参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/8719520.html
一、实现登录验证
1.创建User和Token表
User表用作用户名密码认证,Token表用于存放用户每次成功登陆后的随机Token。
在models.py中添加以下两张表:
# 用户表 class User(models.Model): username = models.CharField(max_length=32) password = models.CharField(max_length=32) # token表 class Token(models.Model): user = models.OneToOneField("User", on_delete=models.CASCADE) token = models.CharField(max_length=128)
执行命令,生成数据库表:
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
2.实现登录验证操作
添加路由条目:
urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), re_path('^publishes/$', views.PublishView.as_view(), name="publish"), re_path('^publishes/(?P<pk>d+)/$', views.PublishDetailView.as_view(), name="publishdetail"), re_path('^books/$', views.BookView.as_view(), name="book"), re_path('^books/(?P<pk>d+)/$', views.BookDetailView.as_view(), name="bookdetail"), re_path('^authors/$', views.AuthorViewSet.as_view({"get": "list", "post": "create"}), name="author"), re_path('^authors/(?P<pk>d+)/$', views.AuthorViewSet.as_view( {"get": "retrieve", "put": "update", "patch": "partial_update", "delete": "destroy"}), name="authordetail"), re_path('^login/$', views.LoginView.as_view(), name="login"), ]
实现视图类LoginView:
# 导入User和Token的model类 from .models import User from .models import Token # 生成一个随机token,username和ctime的MD5加密值 def get_random_str(user): import hashlib import time # 获取当前时间 ctime = str(time.time()) # username的md5 md5 = hashlib.md5(bytes(user, encoding='utf-8')) # 加上ctime md5.update(bytes(ctime, encoding='utf-8')) return md5.hexdigest() class LoginView(APIView): def post(self, request): res = {'code': 1000, "msg": None} try: # 从post请求中获取用户提交的用户名和密码 username = request.data.get("username") password = request.data.get("password") # 判断数据库中的数据是否匹配 user_obj = User.objects.filter(username=username, password=password).first() # 如果不匹配,返回登录失败 if not user_obj: res['code'] = 1001 res['msg'] = "用户名或密码错误" else: # 如果匹配,则生成一个随机token token = get_random_str(username) # 如果token已经存在,则更新,如果不存在,则创建 Token.objects.update_or_create(user=user_obj, defaults={'token': token}) res["token"] = token except Exception as e: res['code'] = 1002 res['msg'] = e return HttpResponse(json.dumps(res))
二、实现token认证
1.实现token认证
要实现认证,只需要在需要认证的视图类中添加 authentication_classes 列表。restframe认证组件会自动去该列表中寻找认证使用的类(类由我们来定义)。例如BookView视图类中:
class BookView(APIView): authentication_classes = [TokenAuth,] pass
查看restframework调用authentication_classes中类的源码,可以看到TokenAuth中必须实现 authenticate方法,以及 authenticate_header 方法:
class TokenAuth(object): # 认证token过程 def authenticate(self, request): token = request.GET.get("token") token_obj = Token.objects.filter(token=token).first() if not token_obj: raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed("验证失败") return (token_obj.user, token_obj) def authenticate_header(self, request): return None
或者,继承 BaseAuthentication也可以:
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication class TokenAuth(BaseAuthentication): # 认证token过程 def authenticate(self, request): token = request.GET.get("token") token_obj = Token.objects.filter(token=token).first() if not token_obj: raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed("验证失败") return (token_obj.user, token_obj)
然后应用于BookView:
class BookView(APIView): authentication_classes = [TokenAuth] def get(self, request): book_list = Book.objects.all() bs = BookModelSerializers(book_list, many=True, context={'request': request}) return Response(bs.data) def post(self, request): bs = BookModelSerializers(data=request.data) if bs.is_valid(): bs.save() return Response(bs.data) else: return Response(bs.errors)
这样,我们想要通过GET请求获取book数据的时候,就需要先访问login页面,获取token,然后在GET请求中附带token,才能正确获取book数据:
2.测试
POST请求访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/,附带用户名和密码,进行登录验证:
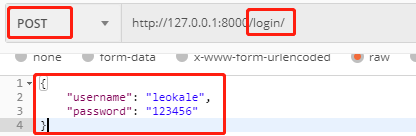
获得返回值:
{"code": 1000, "msg": null, "token": "91dc33a308cd4e8b04e14bb3d23d492b"}
然后GET请求访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?token=91dc33a308cd4e8b04e14bb3d23d492b:

获得返回结果:
[{"id":8,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"Python2标准库3","price":99,"pub_date":"2012-11-20T13:03:33Z","authors":[1,2]},{"id":9,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"Python2标准库4","price":99,"pub_date":"2012-11-20T13:03:33Z","authors":[1,2]},{"id":10,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"Python2标准库5","price":99,"pub_date":"2012-11-20T13:03:33Z","authors":[1,2]},{"id":11,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"Python2标准库6","price":99,"pub_date":"2012-11-20T13:03:33Z","authors":[1,2]},{"id":12,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"Python2标准库7","price":99,"pub_date":"2012-11-20T13:03:33Z","authors":[1,2]},{"id":13,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"Python2标准库","price":99,"pub_date":"2012-11-20T13:03:33Z","authors":[1,2]},{"id":14,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"Python3","price":99,"pub_date":"2020-01-20T13:03:04Z","authors":[3]},{"id":15,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"JAVA","price":99,"pub_date":"2020-01-20T13:03:04Z","authors":[3]},{"id":16,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"JAVA","price":99,"pub_date":"2020-01-20T13:03:04Z","authors":[3]},{"id":17,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"JAVA","price":99,"pub_date":"2020-01-20T13:03:04Z","authors":[3]},{"id":18,"publish":"http://127.0.0.1:8000/publishes/1/","title":"hello","price":99,"pub_date":"2020-01-20T13:03:04Z","authors":[3]}]
如果未携带token,或携带的token错误:
返回结果:
{"detail":"验证失败"}
三、restframework配置
1.引子
在第二节中,我们实现了token的生成和认证,在认证时,我们使用自定义的TokenAuth类来进行认证,但是如果在每个视图类中都加上 authentication_classes 列表,比较冗余。
我们观察restframe的源码,可以看到,当我们不添加 authentication_classes 列表变量时,APIView中 authentication_classes 变量会读取一个默认值:
class APIView(View): # The following policies may be set at either globally, or per-view. renderer_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES parser_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES throttle_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES ... ...
继续查看api_settings所属类的源码:
class APISettings: def __init__(self, user_settings=None, defaults=None, import_strings=None): if user_settings: self._user_settings = self.__check_user_settings(user_settings) self.defaults = defaults or DEFAULTS self.import_strings = import_strings or IMPORT_STRINGS self._cached_attrs = set() ... ...
这里的DEFAULTS就是restframework的默认配置:

DEFAULTS = { # Base API policies 'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': [ 'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer', 'rest_framework.renderers.BrowsableAPIRenderer', ], 'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES': [ 'rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser', 'rest_framework.parsers.FormParser', 'rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser' ], 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [ 'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication', 'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication' ], 'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [ 'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny', ], 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': [], 'DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.negotiation.DefaultContentNegotiation', 'DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.metadata.SimpleMetadata', 'DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS': None, # Generic view behavior 'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': None, 'DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS': [], # Schema 'DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.schemas.openapi.AutoSchema', # Throttling 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': { 'user': None, 'anon': None, }, 'NUM_PROXIES': None, # Pagination 'PAGE_SIZE': None, # Filtering 'SEARCH_PARAM': 'search', 'ORDERING_PARAM': 'ordering', # Versioning 'DEFAULT_VERSION': None, 'ALLOWED_VERSIONS': None, 'VERSION_PARAM': 'version', # Authentication 'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': 'django.contrib.auth.models.AnonymousUser', 'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None, # View configuration 'VIEW_NAME_FUNCTION': 'rest_framework.views.get_view_name', 'VIEW_DESCRIPTION_FUNCTION': 'rest_framework.views.get_view_description', # Exception handling 'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'rest_framework.views.exception_handler', 'NON_FIELD_ERRORS_KEY': 'non_field_errors', # Testing 'TEST_REQUEST_RENDERER_CLASSES': [ 'rest_framework.renderers.MultiPartRenderer', 'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer' ], 'TEST_REQUEST_DEFAULT_FORMAT': 'multipart', # Hyperlink settings 'URL_FORMAT_OVERRIDE': 'format', 'FORMAT_SUFFIX_KWARG': 'format', 'URL_FIELD_NAME': 'url', # Input and output formats 'DATE_FORMAT': ISO_8601, 'DATE_INPUT_FORMATS': [ISO_8601], 'DATETIME_FORMAT': ISO_8601, 'DATETIME_INPUT_FORMATS': [ISO_8601], 'TIME_FORMAT': ISO_8601, 'TIME_INPUT_FORMATS': [ISO_8601], # Encoding 'UNICODE_JSON': True, 'COMPACT_JSON': True, 'STRICT_JSON': True, 'COERCE_DECIMAL_TO_STRING': True, 'UPLOADED_FILES_USE_URL': True, # Browseable API 'HTML_SELECT_CUTOFF': 1000, 'HTML_SELECT_CUTOFF_TEXT': "More than {count} items...", # Schemas 'SCHEMA_COERCE_PATH_PK': True, 'SCHEMA_COERCE_METHOD_NAMES': { 'retrieve': 'read', 'destroy': 'delete' }, }
前面代码中,使用 api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES ,api_settings没有这个属性,所以会自动调用 APISettings 的__getattr__()方法:
def __getattr__(self, attr): if attr not in self.defaults: raise AttributeError("Invalid API setting: '%s'" % attr) try: # Check if present in user settings val = self.user_settings[attr] except KeyError: # Fall back to defaults val = self.defaults[attr] # Coerce import strings into classes if attr in self.import_strings: val = perform_import(val, attr) # Cache the result self._cached_attrs.add(attr) setattr(self, attr, val) return val
__getattr__()方法先判断DEFAULTS中是否存在 DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES ,如果不存在则报错。然后去user_settings中获取 DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES 的值,user_settings是一个属性方法:
@property def user_settings(self): if not hasattr(self, '_user_settings'): self._user_settings = getattr(settings, 'REST_FRAMEWORK', {}) return self._user_settings
这段代码会先去django的settings中查看是否存在名为"REST_FRAMEWORK"的配置项。所以我们要使用自定义的认证类,可以在django的settings中配置REST_FRAMEWORK来指定。
首先,将TokenAuth类从views.py移到单独的一个模块,例如utils.py:
# utils.py from rest_framework import exceptions from .models import Token from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication class TokenAuth(BaseAuthentication): # 认证token过程 def authenticate(self, request): token = request.GET.get("token") token_obj = Token.objects.filter(token=token).first() if not token_obj: raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed("验证失败") return (token_obj.user, token_obj)
然后在django的settings中添加配置:
REST_FRAMEWORK = { "DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": ["demo.utils.TokenAuth"] }
这样,我们的所有视图类在被访问时都会使用TokenAuth类来对token进行验证,但是在访问/login/页面时,由于还没有登录认证,所以不能进行token验证。
可以在LoginView视图类中,加上一个空的 authentication_classes 列表来处理:
class LoginView(APIView): authentication_classes = [] ... ...
这样,访问/login/的时候不会验证token,而访问其他资源的时候会验证token。
ღ♋
