一、选择排序
- 选择排序原理:在长度为nd 数组中,找到位置不适合的元素,直接放入最终合适的位置上,也就是依次在未排序数组中找到最小元素,,直到最后一个元素位置(剩下的最后一个元素n-2最大,无需操作)
- 每轮从无序数组中找到的最小数据,依次放入到从data[0]到data[n-2]中;
- 优点:赋值次数少
- 缺点:忽略了数据已经在适合的位置上,不需要交换的情况
public void SelectionSort<T>(T[] datas) where T: IComparable<T> { int mins; int tamp; for (int i = 0, j, index; i < datas.Count() - 1; i++) { mins = datas[i]; index = i; for (j = i; j < datas.Count(); j++) { if (datas[j] < mins) { mins = datas[j]; // 无谓的数据交换,抛弃 index = j; } } tamp = mins; datas[index] = datas[i]; datas[i] = mins; } }
/// <summary> /// 选择排序 :从左到右找到数据中最小的数,进行多次,每次最小的分别与第一,第二...个元素进行直接交换,直到最n-2(最后一次不需要排序) /// </summary> public void SelectionSort<T>(T[] datas) where T: IComparable<T> { if (datas == null) return; for (int i = 0,j,least; i < datas.Count()-1; i++) { for ( j = i+1,least = i; j < datas.Count(); j++) { if (datas[j].CompareTo(datas[least]) < 0) { least = j; } } if (least != i) { Swap(ref datas[i],ref datas[least]); } } }
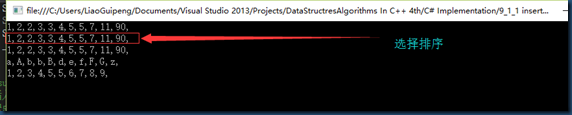
测试数据:
int[] selectionDatas = { 5, 7, 3, 5, 2, 11, 90, 4, 2, 1, 3 }; program.SelectionSort(selectionDatas); DebugExtension.DebugArray(selectionDatas);
排序结果: