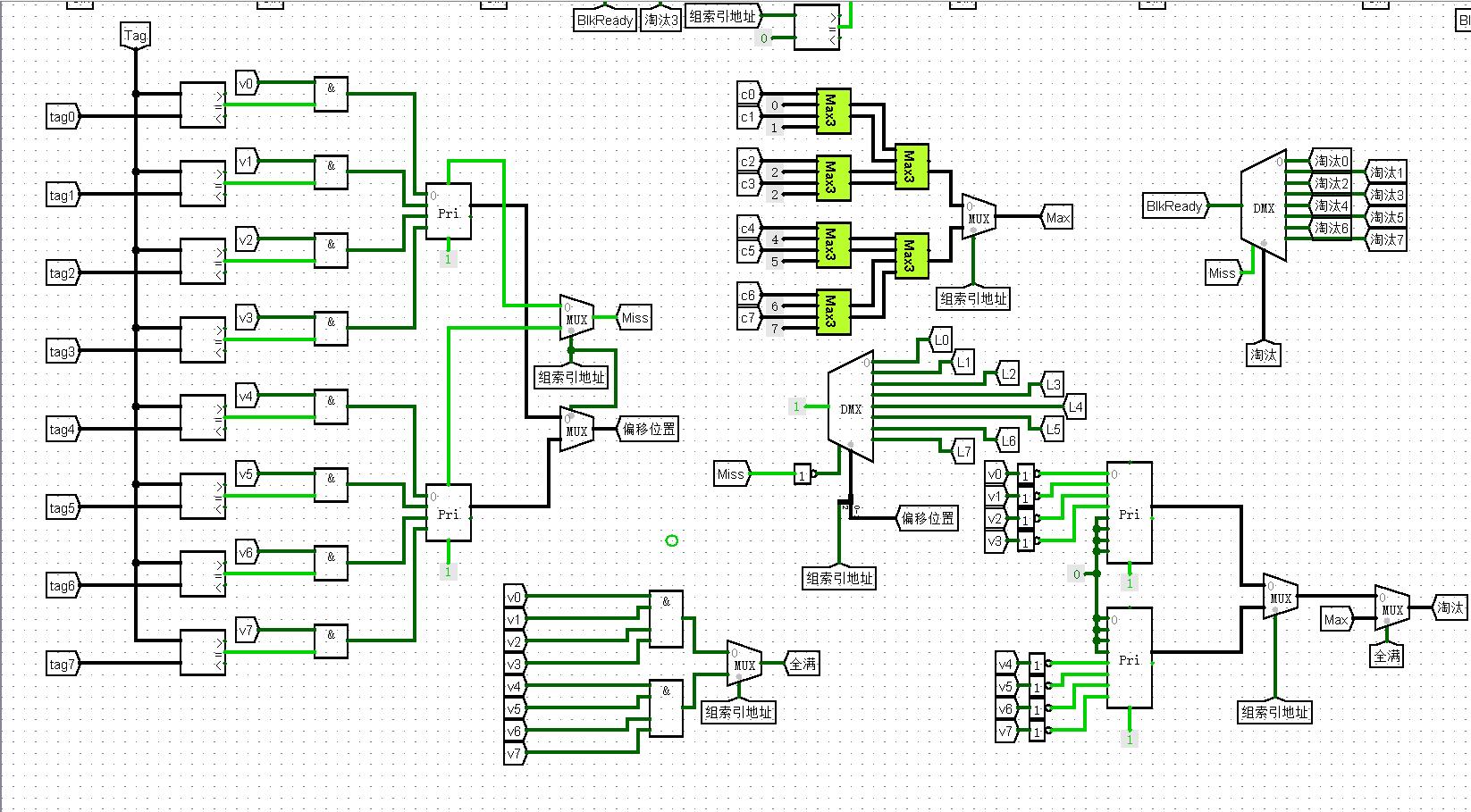
替换算法LRU:
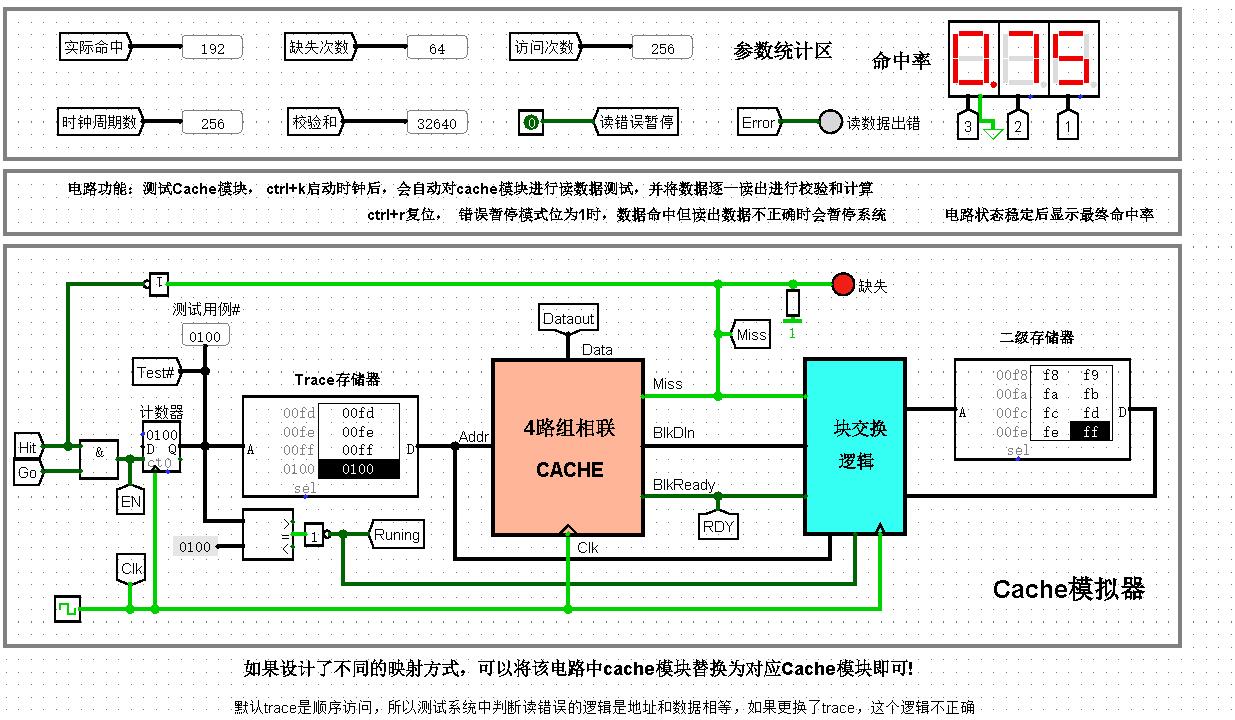
测试图:
软件实现
哈希链表实现
来源题解
LRU 算法实际上是让你设计数据结构:首先要接收一个 capacity 参数作为缓存的最大容量,然后实现两个 API,一个是 put(key, val) 方法存入键值对,另一个是 get(key) 方法获取 key 对应的 val,如果 key 不存在则返回 -1。
注意哦,get 和 put 方法必须都是 O(1)O(1) 的时间复杂度,我们举个具体例子来看看 LRU 算法怎么工作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache(2);
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1);
cache.put(3, 3);
cache.get(2);
cache.put(1, 4);
|
从流程里可以看到,不需要设计计数器来实现对每次未命中的cache槽做计数+1,淘汰时将数值最大的淘汰。
在put时将元素放到了队头,每次get都会将元素提前,我们要做的就是把队尾元素替换掉。
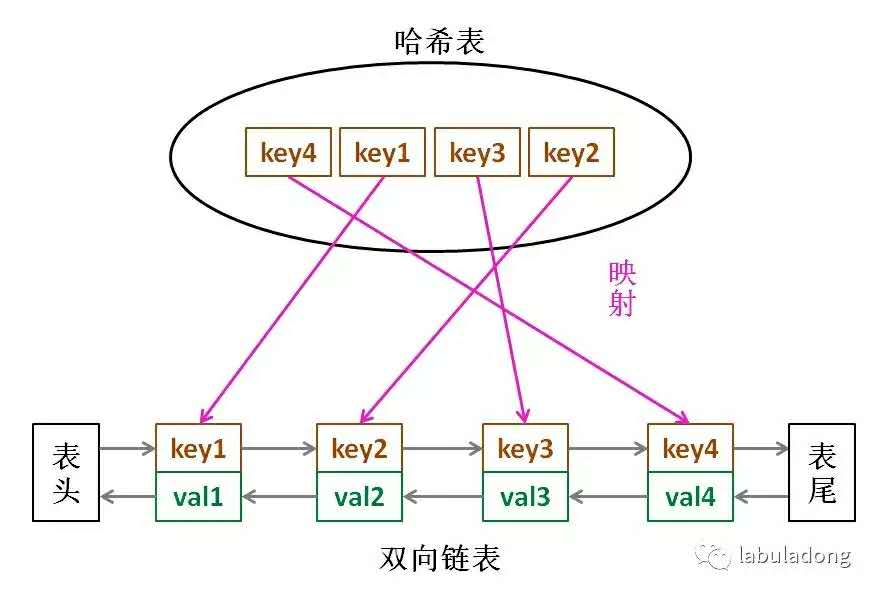
LRU 缓存算法的核心数据结构就是哈希链表,双向链表和哈希表的结合体。这个数据结构长这样:
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
|
class {
public int key,val;
public Node next,prior;
public (int key,int val){
this.val = val;
this.key = key;
}
}
class DoubleList{
private Node head,tail ;
private int size;
public DoubleList(){
head = new Node(0,0);
tail = new Node(0,0);
head.next = tail;< 大专栏 LRU缓存机制/span>
tail.prior = head;
size = 0;
}
public void addFirst(Node x){
x.next = head.next;
x.prior = head;
head.next.prior = x;
head.next = x;
size++;
}
public void remove(Node x){
x.prior.next = x.next;
x.next.prior = x.prior;
size--;
}
public Node removeLast(){
if(tail.prior == head)
return null;
Node last = tail.prior;
remove(last);
return last;
}
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
}
class LRUCache{
private HashMap<Integer ,Node> map;
private DoubleList cache;
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>();
cache = new DoubleList();
}
public int get(int key){
if (!map.containsKey(key))
return -1;
int val = map.get(key).val;
put(key,val);
return val;
}
public void put(int key,int val){
Node x = new Node(key, val);
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
cache.remove(map.get(key));
cache.addFirst(x);
map.put(key, x);
}else{
if (capacity == cache.getSize()) {
Node last = cache.removeLast();
map.remove(last.key);
}
cache.addFirst(x);
map.put(key, x);
}
}
}
|
有序字典
来源题解
利用了LinkedHashMap这样一种数据结构
在构造器里第三个参数accessOrder,设置为false表示不是访问顺序而是插入顺序存储的,这也是默认值,表示LinkedHashMap中存储的顺序是按照调用put方法插入的顺序进行排序的;true则是按照访问顺序,访问过后的元素会到链表的末尾。
0.75F表示负载因子
HashMap有一个初始容量大小,默认是16
static final int DEAFULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
为了减少冲突概率,当HashMap的数组长度达到一个临界值就会触发扩容,把所有元素rehash再放回容器中,这是一个非常耗时的操作。
而这个临界值由负载因子和当前的容量大小来决定:
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITYDEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR
即默认情况下数组长度是160.75=12时,触发扩容操作。
所以使用hash容器时尽量预估自己的数据量来设置初始值。
在理想情况下,使用随机哈希吗,节点出现的频率在hash桶中遵循泊松分布,同时给出了桶中元素的个数和概率的对照表。
从上表可以看出当桶中元素到达8个的时候,概率已经变得非常小,也就是说用0.75作为负载因子,每个碰撞位置的链表长度超过8个是几乎不可能的。
hash容器指定初始容量尽量为2的幂次方。
HashMap负载因子为0.75是空间和时间成本的一种折中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer>{
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
super(capacity, 0.75F, true);
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
return super.getOrDefault(key, -1);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
super.put(key, value);
}
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) {
return size() > capacity;
}
}
|