一、C语言的基础:
1) C结尾文件:源代码文件
2) O结尾文件:目标文件(二进制文件),每个文件经过编译都会形成目标文件,多个目标文件连接后可以形成可执行文件。(gcc -g -c hello2.c)
3) H结尾文件:头文件,存放着C文件中的函数定义,结构体定义等
4) 可执行文件:gcc hello2.c -o hello2.out(生成的文件名)
5)so结尾文件:动态库
二、寻找代码的虚拟地址
1)编写一个C程序

#include <stdio.h> int k=3; int increase_num(int x , int y ) { return x+y; } int main() { printf( " k address is %p ", &k ); printf("&k=========" ); static int i = 4 ; int x = 1; int y = 2 ; // sum(x,y) ; while(1){ } return 0; }
2)产生一个目标文件
gcc -g -c hello2.c
3)查看反编译的详细信息
objdump -s -d hello2.o
4)生成一个可执行文件
gcc hello2.c -o hello2.out
5)找出执行文件的进程号码 -
ps -ef| grep hello2
进程号码为 -> 14103 11192 99 16:12 pts/0 00:00:11 ./hello2.out
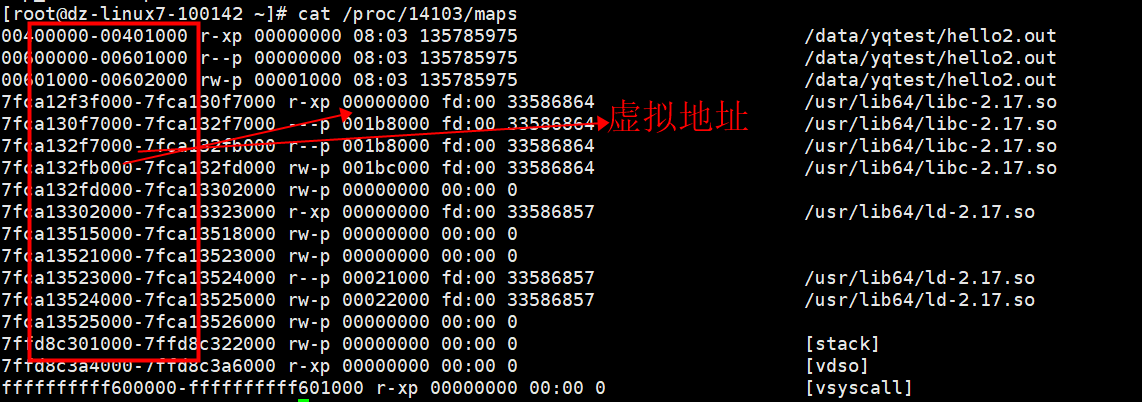
6)查看虚拟地址
cat /proc/14103/map(cat /proc/进程号码/map)
图上的是这个进程占用的虚拟地址: