Infrastructure as Code
https://geekflare.com/infrastructure-as-code-intro/
使用软件开发的原理和实践来实现基础设施的自动化。
写代码来管理 服务器 数据库 网络 日志 应用部署和配置。
Infrastructure as code (IaC) is infrastructure automation using software development principles and practices.
The idea is that you treat your infrastructure like software and then write, test, and execute code to define, deploy, update, and destroy your infrastructure. You write code to manage your servers, databases, networks, logs, application deployment & configuration. When you want to make changes to your infrastructure, you make changes to code, test it, and then apply it to your systems.
WHY
传统使用手动方式管理IT基础设施。
这种方式对于小规模的IT基础设施没有问题,但是对于大规模的情况,就无法接受。
云服务的兴起催生了使用代码来管理基础设施的需求。
Traditionally, if we look back when you wanted a server, you would raise a ticket, and someone from the ops team would create a VM instance or order a physical server. This could be using scripts, point and click, or even manual install.
And then, with every request, there would be more VMs, for DNS, mail, databases, and so on. And then, there were continuous updates to the Operating systems, web servers, JVMs, and everything else. Over time they had slightly different configurations from each other (configuration drift) resulting in snowflake servers. And when something broke, it was a challenge to track what changes were made.
This was still acceptable as long as servers were few and long-lived.
A big change happened with the arrival of cloud service companies like AWS. Many companies, instead of investing in hardware and data centers, started moving their applications to the cloud. And in the cloud, you could deploy a server in minutes, which earlier would take hours or even days.
To maintain optimum performance and availability, you may have to deploy more instances to meet demand. And then later you may have to terminate them to save on costs. As you pay by the hour, you may need to scale up or down every day. Doing this manually, many times a day is clearly challenging.
Capturing the steps required to deploy or terminate instances and other infrastructure components in code enables automation. Automation in cloud and infrastructure provisioning can help deliver value faster and reliably.
Benefits
好处:
自服务--基础设施搭建维护以及使用都可以使用代码的方式满足。
幂等 -- 无论多少次执行, 相对于相同的代码, 生效的环境总是相同的。
消减花费 -- 自动化节省人力维护的成本。
软件快速发布 -- 得益于代码化管理后的自动化过程,修改代码满足需求的变化性。
自备文档 -- 代码即文档
版本控制 -- 如果基础设施有问题, 可以使用回退代码的方式来恢复环境。
验证 测试 -- 使用代码搭建一套非正式环境,是很容易的。
Infrastructure as code offers significant benefits over manual provisioning:
Self-service
As the infrastructure is defined as code, the entire process and deployment can be automated and can be started by anyone in the DevOps team. Users of infrastructure get the resources they need when they need it.
Idempotency
Being idempotent means you define the desired state, and no matter how many times you run the script, the result is the same. It checks the current state and the desired state and only applies the changes which are needed. This can be extremely difficult to achieve with bash scripts.
Tools like Ansible and Terraform have built-in features to make your code idempotent.
Reduced costs
Reduces the time and effort required for provisioning, much less than manual provisioning.
Faster software delivery
Quick provisioning of infrastructure for development, testing, and production results in your ability to deliver software much faster. Since the deployment process is automated, it is also consistent and repeatable.
Self Documenting
The state of the infrastructure is defined in code which is easily readable by anyone.
Version controlled
Traditionally changes to the production systems are considered risky. But then, change is inevitable. You may need to add a new database when you add a new feature. You may need to add new servers or storage to the cluster. Infrastructure as code reduces the effort and risk of making changes to infrastructure.
You can check-in your source files in version control, which means you can track all the changes done to the infrastructure and revert quickly to the previous version if something breaks.
Validation and testing
Infrastructure as code enables testing and applying small changes continuously. As everything is code, you can check for errors using static analysis and automated tests.
Improved security
The shift to infrastructure as code enables you to embed security right from the beginning, and then you can apply changes reliably and safely.
Configuration management vs. provisioning tools
分为配置工具 和 供给工具
供给工具 -- 提供一个全新的环境, 例如虚拟机 或者 容器
配置环境 -- 拿到环境后, 在新环境做配置,和安装软件等
Broadly, tools available fall under two categories –
- Configuration management tools.
- Provisioning tools
Configuration management tools
Configuration management tools are designed to manage users, install and manage software and tools on existing servers. Chef, Puppet, Ansible, and SaltStack are all primarily configuration tools.
You can use configuration management tools to install and update the software on servers.
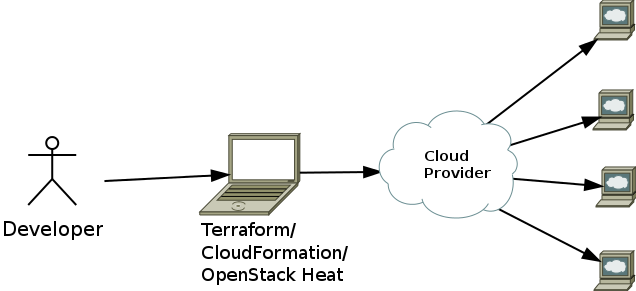
Provisioning tools
Terraform, CloudFormation, OpenStack Heat, on the other hand, are provisioning tools, i.e., used to create servers, database servers, load balancers, queues, subnets, firewalls, and all other components of your infrastructure. These tools make API calls to providers to create the required infrastructure.