1.概念
两个或多个进程在执行的过程中,因为竞争资源而造成互相等待的现象
2.Demo
看下面的例子,对概念有个更加清晰的认识。

1 public class DeadLockDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 Object a = new Object(); 6 Object b = new Object(); 7 8 new Thread(new Runnable() { 9 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 synchronized (a) { 13 try { 14 System.out.println("Thread 1 started"); 15 System.out.println("Got the lock of Object a"); 16 Thread.sleep(1000); 17 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 System.out.println("Try to get the lock of Object b"); 21 synchronized (b) { 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 }).start(); 26 27 new Thread(new Runnable() { 28 29 @Override 30 public void run() { 31 synchronized (b) { 32 try { 33 System.out.println("Thread 2 started"); 34 System.out.println("Got the lock of Object b"); 35 Thread.sleep(1000); 36 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } 39 System.out.println("Try to get the lock of Object a"); 40 synchronized (a) { 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 }).start(); 45 } 46 }
我们看代码,能立刻知道具体状况。可是,实际项目里,代码量巨大,运行时,我们如何排查呢?
3.死锁排查
3.1 Jconsole
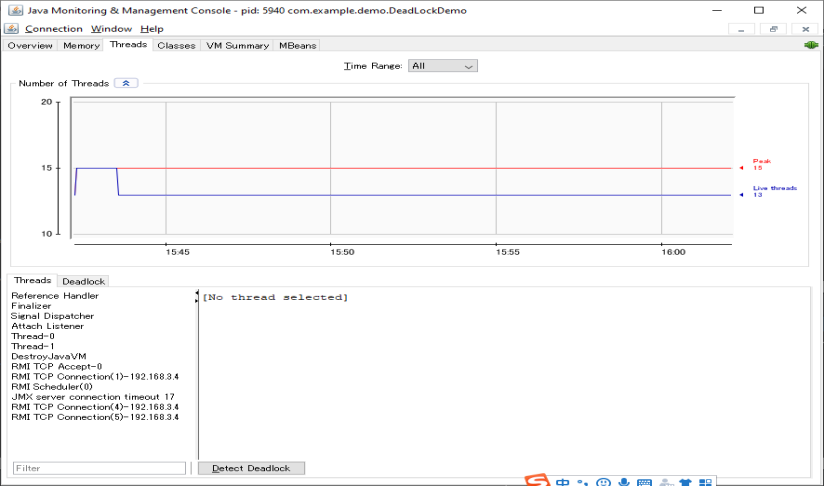
click 【Detect Deadlock】 button and then click【Deadlock】tab to check the Deadlock info.
3.2 jstack
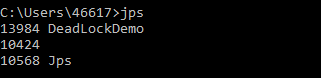
jps查询process id。然后根据id查询stack信息
中间省略。。。
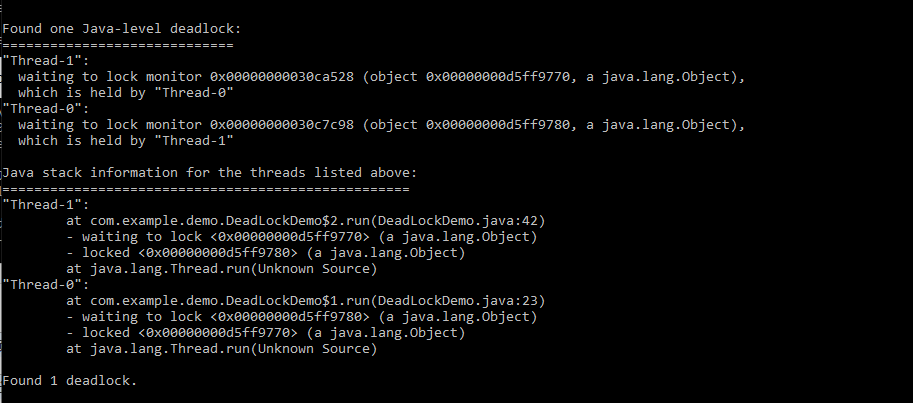
至此,我们学到了如何排查死锁的问题,那么接下来,如何解决死锁的问题呢?
4.死锁产生的四个条件
①互斥量:锁
②自己占用一部分,同时想着占取别人拥有的部分。
③不可蛮力抢占对方的资源
④循环等待
拿最开始的代码的例子来说明。两个线程各自持有一个资源,同时想要拥有对方的资源,但是不能蛮力抢占,只能等到对方放开锁之后,才能去持有,这样就满足了上诉的四个条件,所以,产生了死锁。那么我们,怎么解决死锁的问题呢?
5.解决死锁
只要破坏上诉的任意一个条件即可。
1)使用定时的锁,指定超时时间timeout

1 public class DeadLockDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 ReentrantLock lock1 = new ReentrantLock(); 6 ReentrantLock lock2 = new ReentrantLock(); 7 new Thread(new Runnable() { 8 9 @Override 10 public void run() { 11 lock1.tryLock(); 12 try { 13 System.out.println("Thread 1 started"); 14 System.out.println("Thread 1 Got the lock1"); 15 Thread.sleep(10000); 16 System.out.println("Thread 1 try to get the lock2"); 17 if(lock2.tryLock(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { 18 try { 19 System.out.println("Thread1 : got lock1 and lock2 ..."); 20 } finally { 21 lock2.unlock(); 22 } 23 }; 24 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } finally { 27 lock1.unlock(); 28 } 29 } 30 }).start(); 31 32 new Thread(new Runnable() { 33 34 @Override 35 public void run() { 36 lock2.tryLock(); 37 try { 38 System.out.println("Thread 2 started"); 39 System.out.println("Thread 2 Got the lock2"); 40 Thread.sleep(10000); 41 System.out.println("Thread 2 try to get the lock1"); 42 if(lock1.tryLock(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { 43 try { 44 System.out.println("Thread1 : got lock1 and lock2 ..."); 45 } finally { 46 lock1.unlock(); 47 } 48 }; 49 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } finally { 52 lock2.unlock(); 53 } 54 } 55 }).start(); 56 } 57 58 }
2)按照相同顺序来请求锁

1 public class DeadLockDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 Object a = new Object(); 6 Object b = new Object(); 7 8 new Thread(new Runnable() { 9 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 synchronized (a) { 13 try { 14 System.out.println("Thread 1 started"); 15 System.out.println("Thread 1 Got the lock of Object a"); 16 Thread.sleep(1000); 17 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 synchronized (b) { 21 System.out.println("Thread 1 Got the lock of Object b"); 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 }).start(); 26 27 new Thread(new Runnable() { 28 29 @Override 30 public void run() { 31 synchronized (a) { 32 try { 33 System.out.println("Thread 2 started"); 34 System.out.println("Thread 2 Got the lock of Object a"); 35 Thread.sleep(1000); 36 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } 39 synchronized (b) { 40 System.out.println("Thread 2 Got the lock of Object a"); 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 }).start(); 45 }
