题目描述
NEKO#ΦωΦ has just got a new maze game on her PC!
The game's main puzzle is a maze, in the forms of a 2×n2×n rectangle grid. NEKO's task is to lead a Nekomimi girl from cell (1,1)(1,1) to the gate at (2,n)(2,n) and escape the maze. The girl can only move between cells sharing a common side.
However, at some moments during the game, some cells may change their state: either from normal ground to lava (which forbids movement into that cell), or vice versa (which makes that cell passable again). Initially all cells are of the ground type.
After hours of streaming, NEKO finally figured out there are only qq such moments: the ii-th moment toggles the state of cell (ri,ci)(ri,ci) (either from ground to lava or vice versa).
Knowing this, NEKO wonders, after each of the qq moments, whether it is still possible to move from cell (1,1)(1,1) to cell (2,n)(2,n) without going through any lava cells.
Although NEKO is a great streamer and gamer, she still can't get through quizzes and problems requiring large amount of Brain Power. Can you help her?
The first line contains integers nn, qq (2≤n≤1052≤n≤105, 1≤q≤1051≤q≤105).
The ii-th of qq following lines contains two integers riri, cici (1≤ri≤21≤ri≤2, 1≤ci≤n1≤ci≤n), denoting the coordinates of the cell to be flipped at the ii-th moment.
It is guaranteed that cells (1,1)(1,1) and (2,n)(2,n) never appear in the query list.
For each moment, if it is possible to travel from cell (1,1)(1,1) to cell (2,n)(2,n), print "Yes", otherwise print "No". There should be exactly qq answers, one after every update.
You can print the words in any case (either lowercase, uppercase or mixed).
5 5 2 3 1 4 2 4 2 3 1 4
Yes No No No Yes
We'll crack down the example test here:
- After the first query, the girl still able to reach the goal. One of the shortest path ways should be: (1,1)→(1,2)→(1,3)→(1,4)→(1,5)→(2,5)(1,1)→(1,2)→(1,3)→(1,4)→(1,5)→(2,5).
- After the second query, it's impossible to move to the goal, since the farthest cell she could reach is (1,3)(1,3).
- After the fourth query, the (2,3)(2,3) is not blocked, but now all the 44-th column is blocked, so she still can't reach the goal.
- After the fifth query, the column barrier has been lifted, thus she can go to the final goal again.
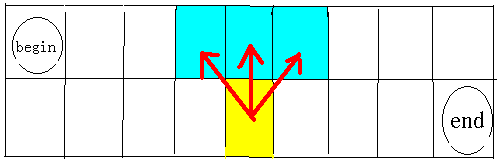
思路分析
我们想要从起点走到终点,必须使得路径上没有任何阻挡。而能够阻挡我们前进的只有三种情况,即;
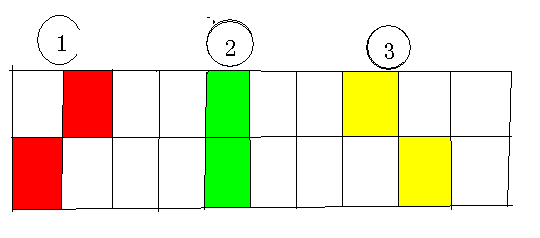
我们可以用cnt来记录所有可以拦截我们的熔岩组数。
当我们接到一个点时,如果它原来不是熔岩,就找一下所有与它相连可能使得道路堵塞的所有点,若加上改点与原来点组成一个可以拦截我们的熔岩组则cnt++;
如果它原来是熔岩,那么就找一下去掉他可以拆除掉的熔岩组数。
如果cnt不等于0,就说明存在可以拦截我们的熔岩组,则输出No;
反之输出Yes即可。
这里关于找与已知点的横坐标相对的横坐标,有两种方法,可以接到横坐标后自减,然后取反,也可以用三减去已知横坐标。算是一个小技巧吧。
这里贴上参考代码。
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 using namespace std; 4 const int N=1e5+100; 5 int a[3][N],x,y; 6 int n,q; 7 int main(){ 8 scanf("%d%d",&n,&q); 9 int cnt=0; 10 int x,y; 11 for(int i=1;i<=q;i++){ 12 scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); 13 if(a[x][y]==0){ 14 a[x][y]=1; 15 for(int i=-1;i<=1;i++){ 16 if(a[3-x][y+i]==1) cnt++; 17 } 18 } 19 else{ 20 a[x][y]=0; 21 for(int i=-1;i<=1;i++){ 22 if(a[3-x][y+i]==1) cnt--; 23 } 24 } 25 if(cnt==0) printf("Yes "); 26 else printf("No "); 27 } 28 return 0; 29 }