题目:用两个栈实现一个队列,用两个队列实现一个栈。
首先要了解栈和队列这两种数据结构各自的特点,栈是一种后入先出(Last In First Out,LIFO)的数据结构,队列是一种先进先出(First In First Out,FIFO)的数据结构。
1. 两个栈实现一个队列
两个栈实现一个队列有如下两种解决思路。
思路一:s1是入栈的,s2是出栈的。
(1)入队列,直接压到s1中去就行了。
(2)出队列,先把s1中的元素全部出栈压入s2中,弹出s2中的栈顶元素,再把s2的所有元素全部压回s1中。
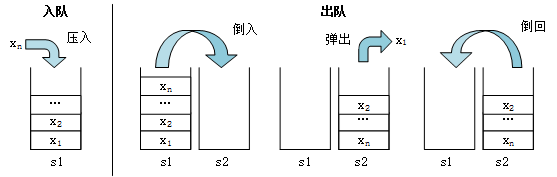
思路一方案实现过程
我们发现,栈s1负责元素的存储,栈s2作为过渡栈,每次元素出队时都需要将元素倒入到栈s2,弹出元素后又将元素倒回到栈s1,可以看出这个过程比较麻烦,因此有了如下思路二。
思路二:s1是入栈的,s2是出栈的。
(1)入队列:直接压入s1即可。
(2)出队列:如果s2不为空,把s2中栈顶元素直接弹出;否则,把s1的所有元素全部弹出压入s2中,再弹出s2的栈顶元素。
元素出队列有两种情况,一种是s1栈不为空,栈s2为空,此时将s1中元素都倒入s2,弹出栈s2的栈顶元素;一种是s1和s2都不为空,此时直接弹出栈s2的栈顶元素。
出队情况一:栈s1不为空,栈s2为空。
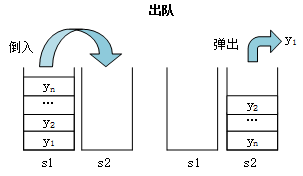
情况一元素出队列过程
出队情况二 :栈s1和s2都不为空。
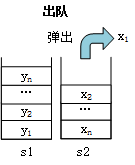
情况二元素出队列过程
相比思路一,思路二的方案减少了元素在两个栈内的转移,显然是一种比较优化的方案。 思路二的实现代码如下:
1 import java.util.Stack; 2 3 public class b09_用两个栈实现队列 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 QueueWithTwoStack queue = new QueueWithTwoStack(); 7 queue.offer(1); 8 queue.offer(2); 9 queue.offer(3); 10 System.out.println(queue.peek()); 11 System.out.println(queue.poll()); 12 System.out.println(queue.peek()); 13 } 14 15 private static class QueueWithTwoStack{ 16 17 public static Stack<Integer> stackPush; //只负责入栈 18 public static Stack<Integer> stackPop; //只负责出栈 19 20 public QueueWithTwoStack() { 21 stackPush = new Stack<>(); 22 stackPop = new Stack<>(); 23 } 24 25 /* 26 * 在队列尾部插入结点 27 */ 28 public void offer(int data) { 29 // 元素直接入栈 30 stackPush.push(data); 31 } 32 33 /* 34 * 在队列头部删除结点 35 */ 36 public int poll() { 37 if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) { //两个栈都为空 38 throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty."); 39 } else if (stackPop.empty()) { 40 // stackPop为空,则将stackPush中的元素倒入stackPop 41 while(!stackPush.empty()){ 42 stackPop.push(stackPush.pop()); 43 } 44 } 45 return stackPop.pop(); 46 } 47 48 /* 49 * 取队列头部结点,不从队列中移除结点 50 */ 51 public int peek() { 52 if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) { 53 throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!"); 54 } else if (stackPop.empty()) { // 用于出栈的栈为空 55 while (!stackPush.empty()) { 56 stackPop.push(stackPush.pop()); 57 } 58 } 59 // 用于出栈的栈不为空则直接去栈顶元素 60 return stackPop.peek(); 61 } 62 } 63 }
2. 两个队列实现一个栈
思路一:q1是专职进出栈的,q2只是个中转站。
(1)入栈:直接入队列q1即可;
(2)出栈:把q1的除最后一个元素外全部转移到队q2中,然后把刚才剩下q1中的那个元素出队列。之后把q2中的全部元素转移回q1中。
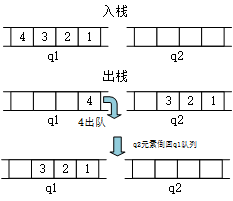
元素入栈出栈过程
思路二:q1和q2同时负责进出栈。
(1)入栈:如果q1和q2都为空,则随便入哪个队列都可;如果一个队列为空一个队列非空,则元素入非空队列;如果两个都非空,则入队列q1即可;
(2)出栈:如果一个队列为空一个队列非空,则将非空队列的队尾元素出队;如果两个队列都非空,则将队列q1的队尾元素出队,其他元素入队列q2。
其实思路二和前面“两个栈实现一个队列”的思路类似,都是减少元素在两个队列之间的转换,都是一种优化的解决方案。思路二的代码实现如下:
1 import java.util.LinkedList; 2 3 public class b09_用两个队列实现栈 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 StackWithTwoQueue stack = new StackWithTwoQueue(); 7 stack.push(1); 8 stack.push(2); 9 stack.push(3); 10 11 System.out.println(stack.peek()); 12 stack.push(4); 13 System.out.println(stack.pop()); 14 System.out.println(stack.pop()); 15 } 16 17 public static class StackWithTwoQueue { 18 static LinkedList<Integer> queue1 = new LinkedList<>(); 19 static LinkedList<Integer> queue2 = new LinkedList<>(); 20 21 /* 22 * 向栈中添加元素 23 */ 24 public static void push(int data) { 25 if (!queue1.isEmpty()) { 26 queue1.offer(data); 27 } else { 28 queue2.offer(data); 29 } 30 } 31 32 /* 33 * 从栈中取出栈顶元素 34 */ 35 public static int pop() { 36 if (!queue1.isEmpty()) { 37 // queue1不为空,则把queue1中除最后一个元素的其他元素移入queue2 38 while(queue1.size() != 1) { 39 queue2.offer(queue1.poll()); 40 } 41 return queue1.poll(); 42 } else if (!queue2.isEmpty()) { 43 // queue2不为空,则把queue2中除最后一个元素的其他元素移入queue1 44 while(queue2.size() != 1) { 45 queue1.offer(queue2.poll()); 46 } 47 return queue2.poll(); 48 } else { 49 System.out.println("Stack is empty!"); 50 } 51 return -1; 52 } 53 54 /* 55 * 取栈顶元素 56 */ 57 public static int peek() { 58 if (!queue1.isEmpty()) { 59 while (queue1.size() != 1) { 60 queue2.offer(queue1.poll()); 61 } 62 // 和pop()函数思路一样,只是最后一个元素取出后需要将该元素再添加到queue2中 63 int val = queue1.poll(); 64 queue2.offer(val); 65 return val; 66 } else if (!queue2.isEmpty()) { 67 while(queue2.size() != 1) { 68 queue1.offer(queue2.poll()); 69 } 70 int val = queue2.poll(); 71 queue1.offer(val); 72 return val; 73 } else { 74 System.out.println("Stack is empty!"); 75 } 76 return -1; 77 } 78 } 79 }
相比思路一,思路二的方案减少了元素在两个栈内的转移,显然是一种比较优化的方案。