AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping是通过扫描方式注册Handler,收到请求时由AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的getHandlerInternal进行分发.
共有5个子类,一个抽象类.
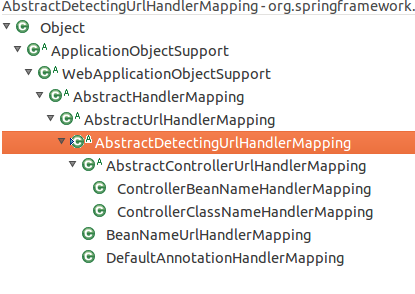
与SimpleUrlHandlerMapping类似,通过覆写initApplicationContext,然后调用detectHandlers进行初始化.
detectHandlers通过BeanFactoryUtils扫描应用下的Object,然后预留determineUrlsForHandler给子类根据Handler生成对应的url.
注册使用的registerHandler依然由AbstractUrlHandlerMapping提供.
// AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Calls the {@link #detectHandlers()} method in addition to the 3 * superclass's initialization. 4 */ 5 @Override 6 public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException { 7 super.initApplicationContext(); 8 detectHandlers(); 9 }
这边一样是调用AbstractHandlerMapping的initApplicationContext初始化拦截器.
主角上场,detectHandlers,扫描Handlers
// AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Register all handlers found in the current ApplicationContext. 3 * <p>The actual URL determination for a handler is up to the concrete 4 * {@link #determineUrlsForHandler(String)} implementation. A bean for 5 * which no such URLs could be determined is simply not considered a handler. 6 * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException if the handler couldn't be registered 7 * @see #determineUrlsForHandler(String) 8 */ 9 protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException { 10 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 11 logger.debug("Looking for URL mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext()); 12 } 13 String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ? 14 BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : 15 getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); 16 17 // Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for. 18 for (String beanName : beanNames) { 19 String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName); 20 if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) { 21 // URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler. 22 registerHandler(urls, beanName); 23 } 24 else { 25 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 26 logger.debug("Rejected bean name '" + beanName + "': no URL paths identified"); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 }
这边预留的模板方法定义如下:
1 /** 2 * Determine the URLs for the given handler bean. 3 * @param beanName the name of the candidate bean 4 * @return the URLs determined for the bean, 5 * or {@code null} or an empty array if none 6 */ 7 protected abstract String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName);
我们再来看看模板方法在BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping和AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping中的实现吧.
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping非常简单,就实现了determineUrlsForHandler.
其中的alias应该是应该就是通过beanName在配置文件中配置的.
// BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Checks name and aliases of the given bean for URLs, starting with "/". 3 */ 4 @Override 5 protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) { 6 List<String> urls = new ArrayList<String>(); 7 if (beanName.startsWith("/")) { 8 urls.add(beanName); 9 } 10 String[] aliases = getApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName); 11 for (String alias : aliases) { 12 if (alias.startsWith("/")) { 13 urls.add(alias); 14 } 15 } 16 return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls); 17 }
再来看看AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping中的实现
isEligibleForMapping判断controller是否被排除在外(通过包package排除或类class排除).
buildUrlsForHandler由子类实现具体的url生成规则
isControllerType判断是否Controller的子类
buildUrlsForHandler预留给子类生产url的模板方法.
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * This implementation delegates to {@link #buildUrlsForHandler}, 3 * provided that {@link #isEligibleForMapping} returns {@code true}. 4 */ 5 @Override 6 protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) { 7 Class beanClass = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName); 8 if (isEligibleForMapping(beanName, beanClass)) { 9 return buildUrlsForHandler(beanName, beanClass); 10 } 11 else { 12 return null; 13 } 14 }
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**判断controller是否被排除在外(通过包package排除或类class排除). 2 * Determine whether the specified controller is excluded from this mapping. 3 * @param beanName the name of the controller bean 4 * @param beanClass the concrete class of the controller bean 5 * @return whether the specified class is excluded 6 * @see #setExcludedPackages 7 * @see #setExcludedClasses 8 */ 9 protected boolean isEligibleForMapping(String beanName, Class beanClass) { 10 if (beanClass == null) { 11 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 12 logger.debug("Excluding controller bean '" + beanName + "' from class name mapping " + 13 "because its bean type could not be determined"); 14 } 15 return false; 16 } 17 if (this.excludedClasses.contains(beanClass)) { 18 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 19 logger.debug("Excluding controller bean '" + beanName + "' from class name mapping " + 20 "because its bean class is explicitly excluded: " + beanClass.getName()); 21 } 22 return false; 23 } 24 String beanClassName = beanClass.getName(); 25 for (String packageName : this.excludedPackages) { 26 if (beanClassName.startsWith(packageName)) { 27 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 28 logger.debug("Excluding controller bean '" + beanName + "' from class name mapping " + 29 "because its bean class is defined in an excluded package: " + beanClass.getName()); 30 } 31 return false; 32 } 33 } 34 return isControllerType(beanClass); 35 }
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Determine whether the given bean class indicates a controller type 3 * that is supported by this mapping strategy. 4 * @param beanClass the class to introspect 5 */ 6 protected boolean isControllerType(Class beanClass) { 7 return this.predicate.isControllerType(beanClass); 8 }
// ControllerTypePredicate
这边提供2个api,分别判断是Controller的子类还是MultiActionController的子类.
1 /** 2 * Internal helper class that identifies controller types. 3 * 4 * @author Juergen Hoeller 5 * @since 2.5.3 6 */ 7 class ControllerTypePredicate { 8 9 public boolean isControllerType(Class beanClass) { 10 return Controller.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass); 11 } 12 13 public boolean isMultiActionControllerType(Class beanClass) { 14 return MultiActionController.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass); 15 } 16 17 }
预留生成url的模板方法
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Abstract template method to be implemented by subclasses. 3 * @param beanName the name of the bean 4 * @param beanClass the type of the bean 5 * @return the URLs determined for the bean 6 */ 7 protected abstract String[] buildUrlsForHandler(String beanName, Class beanClass);
再来看看AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping的2个实现ControllerBeanNameUrlHandlerMapping和ControllerClassNameUrlHandlerMapping.
其实这两个,很简单,一个是根据beanName来生产url,一个是根据className来生产url.
// ControllerBeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
1 @Override 2 protected String[] buildUrlsForHandler(String beanName, Class beanClass) { 3 List<String> urls = new ArrayList<String>(); 4 urls.add(generatePathMapping(beanName)); 5 String[] aliases = getApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName);// 也获取配置的别名 6 for (String alias : aliases) { 7 urls.add(generatePathMapping(alias)); 8 } 9 return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls); 10 }
// ControllerBeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
1 /**对path添加前后缀,还有/ 2 * Prepends a '/' if required and appends the URL suffix to the name. 3 */ 4 protected String generatePathMapping(String beanName) { 5 String name = (beanName.startsWith("/") ? beanName : "/" + beanName); 6 StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder(); 7 if (!name.startsWith(this.urlPrefix)) { 8 path.append(this.urlPrefix); 9 } 10 path.append(name); 11 if (!name.endsWith(this.urlSuffix)) { 12 path.append(this.urlSuffix); 13 } 14 return path.toString(); 15 }
// ControllerClassNameUrlHandlerMapping
直接委托给generatePathMappings实现
1 @Override 2 protected String[] buildUrlsForHandler(String beanName, Class beanClass) { 3 return generatePathMappings(beanClass); 4 }
// ControllerClassNameUrlHandlerMapping
通过buildPathPrefix获取path的前缀
通过ClassUtils获取className,如BookController(不带包名),同时使用cglib代理的问题一并解决
根据大小写是否敏感,转换className(默认caseSensitive = false;)
isMultiActionControllerType判断Controller是否MultiActionController的子类,就是controller是否包含多个handler
1 /** 2 * Generate the actual URL paths for the given controller class. 3 * <p>Subclasses may choose to customize the paths that are generated 4 * by overriding this method. 5 * @param beanClass the controller bean class to generate a mapping for 6 * @return the URL path mappings for the given controller 7 */ 8 protected String[] generatePathMappings(Class beanClass) { 9 StringBuilder pathMapping = buildPathPrefix(beanClass); 10 String className = ClassUtils.getShortName(beanClass); 11 String path = (className.endsWith(CONTROLLER_SUFFIX) ? 12 className.substring(0, className.lastIndexOf(CONTROLLER_SUFFIX)) : className); 13 if (path.length() > 0) { 14 if (this.caseSensitive) { 15 pathMapping.append(path.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase()).append(path.substring(1)); 16 } 17 else { 18 pathMapping.append(path.toLowerCase()); 19 } 20 } 21 if (isMultiActionControllerType(beanClass)) { 22 return new String[] {pathMapping.toString(), pathMapping.toString() + "/*"}; 23 } 24 else { 25 return new String[] {pathMapping.toString() + "*"}; 26 } 27 }
// ControllerClassNameUrlHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Build a path prefix for the given controller bean class. 3 * @param beanClass the controller bean class to generate a mapping for 4 * @return the path prefix, potentially including subpackage names as path elements 5 */ 6 private StringBuilder buildPathPrefix(Class beanClass) { 7 StringBuilder pathMapping = new StringBuilder(); 8 if (this.pathPrefix != null) { 9 pathMapping.append(this.pathPrefix); 10 pathMapping.append("/"); 11 } 12 else { 13 pathMapping.append("/"); 14 } 15 if (this.basePackage != null) { 16 String packageName = ClassUtils.getPackageName(beanClass); 17 if (packageName.startsWith(this.basePackage)) { 18 String subPackage = packageName.substring(this.basePackage.length()).replace('.', '/'); 19 pathMapping.append(this.caseSensitive ? subPackage : subPackage.toLowerCase()); 20 pathMapping.append("/"); 21 } 22 } 23 return pathMapping; 24 }
// AbstractControllerUrlHandlerMapping
predicate.isMultiActionControllerType具体实现看上面的ControllerTypePredicate
1 /** 2 * Determine whether the given bean class indicates a controller type 3 * that dispatches to multiple action methods. 4 * @param beanClass the class to introspect 5 */ 6 protected boolean isMultiActionControllerType(Class beanClass) { 7 return this.predicate.isMultiActionControllerType(beanClass); 8 }