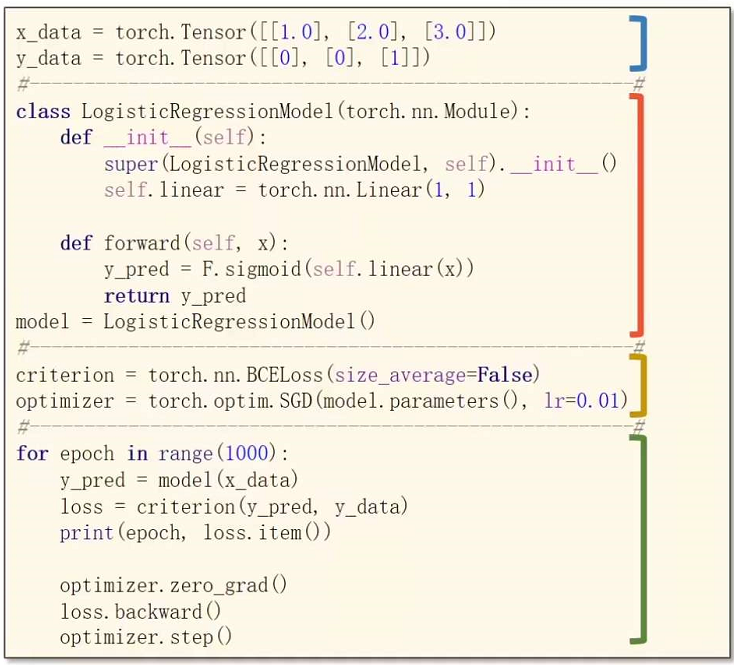
用Pytorch写一个神经网络的步骤:
- Prepare dataset
- Design model using Class (inherit from nn.Module)
- Construct loss and optimizer (using Pytorch API)
- Training cycle (forward, backward, update)
For example:
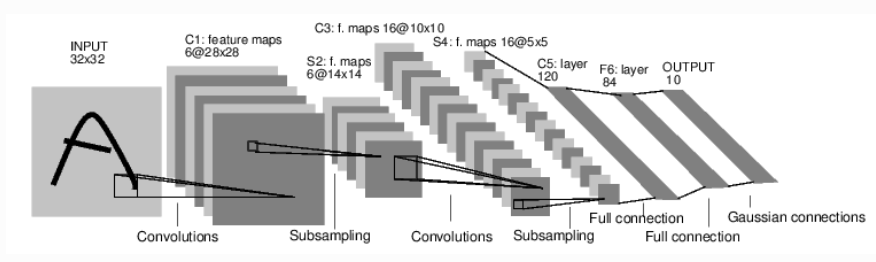
具体案例1:MNIST, 手写数字识别。数据集的简介,以及识别网络:

1)导入数据:totchvision 的包,该包含有支持加载类似Imagenet,CIFAR10,MNIST 等公共数据集的数据加载模块 torchvision.datasets 和支持加载图像数据数据转换模块 torch.utils.data.DataLoader。
batch_size = 512 # step1. load dataset train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( torchvision.datasets.MNIST('mnist_data', train=True, download=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.Compose([ torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), torchvision.transforms.Normalize( (0.1307,), (0.3081,)) ])), batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True) test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( torchvision.datasets.MNIST('mnist_data/', train=False, download=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.Compose([ torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), torchvision.transforms.Normalize( (0.1307,), (0.3081,)) ])), batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) # 显示一张图片 x, y = next(iter(train_loader)) print(x.shape, y.shape, x.min(), x.max()) plot_image(x, y, 'image sample')
2)搭建网络
class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net, self).__init__() # xw+b self.fc1 = nn.Linear(28*28, 256) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 64) self.fc3 = nn.Linear(64, 10) def forward(self, x): # x: [b, 1, 28, 28] # h1 = relu(xw1+b1) x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) # h2 = relu(h1w2+b2) x = F.relu(self.fc2(x)) # h3 = h2w3+b3 x = self.fc3(x) return x
3)定义loss和optimizer
net = Net() # [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3] optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.9) criterion = nn.MSELoss()
4) 训练
for epoch in range(3): for batch_idx, (x, y) in enumerate(train_loader): # x: [b, 1, 28, 28], y: [512] # [b, 1, 28, 28] => [b, 784] x = x.view(x.size(0), 28*28) # => [b, 10] out = net(x) # [b, 10] y_onehot = one_hot(y) # loss = mse(out, y_onehot) loss = criterion(out, y_onehot) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() # w' = w - lr*grad optimizer.step()
具体案例2:ResNet 实现CIFAR10数据集分类任务,链接
import torch from torch import nn from torch.nn import functional as F class ResBlk(nn.Module): """ resnet block """ def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out, stride=1): """ :param ch_in: :param ch_out: :param stride: """ super(ResBlk, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(ch_in, ch_out, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(ch_out, ch_out, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out) self.extra = nn.Sequential() if ch_in != ch_out: self.extra = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(ch_in, ch_out, kernel_size=1, stride=stride), nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out) ) def forward(self, x): """ :param x: :return: """ out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out)) out = out+self.extra(x) out = F.relu(out) return out class ResNet18(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(ResNet18, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=3, padding=0), nn.BatchNorm2d(64) ) self.blk1 = ResBlk(64, 128, stride=2) self.blk2 = ResBlk(128, 256, stride=2) self.blk3 = ResBlk(256, 512, stride=2) self.blk4 = ResBlk(512, 512, stride=2) self.outlayer = nn.Linear(512*1*1, 10) def forward(self, x): """ :param x: :return: """ x = F.relu(self.conv1(x)) x = self.blk1(x) x = self.blk2(x) x = self.blk3(x) x = self.blk4(x) x = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, [1, 1]) x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) x = self.outlayer(x) return x def main(): blk = ResBlk(64, 128, stride=2) temp = torch.randn(2, 64, 32, 32) out = blk(temp) print(out.shape) x = torch.randn(2, 3, 32, 32) model = ResNet18() out = model(x) print('resnet:', out.shape) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
import torch from torch.utils.data import DataLoader from torchvision import datasets from torchvision import transforms from torch import nn, optim #from lenet5 import lenet5 from resnet import ResNet18 def main(): batchsz=32 cifar_train = datasets.CIFAR10('CIFAR',train= True,download=True, transform=transforms.Compose([ transforms.Resize(32,32), transforms.ToTensor() ])) cifar_train=DataLoader(cifar_train,batch_size=batchsz, shuffle=True) cifar_test = datasets.CIFAR10('CIFAR',train= False,download=True, transform=transforms.Compose([ transforms.Resize(32,32), transforms.ToTensor() ])) cifar_test=DataLoader(cifar_test,batch_size=batchsz, shuffle=True) x, label= iter(cifar_train).next() print('x:',x.shape,'label:',label.shape) device = torch.device('cuda') #使用GPU加速, 需要将网络和数据加载到GPU上 # model= lenet5().to(device) model = ResNet18().to(device) criteon = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3) print(model) for epoch in range(1000): model.train() for batchidx, (x, label) in enumerate(cifar_train): # [b, 3, 32, 32] # [b] x, label = x.to(device), label.to(device) logits = model(x) loss = criteon(logits, label) #backprop optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() # print(epoch, loss.item()) model.eval() with torch.no_grad(): #test total_correct =0 total_num =0 for x, label in cifar_test: x, label= x.to(device), label.to(device) logits = model(x) pred = logits.argmax(dim=1) total_correct += torch.eq(pred, label).float().sum().item() total_num +=x.size(0) acc = total_correct/total_num print(epoch, acc) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
判断时候可以有GPU使用:
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
数据并行处理:model = nn.DataParallel(model) #并行化
import torch from torch import nn from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset input_size = 5 output_size = 2 batch_size = 30 data_size = 100 ###################################################################### # Dummy DataSet # ------------- # # Make a dummy (random) dataset. You just need to implement the # getitem # device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") class RandomDataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, size, length): self.len = length self.data = torch.randn(length, size) def __getitem__(self, index): return self.data[index] def __len__(self): return self.len rand_loader = DataLoader(dataset=RandomDataset(input_size, data_size),batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True) class Model(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, output_size): super(Model, self).__init__() self.fc = nn.Linear(input_size, output_size) def forward(self, input): output = self.fc(input) print(" In Model: input size", input.size(), "Output size:", output.size()) return output ###################################################################### # Create Model and DataParallel # ----------------------------- # # This is the core part of the tutorial. First, we need to make a model instance # and check if we have multiple GPUs. If we have multiple GPUs, we can wrap # our model using ``nn.DataParallel``. Then we can put our model on GPUs by # ``model.to(device)`` # model = Model(input_size, output_size) if torch.cuda.device_count() >=1: print("Let's use", torch.cuda.device_count(), "GPUs.") model = nn.DataParallel(model) #并行化 model.to(device) def main(): for data in rand_loader: input = data.to(device) output = model(input) print("Outside: input size", input.size(), "output_size", output.size()) if __name__ == '__main__': main()