转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/17656437
经过前三篇文章的学习,Volley的使用方法我们已经掌握的几乎相同了,可是对于Volley的工作原理。恐怕有非常多朋友还不是非常清晰。
因此。本篇文章中我们就来一起阅读一下Volley的源代码,将它的工作流程总体地梳理一遍。
同一时候,这也是Volley系列的最后一篇文章了。
事实上,Volley的官方文档中本身就附有了一张Volley的工作流程图。例如以下图所看到的。
多数朋友突然看到一张这种图,应该会和我一样,感觉一头雾水吧?没错,眼下我们对Volley背后的工作原理还没有一个概念性的理解,直接就来看这张图自然会有些吃力。只是没关系,以下我们就去分析一下Volley的源代码,之后再又一次来看这张图就会好理解多了。
说起分析源代码,那么应该从哪儿開始看起呢?这就要回想一下Volley的使用方法了,还记得吗。使用Volley的第一步,首先要调用Volley.newRequestQueue(context)方法来获取一个RequestQueue对象,那么我们自然要从这种方法開始看起了,代码例如以下所看到的:
public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context) {
return newRequestQueue(context, null);
}public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context, HttpStack stack) {
File cacheDir = new File(context.getCacheDir(), DEFAULT_CACHE_DIR);
String userAgent = "volley/0";
try {
String packageName = context.getPackageName();
PackageInfo info = context.getPackageManager().getPackageInfo(packageName, 0);
userAgent = packageName + "/" + info.versionCode;
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
}
if (stack == null) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 9) {
stack = new HurlStack();
} else {
stack = new HttpClientStack(AndroidHttpClient.newInstance(userAgent));
}
}
Network network = new BasicNetwork(stack);
RequestQueue queue = new RequestQueue(new DiskBasedCache(cacheDir), network);
queue.start();
return queue;
}实际上HurlStack的内部就是使用HttpURLConnection进行网络通讯的,而HttpClientStack的内部则是使用HttpClient进行网络通讯的。这里为什么这样选择呢?能够參考我之前翻译的一篇文章Android訪问网络,使用HttpURLConnection还是HttpClient?
创建好了HttpStack之后,接下来又创建了一个Network对象,它是用于依据传入的HttpStack对象来处理网络请求的。紧接着new出一个RequestQueue对象。并调用它的start()方法进行启动,然后将RequestQueue返回,这样newRequestQueue()的方法就执行结束了。
那么RequestQueue的start()方法内部究竟执行了什么东西呢?我们跟进去瞧一瞧:
public void start() {
stop(); // Make sure any currently running dispatchers are stopped.
// Create the cache dispatcher and start it.
mCacheDispatcher = new CacheDispatcher(mCacheQueue, mNetworkQueue, mCache, mDelivery);
mCacheDispatcher.start();
// Create network dispatchers (and corresponding threads) up to the pool size.
for (int i = 0; i < mDispatchers.length; i++) {
NetworkDispatcher networkDispatcher = new NetworkDispatcher(mNetworkQueue, mNetwork,
mCache, mDelivery);
mDispatchers[i] = networkDispatcher;
networkDispatcher.start();
}
}得到了RequestQueue之后,我们仅仅须要构建出对应的Request,然后调用RequestQueue的add()方法将Request传入就能够完毕网络请求操作了,那么不用说,add()方法的内部肯定有着非常复杂的逻辑。我们来一起看一下:
public <T> Request<T> add(Request<T> request) {
// Tag the request as belonging to this queue and add it to the set of current requests.
request.setRequestQueue(this);
synchronized (mCurrentRequests) {
mCurrentRequests.add(request);
}
// Process requests in the order they are added.
request.setSequence(getSequenceNumber());
request.addMarker("add-to-queue");
// If the request is uncacheable, skip the cache queue and go straight to the network.
if (!request.shouldCache()) {
mNetworkQueue.add(request);
return request;
}
// Insert request into stage if there's already a request with the same cache key in flight.
synchronized (mWaitingRequests) {
String cacheKey = request.getCacheKey();
if (mWaitingRequests.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
// There is already a request in flight. Queue up.
Queue<Request<?>> stagedRequests = mWaitingRequests.get(cacheKey);
if (stagedRequests == null) {
stagedRequests = new LinkedList<Request<?>>();
}
stagedRequests.add(request);
mWaitingRequests.put(cacheKey, stagedRequests);
if (VolleyLog.DEBUG) {
VolleyLog.v("Request for cacheKey=%s is in flight, putting on hold.", cacheKey);
}
} else {
// Insert 'null' queue for this cacheKey, indicating there is now a request in
// flight.
mWaitingRequests.put(cacheKey, null);
mCacheQueue.add(request);
}
return request;
}
}OK,那么既然默认每条请求都是能够缓存的,自然就被增加到了缓存队列中,于是一直在后台等待的缓存线程就要開始执行起来了,我们看下CacheDispatcher中的run()方法。代码例如以下所看到的:
public class CacheDispatcher extends Thread {
……
@Override
public void run() {
if (DEBUG) VolleyLog.v("start new dispatcher");
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
// Make a blocking call to initialize the cache.
mCache.initialize();
while (true) {
try {
// Get a request from the cache triage queue, blocking until
// at least one is available.
final Request<?> request = mCacheQueue.take();
request.addMarker("cache-queue-take");
// If the request has been canceled, don't bother dispatching it.
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("cache-discard-canceled");
continue;
}
// Attempt to retrieve this item from cache.
Cache.Entry entry = mCache.get(request.getCacheKey());
if (entry == null) {
request.addMarker("cache-miss");
// Cache miss; send off to the network dispatcher.
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}
// If it is completely expired, just send it to the network.
if (entry.isExpired()) {
request.addMarker("cache-hit-expired");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}
// We have a cache hit; parse its data for delivery back to the request.
request.addMarker("cache-hit");
Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse(
new NetworkResponse(entry.data, entry.responseHeaders));
request.addMarker("cache-hit-parsed");
if (!entry.refreshNeeded()) {
// Completely unexpired cache hit. Just deliver the response.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} else {
// Soft-expired cache hit. We can deliver the cached response,
// but we need to also send the request to the network for
// refreshing.
request.addMarker("cache-hit-refresh-needed");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
// Mark the response as intermediate.
response.intermediate = true;
// Post the intermediate response back to the user and have
// the delivery then forward the request along to the network.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Not much we can do about this.
}
}
});
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.
if (mQuit) {
return;
}
continue;
}
}
}
}public class NetworkDispatcher extends Thread {
……
@Override
public void run() {
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
Request<?> request;
while (true) {
try {
// Take a request from the queue.
request = mQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.
if (mQuit) {
return;
}
continue;
}
try {
request.addMarker("network-queue-take");
// If the request was cancelled already, do not perform the
// network request.
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("network-discard-cancelled");
continue;
}
addTrafficStatsTag(request);
// Perform the network request.
NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);
request.addMarker("network-http-complete");
// If the server returned 304 AND we delivered a response already,
// we're done -- don't deliver a second identical response.
if (networkResponse.notModified && request.hasHadResponseDelivered()) {
request.finish("not-modified");
continue;
}
// Parse the response here on the worker thread.
Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse(networkResponse);
request.addMarker("network-parse-complete");
// Write to cache if applicable.
// TODO: Only update cache metadata instead of entire record for 304s.
if (request.shouldCache() && response.cacheEntry != null) {
mCache.put(request.getCacheKey(), response.cacheEntry);
request.addMarker("network-cache-written");
}
// Post the response back.
request.markDelivered();
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} catch (VolleyError volleyError) {
parseAndDeliverNetworkError(request, volleyError);
} catch (Exception e) {
VolleyLog.e(e, "Unhandled exception %s", e.toString());
mDelivery.postError(request, new VolleyError(e));
}
}
}
}
public class BasicNetwork implements Network {
……
@Override
public NetworkResponse performRequest(Request<?> request) throws VolleyError {
long requestStart = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
while (true) {
HttpResponse httpResponse = null;
byte[] responseContents = null;
Map<String, String> responseHeaders = new HashMap<String, String>();
try {
// Gather headers.
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<String, String>();
addCacheHeaders(headers, request.getCacheEntry());
httpResponse = mHttpStack.performRequest(request, headers);
StatusLine statusLine = httpResponse.getStatusLine();
int statusCode = statusLine.getStatusCode();
responseHeaders = convertHeaders(httpResponse.getAllHeaders());
// Handle cache validation.
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED) {
return new NetworkResponse(HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED,
request.getCacheEntry() == null ? null : request.getCacheEntry().data,
responseHeaders, true);
}
// Some responses such as 204s do not have content. We must check.
if (httpResponse.getEntity() != null) {
responseContents = entityToBytes(httpResponse.getEntity());
} else {
// Add 0 byte response as a way of honestly representing a
// no-content request.
responseContents = new byte[0];
}
// if the request is slow, log it.
long requestLifetime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart;
logSlowRequests(requestLifetime, request, responseContents, statusLine);
if (statusCode < 200 || statusCode > 299) {
throw new IOException();
}
return new NetworkResponse(statusCode, responseContents, responseHeaders, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
……
}
}
}
}
这段方法中大多都是一些网络请求细节方面的东西,我们并不须要太多关心。须要注意的是在第14行调用了HttpStack的performRequest()方法。这里的HttpStack就是在一開始调用newRequestQueue()方法是创建的实例。默认情况下假设系统版本大于9就创建的HurlStack对象,否则创建HttpClientStack对象。
前面已经说过。这两个对象的内部实际就是分别使用HttpURLConnection和HttpClient来发送网络请求的,我们就不再跟进去阅读了。之后会将服务器返回的数据组装成一个NetworkResponse对象进行返回。
在NetworkDispatcher中收到了NetworkResponse这个返回值后又会调用Request的parseNetworkResponse()方法来解析NetworkResponse中的数据,以及将数据写入到缓存。这种方法的实现是交给Request的子类来完毕的,由于不同种类的Request解析的方式也肯定不同。
还记得我们在上一篇文章中学习的自己定义Request的方式吗?当中parseNetworkResponse()这种方法就是必须要重写的。
在解析完了NetworkResponse中的数据之后,又会调用ExecutorDelivery的postResponse()方法来回调解析出的数据。代码例如以下所看到的:
public void postResponse(Request<?> request, Response<?> response, Runnable runnable) {
request.markDelivered();
request.addMarker("post-response");
mResponsePoster.execute(new ResponseDeliveryRunnable(request, response, runnable));
}
private class ResponseDeliveryRunnable implements Runnable {
private final Request mRequest;
private final Response mResponse;
private final Runnable mRunnable;
public ResponseDeliveryRunnable(Request request, Response response, Runnable runnable) {
mRequest = request;
mResponse = response;
mRunnable = runnable;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public void run() {
// If this request has canceled, finish it and don't deliver.
if (mRequest.isCanceled()) {
mRequest.finish("canceled-at-delivery");
return;
}
// Deliver a normal response or error, depending.
if (mResponse.isSuccess()) {
mRequest.deliverResponse(mResponse.result);
} else {
mRequest.deliverError(mResponse.error);
}
// If this is an intermediate response, add a marker, otherwise we're done
// and the request can be finished.
if (mResponse.intermediate) {
mRequest.addMarker("intermediate-response");
} else {
mRequest.finish("done");
}
// If we have been provided a post-delivery runnable, run it.
if (mRunnable != null) {
mRunnable.run();
}
}
}代码尽管不多,但我们并不须要行行阅读,抓住重点看就可以。当中在第22行调用了Request的deliverResponse()方法,有没有感觉非常熟悉?没错。这个就是我们在自己定义Request时须要重写的另外一个方法。每一条网络请求的响应都是回调到这种方法中。最后我们再在这种方法中将响应的数据回调到Response.Listener的onResponse()方法中就能够了。
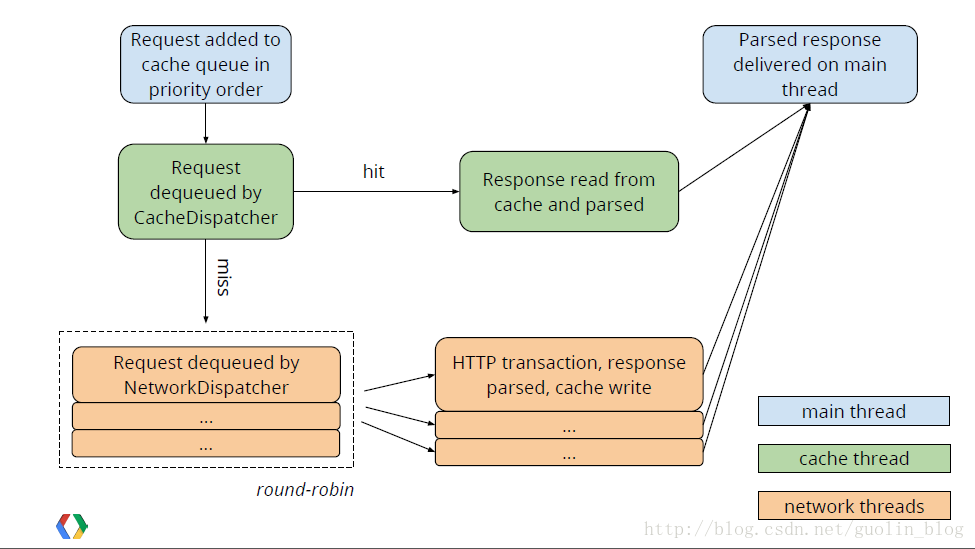
好了。到这里我们就把Volley的完整执行流程所有梳理了一遍,你是不是已经感觉已经非常清晰了呢?对了。还记得在文章一開始的那张流程图吗。刚才还不能理解,如今我们再来又一次看下这张图:
当中蓝色部分代表主线程,绿色部分代表缓存线程,橙色部分代表网络线程。我们在主线程中调用RequestQueue的add()方法来增加一条网络请求。这条请求会先被增加到缓存队列当中,假设发现能够找到对应的缓存结果就直接读取缓存并解析,然后回调给主线程。
假设在缓存中没有找到结果,则将这条请求增加到网络请求队列中,然后处理发送HTTP请求。解析响应结果。写入缓存,并回调主线程。
怎么样,是不是感觉如今理解这张图已经变得轻松简单了?好了,到此为止我们就把Volley的使用方法和源代码所有学习完了。相信你已经对Volley非常熟悉并能够将它应用到实际项目当中了,那么Volley全然解析系列的文章到此结束,感谢大家有耐心看到最后。
关注我的技术公众号,每天都有优质技术文章推送。
关注我的娱乐公众号,工作、学习累了的时候放松一下自己。
微信扫一扫下方二维码就可以关注: