- GUI(Graphical User Interface),图形用户接口
- CLI(Command Line User Interface),命令行用户接口
1. 容器 Container
GUI主要位于 java.awt 和 javax.swing 两个包及其子包中
Container 和 Component 是AWT中的两个核心类,Container是Component子类,Container子类对象可以“容纳”别的Component对象。
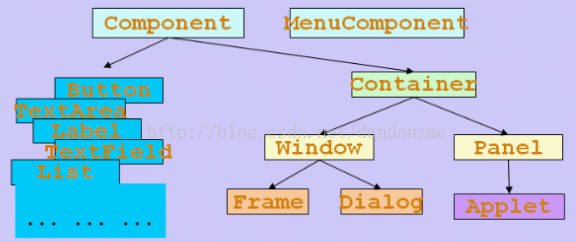
Frame是Window的子类,由Frame或其子类创建的对象为一个窗体。
public static void main(String[] args){ Frame f = new Frame("AwtDemo1"); f.setSize(500, 300); //设置窗体大小(width, high) f.setLocation(300, 200); //设置窗体位置(x, y) //设置Frame显示 f.setVisible(true); }
对于Frame的编程而言,比较常用的方式是继承Frame类,并且在构造函数或者新编写一个函数来设置Frame的信息
public class AwtDemo2 extends Frame{ public AwtDemo2(){ this.setTitle("Awt Demo2"); this.setBounds(500, 300, 300, 200); //x, y, width, height this.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args){ new AwtDemo2(); } }
运行上面代码会生成如下这样一个窗体:
Panel对象可以看成可以容纳Component的空间,可以拥有自己的布局管理器。
2. 组件 Component
代码1:按钮、标签、复选框 、下拉列表等组件
public class ComponentDemo1 extends Frame{ public static void main(String[] args){ new ComponentDemo1(); } public ComponentDemo1(){ //标签Label,第一个参数是标题,第二个参数是排列方式 this.add(new Label("姓名", Label.LEFT)); //文本框,第一个参数是标题,第二个参数是长度 TextField tf = new TextField ("小明", 15); this.add(tf); //文本域TextArea,第一参数是行数,第二个参数是列数 TextArea ta = new TextArea (2, 25); ta.setText ("你好!"); //设置默认内容 this.add(ta); //复选框Checkbox,第一个参数是名称,第二参数可选,表示是否选中状态 Checkbox cb1 = new Checkbox ("系统管理员"); Checkbox cb2 = new Checkbox ("用户", true); Checkbox cb3 = new Checkbox ("过客", true); //将复选框添加到复选框组里,就变成单选框 CheckboxGroup g = new CheckboxGroup(); cb1.setCheckboxGroup (g); cb2.setCheckboxGroup (g); cb3.setCheckboxGroup (g); //setBounds 移动组件并调整其大小。 cb1.setBounds (20,60,140,20); cb2.setBounds (20,80,140,20); cb3.setBounds (20,100,140,20); this.add(cb1); this.add(cb2); this.add(cb3); //下拉列表Choice Choice choice = new Choice(); choice.add("英语"); choice.add("法语"); choice.add("德语"); this.add(choice); //列表List,可以多选 List list = new List(3, true); list.add("大学物理"); list.add("数据结构"); list.add("计算机网络"); this.add(list); this.setTitle("AWT组件库Component演示1"); this.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); this.setBounds(200, 200, 400, 200); this.setVisible(true); } }
运行结果:

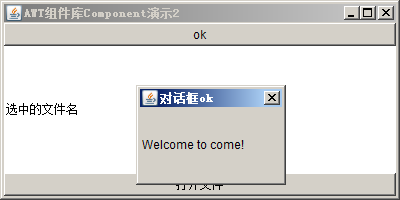
代码2:对话框和文件对话框
public class ComponentDemo2 extends Frame{ public static void main(String[] args){ new ComponentDemo2(); } public ComponentDemo2(){ this.setTitle("AWT组件库Component演示2"); this.setBounds(200, 200, 400, 200); final Label fileLabel = new Label("选中的文件名"); this.add(fileLabel, BorderLayout.CENTER); //默认是BorderLayout //对话框Dialog,第一参数是父窗口,第二参数是标题,第三个参数表示是否显示 final Dialog dialog = new Dialog(this, "对话框ok", false); Label label = new Label("Welcome to come!"); dialog.add(label); dialog.setBounds(300, 300, 150, 100); dialog.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){ dialog.setVisible(false); } }); //按钮Button,第一参数是名称 Button btn = new Button("ok"); btn.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){ public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ dialog.setVisible(true); } }); this.add(btn, BorderLayout.NORTH); //文件对话框FileDialog,第1个参数是父窗口,第2个参数是标题,第3个参数是文件对话框的作用是打开还是保存 final FileDialog fileDialog = new FileDialog(this, "打开文件", FileDialog.LOAD); fileDialog.setBounds(300, 300, 150, 100); Button btn2 = new Button("打开文件"); btn2.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){ public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ fileDialog.setVisible(true); String dir = fileDialog.getDirectory(); String file = fileDialog.getFile();//获取选中的文件名称 fileLabel.setText(dir + "" + file); } }); this.add(btn2, BorderLayout.SOUTH); this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){ System.exit(0); } }); this.setVisible(true); } }
运行结果:
3. 布局管理器 Layout
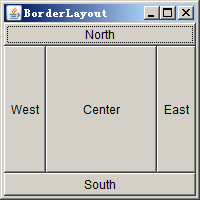
下面这窗体中的组件太乱了,有什么办法让他们变的整齐一些吗?使用布局管理器可以达到布局整齐的效果!

三种布局管理器:
- BorderLayout
- FlowLayout
- GridLayout
简单的代码说明:
1 public class LayoutDemo1 extends Frame{ 2 public static void main (String args[]) { 3 new LayoutDemo1(args[0]); 4 } 5 6 public LayoutDemo1(String layout){ 7 this.setTitle(layout); 8 this.setBounds(300, 200, 200, 200); 9 this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){ 10 public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){ 11 System.exit(0); 12 super.windowClosing(e); 13 } 14 }); 15 16 switch(layout){ 17 case "BorderLayout" : 18 addBorderLayout(); 19 break; 20 case "FlowLayout" : 21 addFlowLayout(); 22 break; 23 case "GridLayout" : 24 addGridLayout(); 25 break; 26 default: 27 addBorderLayout(); 28 break; 29 } 30 this.setVisible(true); 31 } 32 public void addBorderLayout(){ 33 this.setLayout(new BorderLayout()); 34 this.add(new Button("North"), BorderLayout.NORTH); 35 this.add(new Button("South"), BorderLayout.SOUTH); 36 this.add(new Button("East"), BorderLayout.EAST); 37 this.add(new Button("West"), BorderLayout.WEST); 38 this.add(new Button("Center"), BorderLayout.CENTER); 39 } 40 public void addFlowLayout(){ 41 this.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); 42 this.add(new Button("Button1")); 43 this.add(new Button("Button2")); 44 this.add(new Button("Button3")); 45 this.add(new Button("Button4")); 46 } 47 public void addGridLayout(){ 48 //new GridLayout(3,2) 构造一个3行2列的网格 49 setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2)); 50 add(new Button("1")); 51 add(new Button("2")); 52 add(new Button("3")); 53 add(new Button("4")); 54 add(new Button("5")); 55 add(new Button("6")); 56 57 } 58 }
运行结果:


4. 菜单
简单的菜单演示:
class MenuDemo1 extends Frame{ private MenuBar menuBar; private Menu menu, secondLevelMenu; private MenuItem exitItem,subItem; MenuDemo1(){ this.setTitle("MenuDemo1"); this.setBounds(200,200,500,400); //setBounds(x, y, width, high) //菜单栏 menuBar = new MenuBar(); //一级菜单 menu = new Menu("文件"); //二级菜单 secondLevelMenu = new Menu("新建"); //子菜单 exitItem = new MenuItem("退出"); subItem = new MenuItem("Java文件"); secondLevelMenu.add(subItem); menu.add(secondLevelMenu); menu.add(exitItem); menuBar.add(menu); //添加菜单栏 this.setMenuBar(menuBar); this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){ public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){ System.exit(0); } }); this.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args){ new MenuDemo1(); } }
运行结果:
