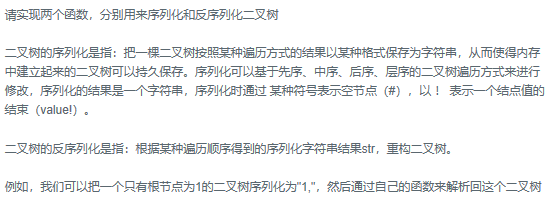
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
String Serialize(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
StringBuilder result=new StringBuilder();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
/* 这种层序不是完全二叉树,只是将每一层的结点串联起来,不包含空结点
int size=queue.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
result.append(node.val+",");
if(node.left!=null)
queue.offer(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.offer(node.right);
}
*/
//可以在队列中添加null的空结点
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
if(node!=null)
{
queue.offer(node.left);
queue.offer(node.right);
result.append(node.val+",");
}
else
{
result.append("#"+",");
}
}
if(result.length()!=0)
result.deleteCharAt(result.length()-1);
return result.toString();
}
TreeNode Deserialize(String str) {
TreeNode head =null;
if(str==null || str.length()==0)
return head;
String[] nodes=str.split(",");
TreeNode[] treenodes=new TreeNode[nodes.length];
for(int i=0;i<nodes.length;i++)
{
if(!nodes[i].equals("#"))
{
treenodes[i]=new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(nodes[i]));
}
}
for(int i=0,j=1;j<treenodes.length;i++)
{
if(treenodes[i]!=null)
{
treenodes[i].left=treenodes[j++];
treenodes[i].right=treenodes[j++];
}
}
return treenodes[0];
}
}
/*
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
//根据前序遍历规则完成序列化与反序列化
//算法思想:根据前序遍历规则完成序列化与反序列化。所谓序列化指的是遍历二叉树为字
//符串;所谓反序列化指的是依据字符串重新构造成二叉树。 依据前序遍历序列来序列化
//二叉树,因为前序遍历序列是从根结点开始的。当在遍历二叉树时碰到Null指针时,这些
//Null指针被序列化为一个特殊的字符“#”。 另外,结点之间的数值用逗号隔开。
public class Solution {
String Serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder res=new StringBuilder();
if(root==null)
{
res.append("#,");
return res.toString();
}
res.append(root.val+",");
res.append(Serialize(root.left));
res.append(Serialize(root.right));
return res.toString();
}
int index=-1;
TreeNode Deserialize(String str) {
index++;
String[] strr=str.split(",");
TreeNode node=null;
if(!strr[index].equals("#"))
{
node=new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(strr[index]));
node.left=Deserialize(str);
node.right=Deserialize(str);
}
return node;
}
}

/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
if(root1==null || root2==null)
{
return false;
}
if(root1.val==root2.val)
{
if(judge(root1,root2))
return true;
}
return HasSubtree(root1.left,root2) || HasSubtree(root1.right, root2);
}
public boolean judge(TreeNode root, TreeNode subtree)
{
if(subtree==null)
return true;
if(root==null)
return false;
if(root.val==subtree.val)
return judge(root.left, subtree.left)&&judge(root.right,subtree.right);
return false;
}
}

/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return 0;
//int left=TreeDepth(root.left);
//int right=TreeDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(TreeDepth(root.left)+1,TreeDepth(root.right)+1);
}
}

/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return;
else{
TreeNode node =root.left;
root.left=root.right;
root.right=node;
}
Mirror(root.left);
Mirror(root.right);
}
}
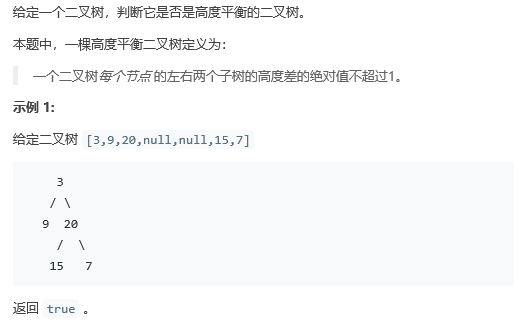
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return Math.abs(depth(root.left) - depth(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
private int depth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(depth(root.left), depth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
 二叉搜索树的中序遍历就是递增序列
二叉搜索树的中序遍历就是递增序列
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
public int kthLargest(TreeNode root, int k) {
if(root==null)
return 0;
inOrder(root);
return(list.get(list.size()-k));
}
public void inOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root!=null){
inOrder(root.left);
list.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}
}
}

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return 0;
int left=maxDepth(root.left);
int right=maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left,right)+1;
}
}




 二叉搜索树的中序遍历就是递增序列
二叉搜索树的中序遍历就是递增序列
