本文主要是说明线程池的几个类的关系。因为有些东西经常搞混。至于线程池的流程,原理,作用等信息,以后想写的时候再追加吧。
1. 线程池相关的类
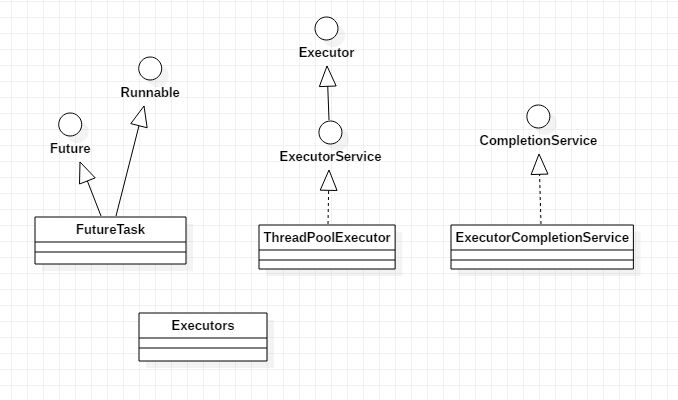
Executor:
只有一个execute(Runnable command)方法;
ExecutorService:
对Executor接口进行了扩展,增加submit(Callable<T> task),关系线程池,执行一组任务等方法。
ExecutorService executor = ...; // 线程池的生成
Executors:
它是一个线程池工厂类,里面提供了多个工开发人员快速使用的线程池,如newFixedThreadPool、newCachedThreadPool、newScheduledThreadPool等,此外它还可以返回一个包装过的ExecutorService,是线程池的配置不可以被更改。(通过调用unconfigurableExecutorService(ExecutorService executor))
TheadPoolExecutor:
创建线程池核心类。或许之前,你创建线程池的时候经常是直接调用Executors的静态方法,但是这个有弊端,你没有明确你对创建的线程池的需求,比如说核心线程数,最大线程数,线程工厂,排队对列等。我们再创建线程池的时候,应该使用TheadPoolExecutor这个类,使用它的构造方法,明确指定线程池配置的核心参数。这一点也是阿里巴巴开发规范手册中提到的。
Runnable、Callable:
为了后面需要,说明一下它们的不同点。
Runnable没有返回值,并且不可以抛出异常;Callable有返回值,并且可以抛出异常。
Future、FutureTask:
线程池提交完任务后,都会返回一个Future。下面,通过代码看一下它们的不同。
1 interface ArchiveSearcher { String search(String target); } 2 class App { 3 ExecutorService executor = ... 4 ArchiveSearcher searcher = ... 5 void showSearch(final String target) 6 throws InterruptedException { 7 Future<String> future 8 = executor.submit(new Callable<String>() { 9 public String call() { 10 return searcher.search(target); 11 }}); 12 displayOtherThings(); // do other things while searching 13 try { 14 displayText(future.get()); // use future 15 } catch (ExecutionException ex) { cleanup(); return; } 16 } 17 }
FutureTask实现了Future接口,它还实现了Runnable接口。上面的构造方法可以用下面的形式进行替换:
1 FutureTask<String> future = 2 new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() { 3 public String call() { 4 return searcher.search(target); 5 }}); 6 executor.execute(future);
(Future和FutureTask的代码,摘自java api 8)
CompletionService、ExecutorCompletionService:
顾名思义,完成服务,它依靠一个单独的Exetuor来执行任务,CompletionService只管理内部完成的队列任务。
我们看下面的示例:
使用ExecutorService
1 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); 2 List<Future> futures = new ArrayList<Future<Integer>>(); 3 futures.add(executorService.submit(A)); 4 futures.add(executorService.submit(B)); 5 futures.add(executorService.submit(C)); 6 futures.add(executorService.submit(D)); 7 8 Then we can iterate over the list to get the computed result of each future: 9 for (Future future:futures) { 10 Integer result = future.get(); // 结果的顺序就是提交的顺序,taskB完成了,但是taskA未完成,那么就会在taskA那里阻塞到完成为止。 11 // rest of the code here. 12 }
使用CompletionService
1 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); 2 CompletionService executorCompletionService= new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executorService ); 3 //Then again we can submit the tasks and get the result like: 4 executorCompletionService.submit(A); 5 executorCompletionService.submit(B); 6 executorCompletionService.submit(C); 7 executorCompletionService.submit(D); 8 9 for (int i=0; i<4; i++) { 10 Integer result = executorCompletionService.take().get(); // 哪个先完成就先获取哪个的结果,跟任务提交顺序无关。 11 // Some processing here 12 }