随便记录下数据结构的作业和实验啥的
线性表
第一次实验课
顺序表中移动零元素
【样例输入】
8
4 0 1 3 0 6 0 8
【样例输出】
{ 4 0 1 3 0 6 0 8 }
{ 4 1 3 6 8 0 0 0 }
seqlist.h

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 6 class SeqList // class : seqlist 7 { 8 public: 9 SeqList(int size); // 构造函数 10 void outPut(); // 输出顺序表 11 void create_SeqList(); //创建顺序表 12 void move_Zero_to_the_last(); // 移动0元素至末尾 13 14 public: 15 int *data; 16 int maxSize; // 定义顺序表最大长度 17 int last; // last pointer 18 19 }; 20 21 22 SeqList::SeqList(int size) 23 { 24 maxSize = size; 25 last = -1; 26 data = new int[maxSize]; // 申请maxSize大小的空间用来存放数据 27 28 if(data == NULL) // 如果data == 空,说明动态申请内存的过程出现错误 29 { 30 cout << "alloca error!" << endl; 31 exit(1); 32 } 33 } 34 35 void SeqList::outPut() 36 { 37 int i; 38 cout << "{ "; // 按格式输出 39 for(i = 0; i <= last; i++) // 循环条件为 i 小于等于 last 40 { 41 cout << data[i] << ' '; 42 } 43 cout << '}'; 44 } 45 46 void SeqList::create_SeqList() 47 { 48 int length; // 数组元素个数 49 cin >> length; 50 51 for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) 52 { 53 cin >> data[i]; // 输入数组元素 54 last++; // last指针递增 55 } 56 } 57 58 void SeqList::move_Zero_to_the_last() 59 { 60 for(int i = 0; i <= last; i++) // 第一层循环用来遍历数组元素 61 { 62 if( data[i] == 0) // 如果发现某个数组元素为0,则与最近的一个非0元素交换 63 { 64 for(int j = i; j <= last; j++) // 第二层循环用来遍历最近的非0元素,如果找到则与data[i](0元素) 交换 65 { 66 if(data[j] != 0) 67 { 68 data[i] = data[j]; // 交换数组中的零元素与最近的一个非0元素 69 data[j] = 0; 70 break; 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 }
main.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "SeqList.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 SeqList s1(100); 9 10 s1.create_SeqList(); // 创建数组 11 s1.outPut(); // 输出数组元素 12 s1.move_Zero_to_the_last(); // 将顺序表中元素的0值全部移动至后方 13 cout << endl; 14 s1.outPut(); // 再次输出元素 15 16 }
单链表中找出最小值并插入链表头部
【样例输入】
7 2 4 5 1 8 -1
【样例输出】
7-->2-->4-->5-->1-->8
1-->7-->2-->4-->5-->8
太懒了没包含头文件

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 6 struct LinkNode // 定义链表节点类型的结构体 7 { 8 LinkNode *link; // 节点的指针 9 int data; // 节点的数据部分 10 11 LinkNode(int num) // 对一个节点进行初始化 12 { 13 link = NULL; 14 data = num; 15 } 16 }; 17 18 19 class SingleList 20 { 21 public: 22 SingleList() // 构造函数 23 { 24 first = new LinkNode(0); 25 } 26 27 void outPut(); // 输出该链表 28 void create_SingleList(); // 创建链表 29 public: 30 LinkNode *first; 31 }; 32 33 34 void SingleList::outPut() 35 { 36 int i = 0; // 定义一个变量辅助按格式输出 37 LinkNode *current = first -> link; // 定义一个current指针辅助输出 38 39 while(true) 40 { 41 if(i == 0) 42 { 43 cout << current -> data; 44 current = current -> link; // 指针后移 45 i++; 46 } 47 48 else 49 { 50 cout << "-->" << current -> data; 51 current = current -> link; // 指针后移 52 } 53 if( current == NULL ) // 遍历完毕,退出循环 54 { 55 cout << endl; 56 break; 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 61 void SingleList::create_SingleList() 62 { 63 int number; // 定义一个变量用来输入链表数据 64 LinkNode *current = first; // 定义两个工作指针 current和work 65 LinkNode *work = first; 66 67 while(true) 68 { 69 cin >> number; 70 if( number == -1) // 输入-1时退出循环 71 break; 72 work = new LinkNode(number); 73 current -> link = work; // 链接单链表 74 current = work; //链表后移 75 } 76 } 77 78 79 LinkNode* find_min(LinkNode *first) 80 { 81 LinkNode *current = first -> link; // 定义一个current指针 82 int min = current -> data; 83 LinkNode *min_link; // 最小元素对应的节点 84 85 while( true ) 86 { 87 if( min > current -> data ) 88 { 89 min = current -> data; // 遍历链表,找到最小元素值 90 min_link = current; // 记录最小元素值对应的节点,作为返回值返回 91 } 92 93 if( current -> link == NULL) // 如果下一个节点为空,说明遍历完成 94 break; 95 else 96 current = current -> link; 97 } 98 if(min == first->link->data) 99 return first->link; // 如果最小值对应的节点为首元节点,则直接返回首元节点 100 return min_link; // 返回最小元素值对应的节点 101 } 102 103 void insert_header(LinkNode *first,LinkNode *min) 104 { 105 LinkNode *current = first -> link; 106 while(true) 107 { 108 if(min == first -> link) 109 { 110 break; // 如果最小元素值对应的节点就是首元节点,则不需要任何操作 111 } 112 113 if(current -> link != min) 114 { 115 current = current -> link; // 遍历链表,找到最小元素值对应的节点 116 } 117 else 118 { 119 current -> link = min -> link; // 使最小元素值对应节点之前的节点的下一个元素为最小元素值对应节点之后的节点,即将最小元素值脱链 120 min -> link = first -> link; // 将最小元素值对应的节点的下一个节点记为原本的首元节点 121 first -> link = min; // 将最小元素值对应的节点记在头节点后面,即为新的首元节点 122 break; 123 } 124 } 125 } 126 127 int main() 128 { 129 SingleList s1; 130 131 s1.create_SingleList(); // 建立链表 132 s1.outPut(); // 输出链表 133 134 LinkNode *min_link; 135 min_link = find_min(s1.first); // 用一个linknode类型的指针接收最小元素值对应的节点 136 insert_header(s1.first,min_link); // 插入到头部成为首元节点 137 s1.outPut(); // 输出改变后的链表 138 }
合并链表
【问题描述】
两个非降序链表的并集,例如将链表1->2->3 和 2->3->5 并为 1->2->3->5,只能输出结果,不能修改两个链表的数据。
【输入形式】
第一行为第一个链表的各结点值,以空格分隔。
第二行为第二个链表的各结点值,以空格分隔。
【输出形式】
合并好的链表,以非降序排列,值与值之间以空格分隔。
【样例输入】
4 7 10 34
1 4 6 29 34 34 52
【样例输出】
1 4 6 7 10 29 34 52
【评分标准】
要使用链表实现,否则不能得分。
这个附加题还是挺难的,做了好久
wtcl orz
SingleList.h

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 /* 6 author: lemon 7 date: 2020-10-16 8 */ 9 10 struct LinkNode // 定义链表节点类型的结构体 11 { 12 LinkNode *link; // 节点的指针 13 int data; // 节点的数据部分 14 15 LinkNode(int num) // 对一个节点进行初始化 16 { 17 link = NULL; 18 data = num; 19 } 20 }; 21 22 23 class SingleList 24 { 25 public: 26 SingleList() // 构造函数 27 { 28 first = new LinkNode(0); 29 } 30 void create_SingleList(); // 创建链表 31 public: 32 LinkNode *first; 33 }; 34 35 36 void SingleList::create_SingleList() 37 { 38 int number; // 定义一个变量用来输入链表数据 39 LinkNode *current = first; // 定义两个工作指针 current和work 40 LinkNode *work = first; 41 42 while(true) 43 { 44 cin >> number; 45 char c = cin.get(); // 获取当前输入字符 46 work = new LinkNode(number); 47 current -> link = work; // 链接单链表 48 current = work; //链表后移 49 if(c == ' ') // 如果当前输入是回车,则退出循环 50 { 51 break; 52 } 53 } 54 }
main.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "SingleList.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 5 /* 6 author: lemon 7 date: 2020-10-16 8 */ 9 10 bool check_link_repeat(LinkNode *p) // 定义一个检查链表上是否有重复元素的函数 11 { 12 if(p -> link != NULL) // 如果节点下一个节点不为空,则进入检查,否则返回false 13 { 14 if(p -> link -> data == p -> data) // 如果当前节点的数据域等于下一个节点的数据域 15 { 16 return true; // 如果通过if,则返回true 17 } 18 else 19 return false; // 否则返回false 20 } 21 else 22 return false; 23 } 24 25 26 void output_TWO_link(LinkNode *s1,LinkNode *s2) 27 { 28 LinkNode *current1 = s1 -> link; // 分别定义两个current指针来对链表进行遍历操作 29 LinkNode *current2 = s2 -> link; 30 31 32 while(current1 != NULL || current2 != NULL) // 如果current1和current2不同时为NULL,就一直循环 33 { 34 35 // ================================= same logic ================================= 36 if(current1 == NULL) // 如果链表1为空 37 { 38 while(current2 != NULL) // 当链表2不为空时进行循环 39 { 40 if(check_link_repeat(current2)) // 首先检查链表2中是否有相同元素 41 { 42 current2 = current2 -> link; // 如果有相同元素,则链表当前指针向后移动一个节点,然后continue 43 continue; 44 } 45 cout << current2 -> data << ' '; // 输出链表2元素,同时指针向后移动 46 current2 = current2 -> link; 47 } 48 break; 49 } 50 51 if(current2 == NULL) // 此if语句和上面的if语句逻辑相同 52 { 53 while(current1 != NULL) // 如果链表1不为空,就进入循环 54 { 55 if(check_link_repeat(current1)) // 检查链表1是否有相同元素 56 { 57 current1 = current1 -> link; 58 continue; 59 } 60 cout << current1 -> data << ' '; 61 current1 = current1 -> link; 62 } 63 break; 64 } 65 // ================================= same logic ================================= 66 67 68 if(current1 -> data == current2 -> data) // 如果链表1的数据元素等于链表2当前的数据元素,根据题目要求只输出一个即可 69 { 70 if(check_link_repeat(current1)) // 66-77行代码:首先对链表1和链表2 进行检查是否有重复元素 71 { 72 current1 = current1 -> link; 73 continue; 74 } 75 76 if(check_link_repeat(current2)) 77 { 78 current2 = current2 -> link; 79 continue; 80 } 81 cout << current1 -> data << ' '; // 输出一个即可 82 current1 = current1 -> link; // 链表1和链表2的指针同时向后移动 83 current2 = current2 -> link; 84 continue; 85 } 86 87 if(current1 -> data < current2 -> data) // 如果链表1的当前数据小于链表2的元素,则输出链表1的元素,并且链表1的指针向后移动 88 { 89 if(check_link_repeat(current1)) // 检查链表1是否有重复元素 90 { 91 current1 = current1 -> link; 92 continue; 93 } 94 cout << current1 -> data << ' '; // 输出链表1当前的元素值 95 current1 = current1 -> link; // 链表1指针向后移动 96 continue; 97 } 98 99 if(current2 -> data < current1 -> data) // 同理,如果链表2的当前数据小于链表1的元素,则输出链表2的元素,并且链表2的指针向后移动 100 { 101 if(check_link_repeat(current2)) 102 { 103 current2 = current2 -> link; 104 continue; 105 } 106 cout << current2 -> data << ' '; 107 current2 = current2 -> link; 108 continue; 109 } 110 } 111 } 112 113 int main() 114 { 115 SingleList s1; 116 SingleList s2; 117 118 s1.create_SingleList(); // 创建链表1和链表2 119 s2.create_SingleList(); 120 121 output_TWO_link(s1.first,s2.first); // 按合并的方式有序输出两个链表 122 cout << endl; // 最后输出回车 123 }
由于平台只能用校园网连,但是现在在宿舍连不到校园网555,只能本地写一些数据来测试了
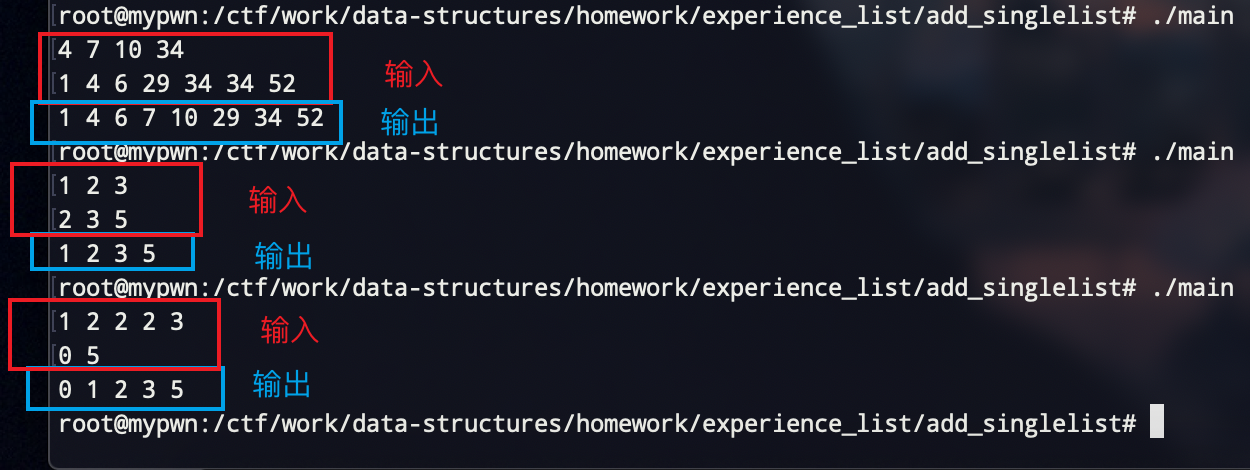
唔,目测应该问题不大
栈和队列 作业
判断回文序列,简单题
Stack.h

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 /* 7 author: lemon 8 date : 2020-10-18 9 */ 10 11 class Stack 12 { 13 public: 14 Stack(int sz); // 构造函数 15 int create_Stack(); // 建立栈 16 bool is_FULL(); // 判满 17 char Pop(); // 元素出栈,并在内部判空 18 19 public: 20 char *elements; // 栈数组 21 int top; // 栈顶指针 22 int maxSize; // 最大元素数量 23 }; 24 25 Stack::Stack(int size): top(-1) , maxSize(size) // 构造函数 26 { 27 elements = new char[maxSize]; // 申请一片连续的存储空间 28 if( elements == NULL ) // 如果分配错误则退出程序 29 { 30 cout << "alloca error!" << endl; 31 exit(0); 32 } 33 } 34 35 int Stack::create_Stack() // 建立栈 36 { 37 int i; 38 string str; 39 cin >> str; // 输入字符串 40 for(i = 0; i < int(str.length()) ; i++) // 逐个字符压栈 41 { 42 if(is_FULL()) // 判满 43 { 44 cout << "stack is full" << endl; 45 exit(0); 46 } 47 elements[++top] = str[i]; // 压栈后栈顶指针上移 48 } 49 return int(str.length()); // 返回字符串的长度 50 } 51 52 bool Stack::is_FULL() 53 { 54 if(top == maxSize - 1) // 如果栈顶指针为maxSize - 1则栈满,返回true 55 return 1; 56 else 57 return 0; 58 } 59 60 61 char Stack::Pop() // 弹栈 62 { 63 char ch; 64 ch = elements[top--]; 65 if( top <= -2) // 如果栈顶指针 比 -2小则栈空,事实上等于-1就已经空了,但是没有以引用的方式返回,所以等于-1的时候要返回元素 66 { 67 top = -1; // 设置top指针为-1 此时栈空 68 exit(0); 69 } 70 return ch; 71 }
main.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include "Stack.h" 5 using namespace std; 6 7 /* 8 author: lemon 9 date : 2020-10-18 10 */ 11 12 void Juage_stack(Stack s1,int length) // 判断字符串是否回文 13 { 14 string higher = ""; // 字符串在栈的前半部分 15 string lower = ""; // 字符串在栈的后半部分 16 int len = length / 2; // 取中间值 17 18 if(length % 2 == 0) // 字符串长度如果是偶数 19 { 20 for(int i = 0; i < len ; i++) 21 { 22 higher = higher + s1.Pop(); // 前半部分出栈,存到higher里 23 } 24 for(int i = 0; i < length - len ; i++) 25 { 26 lower = lower + s1.Pop(); // 后半部分出栈,存到lower里 27 } 28 } 29 30 if(length % 2 != 0) // 如果是奇数,则中间的一个字符需要舍弃 31 { 32 for(int i = 0; i < len ; i++) 33 { 34 higher = higher + s1.Pop(); // 前半部分出栈,存到higher里 35 } 36 int flags = 0; // 设置标志位,舍弃中间元素 37 for(int i = 0; i < length - 1 - len ; i++) 38 { 39 if(flags == 0) 40 { 41 s1.Pop(); // 中间字符出栈,不需要存储 42 flags = flags + 1; 43 } 44 lower = lower + s1.Pop(); // 后半部分出栈,存到lower里 45 } 46 } 47 48 int flags = 0; // 设定回文标志位,字符串中有一对回文则加一 49 for(int i = 0; i < len ; i++) 50 { 51 if(higher[i] == lower[len - 1 - i]) // higher数组从前往后的字符 如果匹配 lower数组的至后向前的字符,则可以判断一对字符回文 52 flags = flags + 1; 53 } 54 55 if(flags == len) // 如果回文的数量等于字符串长度的一半,则可以判断该字符串回文 56 cout << "yes" << endl; 57 else 58 cout << "no" << endl; 59 60 } 61 62 int main() 63 { 64 Stack s1(1000); 65 int string_len = s1.create_Stack(); // 创建栈 66 Juage_stack(s1,string_len); // 判断是否回文 67 68 return 0; 69 }
栈和队列实验
第一题
【问题描述】假设一算术表达式中包括三种括号:圆括号“(”和“)”,方括号“[”和“]”,花括号“{”和“}”,且三种括号可按意 次序嵌套使用,试编写程序判定输入的表达式所含的括号是否正确配对出现(已知表达式已存入数据元素为字符的顺序表中)。若匹配,则返回1,否则返回0。
【输入形式】含括号的算数表达式
【输出形式】1/0
【样例输入】3+(44*[5-{6*[7*(45-10)]}])
【样例输出】1
【样例说明】判断括号是否匹配涉及两方面,括号个数和出现次序的判定。
【评分标准】
stack.h

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 7 class Stack 8 { 9 public: 10 Stack(int sz); // 构造函数 11 int create_Stack(); // 建立栈 12 int quo(); // 匹配括号 13 14 public: 15 char *elements; // 栈数组 16 int top; // 栈顶指针 17 int maxSize; // 最大元素数量 18 }; 19 20 Stack::Stack(int size): top(-1) , maxSize(size) // 构造函数 21 { 22 elements = new char[maxSize]; // 申请一片连续的存储空间 23 if( elements == NULL ) // 如果分配错误则退出程序 24 { 25 cout << "alloca error!" << endl; 26 exit(0); 27 } 28 } 29 30 int Stack::create_Stack() // 建立栈 31 { 32 int i; 33 string str; 34 cin >> str; // 输入字符串 35 for(i = 0; i < int(str.length()) ; i++) // 逐个字符压栈 36 { 37 elements[++top] = str[i]; // 压栈后栈顶指针上移 38 } 39 return int(str.length()); // 返回字符串的长度 40 } 41 42 int Stack::quo() 43 { 44 int temp = top; // 建立一个temp指针方便匹配时遍历 45 char ch[100]; // 存储所有的右括号 46 int j = 0; // 用来取出ch数组对应的元素而设立的变量 47 int flag = 0; // 防止出现单个括号的情况 48 int flags1 = 1; // flags1和2确保后面对flag的操作只进行一次 49 int flags2 = 1; 50 51 for(int i = 0;i < top + 1;i++) 52 { 53 // cout << "elements[" << temp << ']' << '=' << elements[temp] << endl; 54 if(elements[temp] == '}' or elements[temp] == ']' or elements[temp] == ')') 55 { 56 if(flags1) 57 { 58 flag += 1; // 如果有右括号,则flag标志位+1,并且该操作只进行一次 59 flags1 = 0; 60 } 61 ch[i] = elements[temp]; // 如果elements[temp]是右括号,则将其赋值给ch[i] 62 j++; // j++,方便后面对数组操作 63 if(ch[i] == '}') // 将ch数组元素对应的右括号转变为对应的左括号 64 ch[i] = '{'; 65 if(ch[i] == ']') 66 ch[i] = '['; 67 if(ch[i] == ')') 68 ch[i] = '('; 69 } 70 // ([]) 71 if(elements[temp] == '{' or elements[temp] == '[' or elements[temp] == '(') // 如果匹配到左括号 72 { 73 if(flags2) 74 { 75 flag += 1; // 如果有左括号,则flag标志位+1,并且该操作只进行一次 76 flags2 = 0; 77 } 78 if(elements[temp] == ch[j-1]) // 如果和数组相应元素对应 79 { 80 j--; // 数组元素也左移,准备下一次匹配 81 } 82 else // 如果不对应说明不匹配,则return 0 83 return 0; 84 } 85 temp = temp - 1; // temp下移 86 } 87 if(flag == 2 or flag == 0) 88 return 1; // 如果没有出现括号或出现左右括号且都匹配(即没有在for循环中return0),则说明匹配 89 if(flag == 1) 90 return 0; // 如果只出现单括号,则返回0 91 92 return 0; // 防止出现警告信息 93 }
main.cpp

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include "Stack.h" 4 5 // 201931223010 张泽宇 网络1901 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 Stack s1(100); // 建立栈 10 s1.create_Stack(); // 向栈内输入表达式 11 int k = s1.quo(); // 调用quo方法匹配括号 12 cout << k << endl; // 输出匹配结果 13 }
第二题
【问题描述】
已知Q是一个非空队列,S是一个空栈。仅使用少量工作变量以及对队列和栈的基本操作,编写一个算法,将队列Q中的所有元素逆置。
【输入形式】
输入的第一行为队列元素个数,第二行为队列从首至尾的元素
【输出形式】
输出队列的逆置
【样例输入】
3
1 2 3
【样例输出】
3 2 1
【评分标准】
需采用队列与栈的知识,否则不能得分
没写头文件,本来是写的了,交的时候忘了压缩了,就这样吧,我是懒狗
main.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 // 张泽宇 网络1901 201931223010 7 8 // 网络1901 张泽宇 201931223010 9 10 struct QueueNode // 链式队列的节点 11 { 12 int data; // 存储数据 13 QueueNode *link; // 链接下一个队列节点 14 QueueNode(int number,QueueNode *ptr = NULL) // 构造函数,含有头节点 15 { 16 data = number; 17 link = ptr; 18 } 19 }; 20 21 class Queue // 队列类 22 { 23 public: 24 Queue(); // 构造函数 25 void enter_Queue(int num); // 入队 26 void output(); // 输出 27 int out_Queue(); // 出队 28 29 public: 30 QueueNode *front; // 头指针 31 QueueNode *rear; // 尾指针 32 }; 33 34 Queue::Queue() 35 { 36 front = rear = new QueueNode(0); // 创建一个头节点,初始头指针和尾指针都指向该节点 37 } 38 39 void Queue::enter_Queue(int num) 40 { 41 rear -> link = new QueueNode(num); // 入队,new一片空间,然后将尾指针后移 42 rear = rear -> link; 43 } 44 45 void Queue::output() 46 { 47 QueueNode *temp = front -> link; // 建立一个temp帮助输出 48 while(temp != NULL) // 输出队列元素值 49 { 50 cout << temp -> data << ' '; 51 temp = temp -> link; // 指针后移 52 } 53 cout << endl; 54 } 55 56 int Queue::out_Queue() // 出队函数 57 { 58 int x; 59 60 QueueNode *p = front -> link; 61 x = p -> data; // 取队首节点的元素值 62 front -> link = p -> link; // 后移 63 if(p == rear) 64 rear = front; 65 delete p; 66 return x; // 将出队的元素返回 67 } 68 69 70 // 201931223010 张泽宇 网络1901 71 72 class Stack 73 { 74 public: 75 Stack(int sz); // 构造函数 76 void Push(int x); // 入栈 77 int Pop(); // 出栈 78 79 public: 80 int *elements; // 栈数组 81 int top; // 栈顶指针 82 int maxSize; // 最大元素数量 83 }; 84 85 Stack::Stack(int size): top(-1) , maxSize(size) // 构造函数 86 { 87 elements = new int[maxSize]; // 申请一片连续的存储空间 88 if( elements == NULL ) // 如果分配错误则退出程序 89 { 90 cout << "alloca error!" << endl; 91 } 92 } 93 94 void Stack::Push(int x) 95 { 96 elements[++top] = x; // 元素入栈 97 } 98 99 int Stack::Pop() 100 { 101 int x; 102 x = elements[top--]; // 元素出栈并返回 103 return x; 104 } 105 106 int main() 107 { 108 int cout_num,i; // 定义变量 109 Stack s1(8000); // 创建栈对象 110 cin >> cout_num; // 输入的元素个数 111 Queue q1; // 创建队列对象 112 int number; // 将要输入队列的元素 113 114 for(i = 0;i < cout_num; i++) 115 { 116 cin >> number; 117 q1.enter_Queue(number); // 将元素输入队列 118 } 119 120 for(i = 0;i < cout_num; i++) 121 { 122 number = q1.out_Queue(); // 元素出队 123 s1.Push(number); // 将出队的元素入栈,利用栈FILO的性质完成队列逆置 124 } 125 126 for(i = 0;i < cout_num; i++) 127 { 128 number = s1.Pop(); // 元素出栈,经过入栈和出栈,元素已经完成逆置 129 q1.enter_Queue(number); // 将出栈道元素入队 130 } 131 q1.output(); // 输出 132 }
二叉树作业
第一题:【问题描述】首先利用二叉树的前序遍历建立一棵二叉树,然后输入一个x值,在二叉树中搜索结点值为x的结点,找到函数返回该结点的指针,并输出success,找不到函数返回NULL,输出failure,该函数定义为二叉树类的一个成员函数,函数声明可以参考下面:
BinTreeNode<T> * Find (BinTreeNode <T> *root,T item) ; //在二叉树中搜索item
【输入形式】假设二叉树的结点为字符型,输入“#”表示空结点,输入有多行,第一行为建立二叉树用的字符串,具体见Sample Input,二叉树见教材P202页,图5.15,后面每一行为一个要搜索的x值,最后输入一个字符 '#' 结束
【输出形式】输出为多行,搜索x成功则输出success,搜索失败输出failure
【样例输入】
ABC##DE#G##F###
A
D
F
H
#
【样例输出】
success
success
success
failure
没做出来orz,参考了昊琛的代码,wtclllllllll
BinTree.h:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 template <class T> 6 struct BinTreeNode 7 { 8 T data; // 放置数据 9 BinTreeNode<T> *leftchild, *rightchild; // 左孩子和右孩子 10 BinTreeNode (T x, BinTreeNode<T> *lp = NULL, BinTreeNode<T> *rp = NULL) // 构造函数 11 { 12 data = x; 13 leftchild = lp; 14 rightchild = rp; 15 } 16 }; 17 18 template <class T> 19 class BinaryTree 20 { 21 public: 22 BinaryTree (T value) : RefValue(value), root(NULL) { } // 构造函数 23 24 BinTreeNode<T>* search(BinTreeNode<T> *root,T data); // 搜索二叉树的值,返回BinTreeNode类型的指针 25 void CreatTree(BinTreeNode<T> *& root); // 先序创建二叉树 26 27 public: 28 BinTreeNode<T> *root; 29 T RefValue; 30 31 }; 32 33 34 template <class T> 35 void BinaryTree<T>::CreatTree (BinTreeNode<T> *& root) 36 { 37 T item; 38 cin >> item; 39 if( item == '#' ) // 如果输入的值为'#',说明为空,则令root等于NULL 40 { 41 root = NULL; 42 } 43 else 44 { 45 root = new BinTreeNode<T>(item); 46 CreatTree(root -> leftchild); // 递归创建左子树 47 CreatTree(root -> rightchild); // 递归创建右子树 48 } 49 } 50 51 template <class T> 52 BinTreeNode<T> * BinaryTree<T>::search (BinTreeNode<T> *root,T item) // 搜索二叉树的值,返回BinTreeNode类型的指针 53 { 54 BinTreeNode<T> *work; // 设立一个工作指针 55 if (root == NULL) // 如果当前节点为空,则返回空 56 return NULL; 57 if (root->data == item) // 如果搜索成功则返回当前节点指针 58 { 59 return root; 60 } 61 work = search(root->leftchild, item); // 递归搜索左子树 62 if (work != NULL) // 如果不为空则返回节点work 63 return work; 64 work = search(root->rightchild, item); // 递归搜索右子树,到这里说明上一步左子树搜索为空值 65 if (work != NULL) // 如果不为空返回节点work 66 return work; 67 return NULL; 68 }
main.cpp:
1 #include "BinTree.h" 2 #include <string.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 9 BinaryTree<char> n1('0'); // 创建类 10 11 n1.CreatTree(n1.root); // 先序生成二叉树 12 char temp; 13 14 while (1) 15 { 16 cin >> temp; 17 if(temp == '#') // 不为#则继续 18 break; 19 if (n1.search(n1.root, temp) != NULL) // 如果返回值不为空,说明找到,输出success 20 { 21 cout << "success" << endl; 22 } 23 else // 返回值为空则查找失败 24 { 25 cout << "failure" << endl; 26 } 27 } 28 29 return 0; 30 }
第二题:
【问题描述】首先利用二叉树的前序遍历建立一棵二叉树,分别用3个递归函数统计度为0,度为1和度为2的结点个数,并输出结果,这3个函数可以定义为二叉树的成员函数
【输入形式】假设二叉树的结点为字符型,输入“#”表示空结点,输入为一行字符串,具体见样例输入,二叉树见教材P202页,图5.15
【输出形式】输出只有1行,依次输出度为0的结点个数,度为1的结点个数,度为2的结点个数,3个数之间用空格分开,最后一个数据后面有一个空格,具体格式见样例输出
【样例输入】
ABC##DE#G##F###
【样例输出】
3 2 2
【样例说明】
其他测试数据:
输入:A## 输出:1 0 0
输入:AB#D##C#E## 输出:2 2 1
比第一个简单多了QAQ
BinTree.h:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 template <class T> 6 struct BinTreeNode 7 { 8 T data; // 放置数据 9 BinTreeNode<T> *leftchild, *rightchild; // 左孩子和右孩子 10 BinTreeNode (T x, BinTreeNode<T> *lp = NULL, BinTreeNode<T> *rp = NULL) // 构造函数 11 { 12 data = x; 13 leftchild = lp; 14 rightchild = rp; 15 } 16 }; 17 18 template <class T> 19 class BinaryTree 20 { 21 public: 22 BinaryTree (T value) : RefValue(value), root(NULL) { } // 构造函数 23 void CreatTree(BinTreeNode<T> *& root); // 先序创建二叉树 24 void count_node(BinTreeNode<T> *root); // 计算度为0,1,2的节点个数 25 26 public: 27 BinTreeNode<T> *root; 28 T RefValue; 29 int zero = 0; // 度为0,1,2的节点个数,初始值为0 30 int one = 0; 31 int two = 0; 32 33 }; 34 35 36 template <class T> 37 void BinaryTree<T>::CreatTree (BinTreeNode<T> *& root) 38 { 39 T item; 40 cin >> item; 41 if( item == '#' ) // 如果输入的值为'#',说明为空,则令root等于NULL 42 { 43 root = NULL; 44 } 45 else 46 { 47 root = new BinTreeNode<T>(item); 48 CreatTree(root -> leftchild); // 递归创建左子树 49 CreatTree(root -> rightchild); // 递归创建右子树 50 } 51 } 52 53 54 template <class T> 55 void BinaryTree<T>::count_node(BinTreeNode<T> *root) 56 { 57 if(root -> leftchild == NULL && root -> rightchild == NULL) 58 // 如果一个节点的左右孩子都为空,则度为0 59 { 60 zero++; 61 } 62 63 if(root -> leftchild != NULL && root -> rightchild == NULL) 64 // 如果一个节点的左孩子不为空且右子树为空,则度为1,且递归调用计算其右孩子的度 65 { 66 one++; 67 count_node(root -> leftchild); 68 } 69 70 if(root -> rightchild != NULL && root -> leftchild == NULL) 71 // 如果一个节点的右孩子不为空且左子树为空,则度为1,且递归调用计算其左孩子的度 72 { 73 one++; 74 count_node(root -> rightchild); 75 } 76 77 if(root -> leftchild != NULL && root -> rightchild != NULL) 78 { 79 // 如果一个节点的左右孩子都不为空,则度为2,且递归调用其左右孩子的度 80 two++; 81 count_node(root -> leftchild); 82 count_node(root -> rightchild); 83 } 84 }
main.cpp:
1 #include "BinTree.h" 2 #include <string.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 10 BinaryTree<char> n1('0'); // 创建类 11 12 n1.CreatTree(n1.root); // 先序生成二叉树 13 char temp; 14 15 n1.count_node(n1.root); // 计算度分别为0,1,2的节点数量 16 17 cout << n1.zero << ' ' << n1.one << ' ' << n1.two << endl; // 输出度分别为0,1,2的节点数量 18 return 0; 19 }
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 /* 6 author: lemon 7 date: 2020-10-16 8 */ 9 10 struct LinkNode // 定义链表节点类型的结构体 11 { 12 LinkNode *link; // 节点的指针 13 int data; // 节点的数据部分 14 15 LinkNode(int num) // 对一个节点进行初始化 16 { 17 link = NULL; 18 data = num; 19 } 20 }; 21 22 23 class SingleList 24 { 25 public: 26 SingleList() // 构造函数 27 { 28 first = new LinkNode(0); 29 } 30 void create_SingleList(); // 创建链表 31 public: 32 LinkNode *first; 33 }; 34 35 36 void SingleList::create_SingleList() 37 { 38 int number; // 定义一个变量用来输入链表数据 39 LinkNode *current = first; // 定义两个工作指针 current和work 40 LinkNode *work = first; 41 42 while(true) 43 { 44 cin >> number; 45 char c = cin.get(); // 获取当前输入字符 46 work = new LinkNode(number); 47 current -> link = work; // 链接单链表 48 current = work; //链表后移 49 if(c == ' ') // 如果当前输入是回车,则退出循环 50 { 51 break; 52 main.cp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "SingleList.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 5 /* 6 author: lemon 7 date: 2020-10-16 8 */ 9 10 bool check_link_repeat(LinkNode *p) // 定义一个检查链表上是否有重复元素的函数 11 { 12 if(p -> link != NULL) // 如果节点下一个节点不为空,则进入检查,否则返回false 13 { 14 if(p -> link -> data == p -> data) // 如果当前节点的数据域等于下一个节点的数据域 15 { 16 return true; // 如果通过if,则返回true 17 } 18 else 19 return false; // 否则返回false 20 } 21 else 22 return false; 23 } 24 25 26 void output_TWO_link(LinkNode *s1,LinkNode *s2) 27 { 28 LinkNode *current1 = s1 -> link; // 分别定义两个current指针来对链表进行遍历操作 29 LinkNode *current2 = s2 -> link; 30 31 32 while(current1 != NULL || current2 != NULL) // 如果current1和current2不同时为NULL,就一直循环 33 { 34 35 // ================================= same logic ================================= 36 if(current1 == NULL) // 如果链表1为空 37 { 38 while(current2 != NULL) // 当链表2不为空时进行循环 39 { 40 if(check_link_repeat(current2)) // 首先检查链表2中是否有相同元素 41 { 42 current2 = current2 -> link; // 如果有相同元素,则链表当前指针向后移动一个节点,然后continue 43 continue; 44 } 45 cout << current2 -> data << ' '; // 输出链表2元素,同时指针向后移动 46 current2 = current2 -> link; 47 } 48 break; 49 } 50 51 if(current2 == NULL) // 此if语句和上面的if语句逻辑相同 52 { 53 while(current1 != NULL) // 如果链表1不为空,就进入循环 54 { 55 if(check_link_repeat(current1)) // 检查链表1是否有相同元素 56 { 57 current1 = current1 -> link; 58 continue; 59 } 60 cout << current1 -> data << ' '; 61 current1 = current1 -> link; 62 } 63 break; 64 } 65 // ================================= same logic ================================= 66 67 68 if(current1 -> data == current2 -> data) // 如果链表1的数据元素等于链表2当前的数据元素,根据题目要求只输出一个即可 69 { 70 if(check_link_repeat(current1)) // 66-77行代码:首先对链表1和链表2 进行检查是否有重复元素 71 { 72 current1 = current1 -> link; 73 continue; 74 } 75 76 if(check_link_repeat(current2)) 77 { 78 current2 = current2 -> link; 79 continue; 80 } 81 cout << current1 -> data << ' '; // 输出一个即可 82 current1 = current1 -> link; // 链表1和链表2的指针同时向后移动 83 current2 = current2 -> link; 84 continue; 85 } 86 87 if(current1 -> data < current2 -> data) // 如果链表1的当前数据小于链表2的元素,则输出链表1的元素,并且链表1的指针向后移动 88 { 89 if(check_link_repeat(current1)) // 检查链表1是否有重复元素 90 { 91 current1 = current1 -> link; 92 continue; 93 } 94 cout << current1 -> data << ' '; // 输出链表1当前的元素值 95 current1 = current1 -> link; // 链表1指针向后移动 96 continue; 97 } 98 99 if(current2 -> data < current1 -> data) // 同理,如果链表2的当前数据小于链表1的元素,则输出链表2的元素,并且链表2的指针向后移动 100 { 101 if(check_link_repeat(current2)) 102 { 103 current2 = current2 -> link; 104 continue; 105 } 106 cout << current2 -> data << ' '; 107 current2 = current2 -> link; 108 continue; 109 } 110 } 111 } 112 113 int main() 114 { 115 SingleList s1; 116 SingleList s2; 117 118 s1.create_SingleList(); // 创建链表1和链表2 119 s2.create_SingleList(); 120 121 output_TWO_link(s1.first,s2.first); // 按合并的方式有序输出两个链表 122 cout << endl; // 最后输出回车 1
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 6 struct LinkNode // 定义链表节点类型的结构体 7 { 8 LinkNode *link; // 节点的指针 9 int data; // 节点的数据部分 10 11 LinkNode(int num) // 对一个节点进行初始化 12 { 13 link = NULL; 14 data = num; 15 } 16 }; 17 18 19 class SingleList 20 { 21 public: 22 SingleList() // 构造函数 23 { 24 first = new LinkNode(0); 25 } 26 27 void outPut(); // 输出该链表 28 void create_SingleList(); // 创建链表 29 public: 30 LinkNode *first; 31 }; 32 33 34 void SingleList::outPut() 35 { 36 int i = 0; // 定义一个变量辅助按格式输出 37 LinkNode *current = first -> link; // 定义一个current指针辅助输出 38 39 while(true) 40 { 41 if(i == 0) 42 { 43 cout << current -> data; 44 current = current -> link; // 指针后移 45 i++; 46 } 47 48 else 49 { 50 cout << "-->" << current -> data; 51 current = current -> link; // 指针后移 52 } 53 if( current == NULL ) // 遍历完毕,退出循环 54 { 55 cout << endl; 56 break; 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 61 void SingleList::create_SingleList() 62 { 63 int number; // 定义一个变量用来输入链表数据 64 LinkNode *current = first; // 定义两个工作指针 current和work 65 LinkNode *work = first; 66 67 while(true) 68 { 69 cin >> number; 70 if( number == -1) // 输入-1时退出循环 71 break; 72 work = new LinkNode(number); 73 current -> link = work; // 链接单链表 74 current = work; //链表后移 75 } 76 } 77 78 79 LinkNode* find_min(LinkNode *first) 80 { 81 LinkNode *current = first -> link; // 定义一个current指针 82 int min = current -> data; 83 LinkNode *min_link; // 最小元素对应的节点 84 85 while( true ) 86 { 87 if( min > current -> data ) 88 { 89 min = current -> data; // 遍历链表,找到最小元素值 90 min_link = current; // 记录最小元素值对应的节点,作为返回值返回 91 } 92 93 if( current -> link == NULL) // 如果下一个节点为空,说明遍历完成 94 break; 95 else 96 current = current -> link; 97 } 98 if(min == first->link->data) 99 return first->link; // 如果最小值对应的节点为首元节点,则直接返回首元节点 100 return min_link; // 返回最小元素值对应的节点 101 } 102 103 void insert_header(LinkNode *first,LinkNode *min) 104 { 105 LinkNode *current = first -> link; 106 while(true) 107 { 108 if(min == first -> link) 109 { 110 break; // 如果最小元素值对应的节点就是首元节点,则不需要任何操作 111 } 112 113 if(current -> link != min) 114 { 115 current = current -> link; // 遍历链表,找到最小元素值对应的节点 116 } 117 else 118 { 119 current -> link = min -> link; // 使最小元素值对应节点之前的节点的下一个元素为最小元素值对应节点之后的节点,即将最小元素值脱链 120 min -> link = first -> link; // 将最小元素值对应的节点的下一个节点记为原本的首元节点 121 first -> link = min; // 将最小元素值对应的节点记在头节点后面,即为新的首元节点 122 break; 123 } 124 } 125 } 126 127 int main() 128 { 129 SingleList s1; 130 131 s1.create_SingleList(); // 建立链表 132 s1.outPut(); // 输出链表 133 134 LinkNode *min_link; 135 min_link = find_min(s1.first); // 用一个linknode类型的指针接收最小元素值对应的节点 136 insert_header(s1.first,min_link); // 插入到头部成为首元节点 137 s1.outPut(); // 输出改变后的链表 1
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 201931223010 张泽宇 网络1901 6 7 struct LinkNode // 定义链表节点类型的结构体 8 { 9 LinkNode *link; // 节点的指针 10 int data; // 节点的数据部分 11 12 LinkNode(int num) // 对一个节点进行初始化 13 { 14 link = NULL; 15 data = num; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 20 class SingleList 21 { 22 public: 23 SingleList() // 构造函数 24 { 25 first = new LinkNode(0); 26 } 27 28 void outPut(); // 输出该链表 29 void create_SingleList(); // 创建链表 30 public: 31 LinkNode *first; 32 }; 33 34 35 void SingleList::outPut() 36 { 37 int i = 0; // 定义一个变量辅助按格式输出 38 LinkNode *current = first -> link; // 定义一个current指针辅助输出 39 40 while(true) 41 { 42 if(i == 0) 43 { 44 cout << current -> data; 45 current = current -> link; // 指针后移 46 i++; 47 } 48 49 else 50 { 51 cout << "-->" << current -> data; 52 current = current -> link; // 指针后移 53 } 54 if( current == NULL ) // 遍历完毕,退出循环 55 { 56 cout << endl; 57 break; 58 } 59 } 60 } 61 62 void SingleList::create_SingleList() 63 { 64 int number; // 定义一个变量用来输入链表数据 65 LinkNode *current = first; // 定义两个工作指针 current和work 66 LinkNode *work = first; 67 68 while(true) 69 { 70 cin >> number; 71 if( number == -1) // 输入-1时退出循环 72 break; 73 work = new LinkNode(number); 74 current -> link = work; // 链接单链表 75 current = work; //链表后移 76 } 77 } 78 79 80 LinkNode* find_min(LinkNode *first) 81 { 82 LinkNode *current = first -> link; // 定义一个current指针 83 int min = current -> data; 84 LinkNode *min_link; // 最小元素对应的节点 85 86 while( true ) 87 { 88 if( min > current -> data ) 89 { 90 min = current -> data; // 遍历链表,找到最小元素值 91 min_link = current; // 记录最小元素值对应的节点,作为返回值返回 92 } 93 94 if( current -> link == NULL) // 如果下一个节点为空,说明遍历完成 95 break; 96 else 97 current = current -> link; 98 } 99 if(min == first->link->data) 100 return first->link; // 如果最小值对应的节点为首元节点,则直接返回首元节点 101 return min_link; // 返回最小元素值对应的节点 102 } 103 104 void insert_header(LinkNode *first,LinkNode *min) 105 { 106 LinkNode *current = first -> link; 107 while(true) 108 { 109 if(min == first -> link) 110 { 111 break; // 如果最小元素值对应的节点就是首元节点,则不需要任何操作 112 } 113 114 if(current -> link != min) 115 { 116 current = current -> link; // 遍历链表,找到最小元素值对应的节点 117 } 118 else 119 { 120 current -> link = min -> link; // 使最小元素值对应节点之前的节点的下一个元素为最小元素值对应节点之后的节点,即将最小元素值脱链 121 min -> link = first -> link; // 将最小元素值对应的节点的下一个节点记为原本的首元节点 122 first -> link = min; // 将最小元素值对应的节点记在头节点后面,即为新的首元节点 123 break; 124 } 125 } 126 } 127 128 int main() 129 { 130 SingleList s1; 131 132 s1.create_SingleList(); // 建立链表 133 s1.outPut(); // 输出链表 134 135 LinkNode *min_link; 136 min_link = find_min(s1.first); // 用一个linknode类型的指针接收最小元素值对应的节点 137 insert_header(s1.first,min_link); // 插入到头部成为首元节点 138 s1.outPut();
