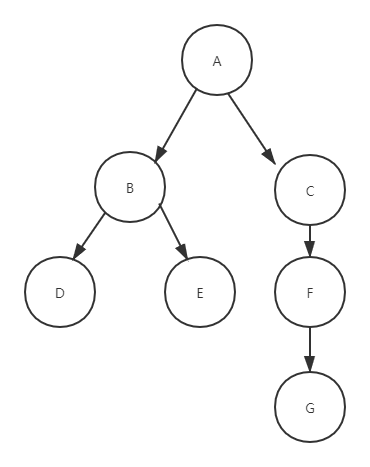
树如图所示:
方法一:用递归的方法,思路清晰但效率很慢并且不灵活:
思路:递归查询,使用深度优先算法,第一遍找A-->B-->D,将D加到B中,再找B->E,将E加到B中,然后将B加到A中,然后找到A-->C-->F-->G,将G加到F中,将F加到C中,将C加到A中。
1 /** 2 * 递归生成树 3 * 方法详细描述 4 * 5 * @author 龙谷情 6 * @date 2021/3/31 17:47 7 * @param [list, pid, idNm, pidNm] 要处理的集合,很节点的父级id,id的键名,父级id的键名 8 * @return java.util.List<java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Object>>[返回类型说明] 9 * @exception/throws [异常类型] [异常说明] 10 * @since [v1.0] 11 */ 12 public static List<Map<String, Object>> getTreeRecursion(List<Map<String, Object>> list, String pid, String idNm, String pidNm) { 13 List<Map<String, Object>> res = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>(); 14 if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(list)) { 15 for (Map<String, Object> map : list) { 16 if ((pid == null && map.get(pidNm) == null) || (map.get(pidNm) != null && map.get(pidNm).equals(pid))) { 17 String id = (String) map.get(idNm); 18 map.put("children", getTreeRecursion(list, id, idNm,pidNm)); 19 res.add(map); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 return res; 24 }
方法二:通过具体的地址索引进行生成,不用多次对list进行循环查询,效率较高
思路:遍历list,将每个节点的父级id作为key,value是一个数组,保存自己和有相同父级id的其他节点,假设此map为treeNoteListMap,如果是根节点,保存到一个map中,设为tree,如果不是,则继续往下进行,查询treeNoteListMap中的key和此节点id相同的数组元素,将这个元素添加到这个节点下,如果没有,添加一个空的数组,遍历一遍,即可通过索引将树生成
/** * 不通过递归进行查询 * 方法详细描述 * * @author 赵学壮 * @date 2021/3/31 17:56 * @param [rootId, noteList, pidName, idName] 根节点id,待处理集合,id的键名,父级id的键名 * @return java.util.Map[返回类型说明] * @exception/throws [异常类型] [异常说明] * @since [v1.0] */ private static Map getTree(String rootId, List<Map<String, Object>> noteList,String pidName,String idName) { Map tree = null; Map<String,List<Map<String,Object>>> treeNoteListMap = new HashMap<>(16); for (Map<String,Object> note:noteList){ if (rootId.equals(note.get(idName))){ tree = note; } if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(note.get(pidName).toString())){ List<Map<String,Object>> mapList = treeNoteListMap.get(note.get(pidName).toString()); if (null==mapList){ mapList = new ArrayList<>(); } mapList.add(note); treeNoteListMap.put(note.get(pidName).toString(),mapList); } if (null == treeNoteListMap.get(note.get(idName))){ treeNoteListMap.put(note.get(idName).toString(),new ArrayList<>()); } note.put("children",treeNoteListMap.get(note.get(idName))); } return tree; }
测试:
一:小数据测试:
测试代码如下:

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 String inId = "ida"; 3 List<Map<String,Object>> noteList = new ArrayList<>(); 4 Map<String,Object> note0 = new HashMap<>(16); 5 note0.put("id","ida"); 6 note0.put("pid",""); 7 note0.put("name","A"); 8 noteList.add(note0); 9 10 Map<String,Object> note1 = new HashMap<>(16); 11 note1.put("id","idb"); 12 note1.put("pid","ida"); 13 note1.put("name","B"); 14 noteList.add(note1); 15 16 Map<String,Object> note2 = new HashMap<>(16); 17 note2.put("id","idc"); 18 note2.put("pid","ida"); 19 note2.put("name","C"); 20 noteList.add(note2); 21 22 Map<String,Object> note5 = new HashMap<>(16); 23 note5.put("id","idf"); 24 note5.put("pid","idc"); 25 note5.put("name","F"); 26 noteList.add(note5); 27 28 Map<String,Object> note6 = new HashMap<>(16); 29 note6.put("id","idg"); 30 note6.put("pid","idf"); 31 note6.put("name","G"); 32 noteList.add(note6); 33 34 Map<String,Object> note3 = new HashMap<>(16); 35 note3.put("id","idd"); 36 note3.put("pid","idb"); 37 note3.put("name","D"); 38 noteList.add(note3); 39 40 Map<String,Object> note4 = new HashMap<>(16); 41 note4.put("id","ide"); 42 note4.put("pid","idb"); 43 note4.put("name","E"); 44 noteList.add(note4); 45 46 47 Long l1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 48 Map tree = getTree(inId,noteList,"pid","id"); 49 Long l2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 50 System.out.println(l2-l1); 51 JSONObject object = new JSONObject(tree); 52 System.out.println(object); 53 54 55 Long l3 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 56 List<Map<String, Object>> treeRecursionList = getTreeRecursion(noteList,"","id","pid"); 57 Long l4 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 58 System.out.println(l4-l3); 59 JSONObject objectRecursion = new JSONObject(treeRecursionList.get(0)); 60 System.out.println(objectRecursion); 61 }
将获得的json结果格式化得到:
{
"children": [{
"children": [{
"children": [],
"name": "D",
"pid": "idb",
"id": "idd"
}, {
"children": [],
"name": "E",
"pid": "idb",
"id": "ide"
}],
"name": "B",
"pid": "ida",
"id": "idb"
}, {
"children": [{
"children": [{
"children": [],
"name": "G",
"pid": "idf",
"id": "idg"
}],
"name": "F",
"pid": "idc",
"id": "idf"
}],
"name": "C",
"pid": "ida",
"id": "idc"
}],
"name": "A",
"pid": "",
"id": "ida"
}
