无聊,决定水一把。
CI(CodeIgniter)是我最早接触的一个框架,到现在也只是用了其中一点零碎的方法。一直想对其流程做个小结,却总是因各种各样的“理由”挨着。看见别人图表齐上阵,没那耐心,就从代码说起吧,权当做个笔记,纪念一下。
看在线的用户手册,也知道,将CI下载下来(最新版本2.2.1),解压到机子上,比如www目录,可改个根目录名(原名CodeIgniter-2.2-stable太长),初步目录文件如下,当然这在是windows下面。

访问下,如localhost/ci/index.php,就进入CI默认的Welcome页面

如何一步步加载这个页面的?首先访问的是index.php脚本

1 <?php 2 3 /* 4 *--------------------------------------------------------------- 5 * APPLICATION ENVIRONMENT 6 *--------------------------------------------------------------- 7 * 8 * You can load different configurations depending on your 9 * current environment. Setting the environment also influences 10 * things like logging and error reporting. 11 * 12 * This can be set to anything, but default usage is: 13 * 14 * development 15 * testing 16 * production 17 * 18 * NOTE: If you change these, also change the error_reporting() code below 19 * 20 */ 21 define('ENVIRONMENT', 'development'); 22 /* 23 *--------------------------------------------------------------- 24 * ERROR REPORTING 25 *--------------------------------------------------------------- 26 * 27 * Different environments will require different levels of error reporting. 28 * By default development will show errors but testing and live will hide them. 29 */ 30 31 if (defined('ENVIRONMENT')) 32 { 33 switch (ENVIRONMENT) 34 { 35 case 'development': 36 error_reporting(E_ALL); 37 break; 38 39 case 'testing': 40 case 'production': 41 error_reporting(0); 42 break; 43 44 default: 45 exit('The application environment is not set correctly.'); 46 } 47 } 48 49 /* 50 *--------------------------------------------------------------- 51 * SYSTEM FOLDER NAME 52 *--------------------------------------------------------------- 53 * 54 * This variable must contain the name of your "system" folder. 55 * Include the path if the folder is not in the same directory 56 * as this file. 57 * 58 */ 59 $system_path = 'system'; 60 61 /* 62 *--------------------------------------------------------------- 63 * APPLICATION FOLDER NAME 64 *--------------------------------------------------------------- 65 * 66 * If you want this front controller to use a different "application" 67 * folder then the default one you can set its name here. The folder 68 * can also be renamed or relocated anywhere on your server. If 69 * you do, use a full server path. For more info please see the user guide: 70 * http://codeigniter.com/user_guide/general/managing_apps.html 71 * 72 * NO TRAILING SLASH! 73 * 74 */ 75 $application_folder = 'application'; 76 77 /* 78 * -------------------------------------------------------------------- 79 * DEFAULT CONTROLLER 80 * -------------------------------------------------------------------- 81 * 82 * Normally you will set your default controller in the routes.php file. 83 * You can, however, force a custom routing by hard-coding a 84 * specific controller class/function here. For most applications, you 85 * WILL NOT set your routing here, but it's an option for those 86 * special instances where you might want to override the standard 87 * routing in a specific front controller that shares a common CI installation. 88 * 89 * IMPORTANT: If you set the routing here, NO OTHER controller will be 90 * callable. In essence, this preference limits your application to ONE 91 * specific controller. Leave the function name blank if you need 92 * to call functions dynamically via the URI. 93 * 94 * Un-comment the $routing array below to use this feature 95 * 96 */ 97 // The directory name, relative to the "controllers" folder. Leave blank 98 // if your controller is not in a sub-folder within the "controllers" folder 99 // $routing['directory'] = ''; 100 101 // The controller class file name. Example: Mycontroller 102 // $routing['controller'] = ''; 103 104 // The controller function you wish to be called. 105 // $routing['function'] = ''; 106 107 108 /* 109 * ------------------------------------------------------------------- 110 * CUSTOM CONFIG VALUES 111 * ------------------------------------------------------------------- 112 * 113 * The $assign_to_config array below will be passed dynamically to the 114 * config class when initialized. This allows you to set custom config 115 * items or override any default config values found in the config.php file. 116 * This can be handy as it permits you to share one application between 117 * multiple front controller files, with each file containing different 118 * config values. 119 * 120 * Un-comment the $assign_to_config array below to use this feature 121 * 122 */ 123 // $assign_to_config['name_of_config_item'] = 'value of config item'; 124 125 126 127 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 128 // END OF USER CONFIGURABLE SETTINGS. DO NOT EDIT BELOW THIS LINE 129 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 130 131 /* 132 * --------------------------------------------------------------- 133 * Resolve the system path for increased reliability 134 * --------------------------------------------------------------- 135 */ 136 137 // Set the current directory correctly for CLI requests 138 if (defined('STDIN')) 139 { 140 chdir(dirname(__FILE__)); 141 } 142 143 if (realpath($system_path) !== FALSE) 144 { 145 $system_path = realpath($system_path).'/'; 146 } 147 148 // ensure there's a trailing slash 149 $system_path = rtrim($system_path, '/').'/'; 150 151 // Is the system path correct? 152 if ( ! is_dir($system_path)) 153 { 154 exit("Your system folder path does not appear to be set correctly. Please open the following file and correct this: ".pathinfo(__FILE__, PATHINFO_BASENAME)); 155 } 156 157 /* 158 * ------------------------------------------------------------------- 159 * Now that we know the path, set the main path constants 160 * ------------------------------------------------------------------- 161 */ 162 // The name of THIS file 163 define('SELF', pathinfo(__FILE__, PATHINFO_BASENAME)); 164 165 // The PHP file extension 166 // this global constant is deprecated. 167 define('EXT', '.php'); 168 169 // Path to the system folder 170 define('BASEPATH', str_replace("\", "/", $system_path)); 171 172 // Path to the front controller (this file) 173 define('FCPATH', str_replace(SELF, '', __FILE__)); 174 175 // Name of the "system folder" 176 define('SYSDIR', trim(strrchr(trim(BASEPATH, '/'), '/'), '/')); 177 178 179 // The path to the "application" folder 180 if (is_dir($application_folder)) 181 { 182 define('APPPATH', $application_folder.'/'); 183 } 184 else 185 { 186 if ( ! is_dir(BASEPATH.$application_folder.'/')) 187 { 188 exit("Your application folder path does not appear to be set correctly. Please open the following file and correct this: ".SELF); 189 } 190 191 define('APPPATH', BASEPATH.$application_folder.'/'); 192 } 193 194 /* 195 * -------------------------------------------------------------------- 196 * LOAD THE BOOTSTRAP FILE 197 * -------------------------------------------------------------------- 198 * 199 * And away we go... 200 * 201 */ 202 require_once BASEPATH.'core/CodeIgniter.php'; 203 204 /* End of file index.php */ 205 /* Location: ./index.php */
21行:首先定义一个ENVIRONMENT常量为development,即开发环境。
31-47行:switch语句,由于当前环境是development,所以是设置报告所有级别的错误。
49-59行:$system_path变量定义CI的默认的系统脚本目录是 system,61-75行定义当前默认的供我们主要开发用的目录为 application。
77-105行:全部注释掉了,这里是我们可以强制设置系统加载时默认的目录名($routing['directory'])、控制器名($routing['directory'])和方法名($routing['directory']),虽然一般这些是设置在applicationconfig outes.php中(下图),访问的Welcome页面也是通过这个默认控制器Welcome类进行的,这里只是作为一个选择性的方式,其实没必要弄

108-129行:全部注释掉,用于自定义配置变量(CUSTOM CONFIG VALUES),前一篇说过,任何后端project中,总有些配置信息,只是各个项目或框架加载方式不同,这个$assign_to_config数组就存放我们的自定义配置信息,如$assign_to_config['home'] = 'localhost'; ,之所以注释掉,又是因为这只是一个可选的操作,CI的用户自定义配置信息,一般放在applicationconfig目录下边,以自动加载信息(autoload.php),普通配置信息(config.php)、常量(constants.php)、数据库(database.php)等分开文件存储,所以一般不会在这里的去配置一个要用到的变量,$assign_to_config默认是没有定义的。

从131行到index.php文件末尾主要是对一些路径变量的定义。
137-141行:是为CLI(Command-Interface Line)的调用方式准备的,是直接在Mac/Linux系统上通过终端命令运行脚本,这个在CI中文官网(http://codeigniter.org.cn/user_guide/general/cli.html)也有介绍,如果定义了名为STDIN的常量,则将执行目录改为当前文件所在目录,当然前面没有出现过STDIN这个常量的定义,这里就不会执行了。

143-155行:确定框架存放系统脚本的目录变量$system_path,也就是前面图中的system目录,这里会检测它的有效性,无效的话程序就挂在这里了。
157-192行:定义若干主要目录常量,分别是SELF:当前脚本的文件名、EXT:脚本扩展名、BASEPATH:system目录的路径、FCPATH:当前脚本所在的目录、SYSDIR:system目录的目录名,不改动的话就是system。
179-194行:定义APPPATH常量,确定application所在的目录,就是以后我们主要开发的地方,使用is_dir检测,稍微注意的是is_dir可以检测相对目录,所以实际运行的是if里边的代码,APPPATH得到的是相对路径。
最后打印看看这些变(常)量的值都是啥,有的与存放目录相关:

202行:加载BASEPATH.'core/CodeIgniter.php'脚本,就是system目录下的核心类文件目录下的文件,进入到CI的核心类目录下的文件了。
=====================================================================================================

1 <?php if ( ! defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed'); 2 /** 3 * CodeIgniter 4 * 5 * An open source application development framework for PHP 5.1.6 or newer 6 * 7 * @package CodeIgniter 8 * @author EllisLab Dev Team 9 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2008 - 2014, EllisLab, Inc. 10 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2014 - 2015, British Columbia Institute of Technology (http://bcit.ca/) 11 * @license http://codeigniter.com/user_guide/license.html 12 * @link http://codeigniter.com 13 * @since Version 1.0 14 * @filesource 15 */ 16 17 // ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 18 19 /** 20 * System Initialization File 21 * 22 * Loads the base classes and executes the request. 23 * 24 * @package CodeIgniter 25 * @subpackage codeigniter 26 * @category Front-controller 27 * @author EllisLab Dev Team 28 * @link http://codeigniter.com/user_guide/ 29 */ 30 31 /** 32 * CodeIgniter Version 33 * 34 * @var string 35 * 36 */ 37 define('CI_VERSION', '2.2.1'); 38 39 /** 40 * CodeIgniter Branch (Core = TRUE, Reactor = FALSE) 41 * 42 * @var boolean 43 * 44 */ 45 define('CI_CORE', FALSE); 46 47 /* 48 * ------------------------------------------------------ 49 * Load the global functions 50 * ------------------------------------------------------ 51 */ 52 require(BASEPATH.'core/Common.php'); 53 54 /* 55 * ------------------------------------------------------ 56 * Load the framework constants 57 * ------------------------------------------------------ 58 */ 59 if (defined('ENVIRONMENT') AND file_exists(APPPATH.'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/constants.php')) 60 { 61 require(APPPATH.'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/constants.php'); 62 } 63 else 64 { 65 require(APPPATH.'config/constants.php'); 66 } 67 68 /* 69 * ------------------------------------------------------ 70 * Define a custom error handler so we can log PHP errors 71 * ------------------------------------------------------ 72 */ 73 set_error_handler('_exception_handler'); 74 75 if ( ! is_php('5.3')) 76 { 77 @set_magic_quotes_runtime(0); // Kill magic quotes 78 } 79 80 /* 81 * ------------------------------------------------------ 82 * Set the subclass_prefix 83 * ------------------------------------------------------ 84 * 85 * Normally the "subclass_prefix" is set in the config file. 86 * The subclass prefix allows CI to know if a core class is 87 * being extended via a library in the local application 88 * "libraries" folder. Since CI allows config items to be 89 * overriden via data set in the main index. php file, 90 * before proceeding we need to know if a subclass_prefix 91 * override exists. If so, we will set this value now, 92 * before any classes are loaded 93 * Note: Since the config file data is cached it doesn't 94 * hurt to load it here. 95 */ 96 if (isset($assign_to_config['subclass_prefix']) AND $assign_to_config['subclass_prefix'] != '') 97 { 98 get_config(array('subclass_prefix' => $assign_to_config['subclass_prefix'])); 99 } 100 101 /* 102 * ------------------------------------------------------ 103 * Set a liberal script execution time limit 104 * ------------------------------------------------------ 105 */ 106 if (function_exists("set_time_limit") == TRUE AND @ini_get("safe_mode") == 0) 107 { 108 @set_time_limit(300); 109 } 110 111 /* 112 * ------------------------------------------------------ 113 * Start the timer... tick tock tick tock... 114 * ------------------------------------------------------ 115 */ 116 $BM =& load_class('Benchmark', 'core'); 117 $BM->mark('total_execution_time_start'); 118 $BM->mark('loading_time:_base_classes_start'); 119 120 /* 121 * ------------------------------------------------------ 122 * Instantiate the hooks class 123 * ------------------------------------------------------ 124 */ 125 $EXT =& load_class('Hooks', 'core'); 126 127 /* 128 * ------------------------------------------------------ 129 * Is there a "pre_system" hook? 130 * ------------------------------------------------------ 131 */ 132 $EXT->_call_hook('pre_system'); 133 134 /* 135 * ------------------------------------------------------ 136 * Instantiate the config class 137 * ------------------------------------------------------ 138 */ 139 $CFG =& load_class('Config', 'core'); 140 141 // Do we have any manually set config items in the index.php file? 142 if (isset($assign_to_config)) 143 { 144 $CFG->_assign_to_config($assign_to_config); 145 } 146 147 /* 148 * ------------------------------------------------------ 149 * Instantiate the UTF-8 class 150 * ------------------------------------------------------ 151 * 152 * Note: Order here is rather important as the UTF-8 153 * class needs to be used very early on, but it cannot 154 * properly determine if UTf-8 can be supported until 155 * after the Config class is instantiated. 156 * 157 */ 158 159 $UNI =& load_class('Utf8', 'core'); 160 161 /* 162 * ------------------------------------------------------ 163 * Instantiate the URI class 164 * ------------------------------------------------------ 165 */ 166 $URI =& load_class('URI', 'core'); 167 168 /* 169 * ------------------------------------------------------ 170 * Instantiate the routing class and set the routing 171 * ------------------------------------------------------ 172 */ 173 $RTR =& load_class('Router', 'core'); 174 $RTR->_set_routing(); 175 176 // Set any routing overrides that may exist in the main index file 177 if (isset($routing)) 178 { 179 $RTR->_set_overrides($routing); 180 } 181 182 /* 183 * ------------------------------------------------------ 184 * Instantiate the output class 185 * ------------------------------------------------------ 186 */ 187 $OUT =& load_class('Output', 'core'); 188 189 /* 190 * ------------------------------------------------------ 191 * Is there a valid cache file? If so, we're done... 192 * ------------------------------------------------------ 193 */ 194 if ($EXT->_call_hook('cache_override') === FALSE) 195 { 196 if ($OUT->_display_cache($CFG, $URI) == TRUE) 197 { 198 exit; 199 } 200 } 201 202 /* 203 * ----------------------------------------------------- 204 * Load the security class for xss and csrf support 205 * ----------------------------------------------------- 206 */ 207 $SEC =& load_class('Security', 'core'); 208 209 /* 210 * ------------------------------------------------------ 211 * Load the Input class and sanitize globals 212 * ------------------------------------------------------ 213 */ 214 $IN =& load_class('Input', 'core'); 215 216 /* 217 * ------------------------------------------------------ 218 * Load the Language class 219 * ------------------------------------------------------ 220 */ 221 $LANG =& load_class('Lang', 'core'); 222 223 /* 224 * ------------------------------------------------------ 225 * Load the app controller and local controller 226 * ------------------------------------------------------ 227 * 228 */ 229 // Load the base controller class 230 require BASEPATH.'core/Controller.php'; 231 232 function &get_instance() 233 { 234 return CI_Controller::get_instance(); 235 } 236 237 238 if (file_exists(APPPATH.'core/'.$CFG->config['subclass_prefix'].'Controller.php')) 239 { 240 require APPPATH.'core/'.$CFG->config['subclass_prefix'].'Controller.php'; 241 } 242 243 // Load the local application controller 244 // Note: The Router class automatically validates the controller path using the router->_validate_request(). 245 // If this include fails it means that the default controller in the Routes.php file is not resolving to something valid. 246 if ( ! file_exists(APPPATH.'controllers/'.$RTR->fetch_directory().$RTR->fetch_class().'.php')) 247 { 248 show_error('Unable to load your default controller. Please make sure the controller specified in your Routes.php file is valid.'); 249 } 250 251 include(APPPATH.'controllers/'.$RTR->fetch_directory().$RTR->fetch_class().'.php'); 252 253 // Set a mark point for benchmarking 254 $BM->mark('loading_time:_base_classes_end'); 255 256 /* 257 * ------------------------------------------------------ 258 * Security check 259 * ------------------------------------------------------ 260 * 261 * None of the functions in the app controller or the 262 * loader class can be called via the URI, nor can 263 * controller functions that begin with an underscore 264 */ 265 $class = $RTR->fetch_class(); 266 $method = $RTR->fetch_method(); 267 268 if ( ! class_exists($class) 269 OR strncmp($method, '_', 1) == 0 270 OR in_array(strtolower($method), array_map('strtolower', get_class_methods('CI_Controller'))) 271 ) 272 { 273 if ( ! empty($RTR->routes['404_override'])) 274 { 275 $x = explode('/', $RTR->routes['404_override']); 276 $class = $x[0]; 277 $method = (isset($x[1]) ? $x[1] : 'index'); 278 if ( ! class_exists($class)) 279 { 280 if ( ! file_exists(APPPATH.'controllers/'.$class.'.php')) 281 { 282 show_404("{$class}/{$method}"); 283 } 284 285 include_once(APPPATH.'controllers/'.$class.'.php'); 286 } 287 } 288 else 289 { 290 show_404("{$class}/{$method}"); 291 } 292 } 293 294 /* 295 * ------------------------------------------------------ 296 * Is there a "pre_controller" hook? 297 * ------------------------------------------------------ 298 */ 299 $EXT->_call_hook('pre_controller'); 300 301 /* 302 * ------------------------------------------------------ 303 * Instantiate the requested controller 304 * ------------------------------------------------------ 305 */ 306 // Mark a start point so we can benchmark the controller 307 $BM->mark('controller_execution_time_( '.$class.' / '.$method.' )_start'); 308 309 $CI = new $class(); 310 311 /* 312 * ------------------------------------------------------ 313 * Is there a "post_controller_constructor" hook? 314 * ------------------------------------------------------ 315 */ 316 $EXT->_call_hook('post_controller_constructor'); 317 318 /* 319 * ------------------------------------------------------ 320 * Call the requested method 321 * ------------------------------------------------------ 322 */ 323 // Is there a "remap" function? If so, we call it instead 324 if (method_exists($CI, '_remap')) 325 { 326 $CI->_remap($method, array_slice($URI->rsegments, 2)); 327 } 328 else 329 { 330 // is_callable() returns TRUE on some versions of PHP 5 for private and protected 331 // methods, so we'll use this workaround for consistent behavior 332 if ( ! in_array(strtolower($method), array_map('strtolower', get_class_methods($CI)))) 333 { 334 // Check and see if we are using a 404 override and use it. 335 if ( ! empty($RTR->routes['404_override'])) 336 { 337 $x = explode('/', $RTR->routes['404_override']); 338 $class = $x[0]; 339 $method = (isset($x[1]) ? $x[1] : 'index'); 340 if ( ! class_exists($class)) 341 { 342 if ( ! file_exists(APPPATH.'controllers/'.$class.'.php')) 343 { 344 show_404("{$class}/{$method}"); 345 } 346 347 include_once(APPPATH.'controllers/'.$class.'.php'); 348 unset($CI); 349 $CI = new $class(); 350 } 351 } 352 else 353 { 354 show_404("{$class}/{$method}"); 355 } 356 } 357 358 // Call the requested method. 359 // Any URI segments present (besides the class/function) will be passed to the method for convenience 360 call_user_func_array(array(&$CI, $method), array_slice($URI->rsegments, 2)); 361 } 362 363 364 // Mark a benchmark end point 365 $BM->mark('controller_execution_time_( '.$class.' / '.$method.' )_end'); 366 367 /* 368 * ------------------------------------------------------ 369 * Is there a "post_controller" hook? 370 * ------------------------------------------------------ 371 */ 372 $EXT->_call_hook('post_controller'); 373 374 /* 375 * ------------------------------------------------------ 376 * Send the final rendered output to the browser 377 * ------------------------------------------------------ 378 */ 379 if ($EXT->_call_hook('display_override') === FALSE) 380 { 381 $OUT->_display(); 382 } 383 384 /* 385 * ------------------------------------------------------ 386 * Is there a "post_system" hook? 387 * ------------------------------------------------------ 388 */ 389 $EXT->_call_hook('post_system'); 390 391 /* 392 * ------------------------------------------------------ 393 * Close the DB connection if one exists 394 * ------------------------------------------------------ 395 */ 396 if (class_exists('CI_DB') AND isset($CI->db)) 397 { 398 $CI->db->close(); 399 } 400 401 402 /* End of file CodeIgniter.php */ 403 /* Location: ./system/core/CodeIgniter.php */
在CodeIgniter中,可以看到开头的英文描述,该脚本时系统初始化文件,主要作用是装载基类和执行请求。
31-45行:定义了CI_VERSION常量,描述当前框架版本,CI_CORE常量,目前我也不清楚没探究过,注释是CI的分支,啥意思?
52行:加载系统核心目录下的Common.php文件,Load the global functions,记得前一篇中说到,一般一个项目会将很多公共方法放在一个脚本中加载进来,通常取名Utilities.php,也可是Common.php,这里的Common.php也是这个意思,如它的解释是“加载全局函数”,即这里的函数都是后边直接拿来用的。在这个脚本中有两个重要的方法(目前来说)一个是get_config,单独拿出来如下

1 <?php 2 /** 3 * Loads the main config.php file 4 * 5 * This function lets us grab the config file even if the Config class 6 * hasn't been instantiated yet 7 * 8 * @access private 9 * @return array 10 */ 11 if ( ! function_exists('get_config')) 12 { 13 function &get_config($replace = array()) 14 { 15 static $_config; 16 17 if (isset($_config)) 18 { 19 return $_config[0]; 20 } 21 22 // Is the config file in the environment folder? 23 if ( ! defined('ENVIRONMENT') OR ! file_exists($file_path = APPPATH.'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/config.php')) 24 { 25 $file_path = APPPATH.'config/config.php'; 26 } 27 28 // Fetch the config file 29 if ( ! file_exists($file_path)) 30 { 31 exit('The configuration file does not exist.'); 32 } 33 34 require($file_path); 35 36 // Does the $config array exist in the file? 37 if ( ! isset($config) OR ! is_array($config)) 38 { 39 exit('Your config file does not appear to be formatted correctly.'); 40 } 41 42 // Are any values being dynamically replaced? 43 if (count($replace) > 0) 44 { 45 foreach ($replace as $key => $val) 46 { 47 if (isset($config[$key])) 48 { 49 $config[$key] = $val; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 54 $_config[0] =& $config; 55 return $_config[0]; 56 } 57 }
注释说它加载主要的config.php文件,它使得我们能抓取到配置文件,即便配置类还未被实例化。在CI中,有专门的核心配置类CI_Config来加载配置信息,而这里的get_config方法也能获得主要配置信息,注意是主要配置信息,在application/config目录下有很多其他的配置信息文件(前面在自定义配置变量时也说过CI将配置信息分为了很多文件),其中有一个config.php文件就是get_config能获取到的,这个文件存放的就是基本信息,如果你还想获取其他的配置信息,貌似就要用配置类了。所以如果想添加节本配置信息就在这个里边。
如果是第一次调用get_config方法,先声明静态变量$_config,如果已定义则直接返回它的索引为0的子数组。然后查看APPPATH/config/ENVIRONMENT/config.php文件是否存在(前面打印已知ENVIRONMENT常量值,未改动就是development,原始的框架中没有这个目录,所以这里加载的是application/config/config.php(只加载了这一个,其他的配置文件没有),可以打开看看config.php中定义了一个$config数组,一些基本定义如基础链接、链接后缀、编码、语言、缓存、日志、钩子等等。如果传入一个关联数组,它会将键-值(临时)加入$_config中。总之,get_config方法主要得到的是config.php中定义的数组变量。
与get_config相关的config_item方法则是得到这个数组变量中的某一项。
另一个比较重要的方法是load_class:

1 <?php 2 /** 3 * Class registry 4 * 5 * This function acts as a singleton. If the requested class does not 6 * exist it is instantiated and set to a static variable. If it has 7 * previously been instantiated the variable is returned. 8 * 9 * @access public 10 * @param string the class name being requested 11 * @param string the directory where the class should be found 12 * @param string the class name prefix 13 * @return object 14 */ 15 if ( ! function_exists('load_class')) 16 { 17 function &load_class($class, $directory = 'libraries', $prefix = 'CI_') 18 { 19 static $_classes = array(); 20 21 // Does the class exist? If so, we're done... 22 if (isset($_classes[$class])) 23 { 24 return $_classes[$class]; 25 } 26 27 $name = FALSE; 28 29 // Look for the class first in the local application/libraries folder 30 // then in the native system/libraries folder 31 foreach (array(APPPATH, BASEPATH) as $path) 32 { 33 if (file_exists($path.$directory.'/'.$class.'.php')) 34 { 35 $name = $prefix.$class; 36 37 if (class_exists($name) === FALSE) 38 { 39 require($path.$directory.'/'.$class.'.php'); 40 } 41 42 break; 43 } 44 } 45 46 // Is the request a class extension? If so we load it too 47 if (file_exists(APPPATH.$directory.'/'.config_item('subclass_prefix').$class.'.php')) 48 { 49 $name = config_item('subclass_prefix').$class; 50 51 if (class_exists($name) === FALSE) 52 { 53 require(APPPATH.$directory.'/'.config_item('subclass_prefix').$class.'.php'); 54 } 55 } 56 57 // Did we find the class? 58 if ($name === FALSE) 59 { 60 // Note: We use exit() rather then show_error() in order to avoid a 61 // self-referencing loop with the Excptions class 62 exit('Unable to locate the specified class: '.$class.'.php'); 63 } 64 65 // Keep track of what we just loaded 66 is_loaded($class); 67 68 $_classes[$class] = new $name(); 69 return $_classes[$class]; 70 } 71 }
先看它的注释:这个方法作为一个单例,如果被请求的类没有出现过,则该类会被实例化为一个static variable,如果先前被实例化过则直接返回它。它的三个参数分别是请求的类名、所在目录,类名前缀。可以看到,目录默认是libraries,在application和system中均有它,它就是存放我们自定义的类库或者CI自带的类库的地方,就是自定义工具和CI提供的工具,如日历类、加密类、Ftp类、日志类、Session会话类、Email邮件收发类、JavaScript类、ZIP压缩类等等。或许你已经注意到这里返回的是引用而非值,就像它将加载的类作为静态变量一样,这些细节地方最终提高了整个系统的访问速度。
大致流程:先定义一个静态数组,若数组中已有该类直接返回。先后扫描APPPATH和BASEPATH(前面已知这俩常量值)文件夹下的$directory(默认值是libraries)目录下的$class.php文件是否存在,存在则加上CI的标准类前缀CI_(第三个参数的默认值),在检查类存在与否,存在则require该文件(class_exists()先判断类是否存,存在时就不加载该类文件),一旦文件出现则加载它,并break跳出。注意扫描顺序,先APPPATH后BASEPATH,假如只传第一个参数类名,则优先在我们自己开发的application目录libraries中寻找,然后才去system目录的libraries下边。
由于我们可以对CI的核心类进行扩展(继承它们),所以在扫描完APPPATH和BASEPATH的核心类(名称以CI_为前缀)目录后,还要扫描APPPATH的libraries下边是否有自定义的扩展类(默认以MY_为前缀),有的话也要加载它们,然后实例化一个对应对象(有扩展类是扩展类)存入$_classes静态数组并返回该对象。
对Common.php有大致了解后回到CodeIgniter.php脚本。
54-66行:加载APPPATH.'config/constants.php'脚本,constants.php如同名字一样放的是framework constants,集中定义了一些常量,所以我们在添加常量时就可以放到这里边来定义。

68-78行:首先定义了一个自定义错误处理方法_exception_handler。判断php版本,非5.3关闭magic_quotes引用,这个配置在5.3版本已弃用,提高安全性。
80-99行:这里就是将前面说过的$assign_to_config自定义配置信息数组临时加到$_config数组中,通过get_config方法实现,前面说过$assign_to_config默认是没有定义的,这里的if语句也不会运行。
101-109行:设置自定义脚本最大执行时间为300秒(略长,跑日志的话得更长)
111-118行:加载核心类Benchmark,设置两个标记点。Benchmark基准测试类,就是测试某个开始标记到结束标记之间占用的内存大小、执行时间等信息,测试嘛,当然它要结合CI中一个叫分析器的东西使用。
120-132行:加载核心类Hooks,钩子,设置了一个系统开始执行的钩子(实际未执行,因为application/config/config.php关于它的配置信息默认设置为false,即不启用钩子)。它就就相当于一个触发器,在某个东西要执行前开始执行某些代码,比如控制器加载前、加载后等,一旦控制器加载就运行指定的代码。在这里,它尝试调用一个pre_system(系统执行前)的扩展,默认不执行。
134-145行:加载核心类Config,配置类,它用来加载其他需需要的配置信息,并且它再次加载$assign_to_config数组中配置信息如果该数组定义了的话。
147-159行:加载核心类Utf8,编码类。
161-166行:加载核心类URI,路由。
168-180行:加载核心类Router,路径处理类,_set_routing方法设置好访问路径。如果路径配置数组$routing(前面提到默认是注释掉的)定义了的话,将覆盖默认的路由配置。如果你输入了不存在的脚本路径,在这一步就停住,开始报404了,当然还得Router里边的方法处理。
Router类里面,URI作为它的一个成员存在,实际处理方法在URI类中,熟悉点的都知道CI的访问方式默认是段(segment)的形式,据说更有利于搜索引擎。一个简单的访问方式是这样的localhost/ci/index.php/Controller/Function/Arguments,它们将访问的形式解析为需要的控制器,调用的方法,以及提供的参数列表,当然也可启用传统的查询字符串形式。具体方法略复杂。
187行:加载核心类Output。
189-200行:通过Hooks类和Output类检测有无缓存,有的话直接输出缓存页面,跳出脚本了。这也是在CI的介绍中应用程序流程图部分,当路径处理完后,若有缓存直接输出的原因。

207行:加载核心类Security。
214行:加载核心类Input。
221行:加载核心类Lang,语言处理。
229-235行:加载核心类Controller,它是所有控制器的基类,而get_instance全局方法也能得到它的实例,Controller的牛逼之处在于,它将前面所有通过load_calss载入的libraries(默认)目录(APPPATH和BASEPATH)中的工具库全部实例化为对象,并作为它的属性成员。所以这里的get_instance方法得到的实例也被CI称为超级对象(super object),因为通过这个对象就可以获取所有通过前面加载的对象实例。
238-242行:加载自定义的,对上一步的核心类CI_Controller的扩展类的文件,默认就是MY_Controller,当然前提是如果你扩展了的的话。
243-251行:通过核心类Router的实例,提取当前访问的控制器所在的目录和类名,不存在则报错,存在则加载它,这里就加载了默认的welcome控制器文件。当然如果你自己定义了控制器类文件并访问,也是在这里被include进来的(通过Router类提取子目录$RTR->fetch_directory(),若存在,提取类名$RTR->fetch_class()来找),大概在246行的if语句块,就是检查这个类文件是否存在。
252行:设置一个基准测试结束标记,标记加载基本核心类结束(这些测试默认不会执行)。
256-292行:安全检查。先通过Router类取得类名和要执行的方法名,if条件检查3项内容。1. 上面的243-251行是找到了控制器对应的脚本,并且加载了它,但是假如这只是一个名字匹配的空脚本呢?里边什么都没写就不行了,于是要检查类的定义是否存在(class_exists),2. 以下划线_开头的方法名不能执行,直接报错,当然这是CI自己的的规则,也就是说无论你的类定义的以_开头的方法即使是公有访问属性也不行(除了一个_remap),3. 当类中的方法根控制器核心类中的方法同名时也不行。定义方法名时有个印象就行了。进入if中就很可能会404了。
298行:Hooks类尝试调用一个pre_controller(控制器执行前)的扩展,默认没有。
301-309行:基准测试类设置一个起点标记,目的在于测试控制器执行的时长(默认不显示测试信息),并且实例化前面加载的控制器类,默认的就是Welcome。
315行:Hooks尝试执行post_controller_constructor(所调用的控制器类构造完成后)的扩展,默认没有。
317-364行:开始调用指定的控制器类的指定方法(当然这里是默认控制器Welcome的默认方法index)。看看这个流程,首先一个if判断,如果你的控制器类中有方法_remap,只调用它了,所以前面说以下划线开头的方法除了_remap,这也是CI的一个类的方法的规则,有了这个重映射方法,只调它。默认的Welcome控制器中没有_remap方法,进入else,else中还有个if,再次判断,我们调用的方法是否在这个控制器类中,如果不在的话注定要404了,只是404的调用脚本稍有不同。假如我们得application/config/routes.php文件中的routes['404_override']选项不为空(它就是我们自定义的404错误页脚本路径),将去解析它指定的目录中类名与方法名,如果类定义不存在且文件(自定义404文件)也不存在,就直接调调show_404展示CI默认的404页,只是类定义不存在的话就加载该文件,删除原对象,再new一个新的404对象(348行),当然因类定义不存在,这里理论上是要报错的;假如routes['404_override']选项为空,那么直接启用show_404方法。这个show_404是公用方法,自然是在system/core目录下的Common.php脚本里定义的。
如果我们调用的方法在这个控制器定义中,就要运行这行了:call_user_func_array(array(&$CI, $method), array_slice($URI->rsegments, 2));,调用$CI实例的$method方法,参数就是后边的数组(URI核心类对象的成员rsegments,它被重新索引,从下标2开始是解析的所调用方法的各个参数),$CI就是我们得控制器类实例,$method是对应调用方法。至此,才真正的调用了一个控制器的方法(默认Welcome的index方法),而这还是最简单的情况>3<
它然后就是进入Welcome控制器类调用index方法加载一个默认的页面了,就是开头的欢迎页。在index加载欢迎页($this->load->view(...))又加载了核心类
CodeIgniter.php后面剩下的几行
364行:设置一个基准测试标记点,控制器执行结束标记。
378-381行:如果调用Hooks钩子在输出覆盖(display_override)的扩展失败的话,做最后到浏览器的信息输出(这个输出主要做一些写入缓存,整个方法执行、页面加载等的时间、内存等的统计,头信息的设置、日志的记录等等...)。调用默认方法的话实际上从这开始到CodeIgniter.php结束没执行。
388行:尝试调用Hooks钩子扩展的,在系统执行结束时。
390-398行:如果还有数据库类实例的,关闭掉它的连接。
CodeIgniter.php结束。
OK,来看看调用一个默认的Welcome控制器默认方法都间接加载了哪些文件

可以看到有CI介绍的系统类清单全在里边。
但是最后的Loader类好像没有在CodeIgniter中明确加载,确实,它是在实例化Welcome类时,调它的父类CI_Controller的构造函数里边通过load_class加载的。
如果输入一个错误的链接访问如localhost/ci/index.php/welcome/func,404是当然的

多加载了一个Exception类,这个小细节就体现了CI的原则,“组件的导入和函数的执行只有在被要求的时候才执行,而不是在全局范围”。所以CI还是很不错的一个框架。
时间又被拉长了。。。
日后再补下其他的,主要是数据库和缓存文件的加载麻烦点,其他的还行。
====================================================================================================
补充下CI_Controller核心类,前面,说过在加载我们自己的控制器类时,首先就要加载核心控制器类并会调用它的构造函数初始化它,还是看看它,复习下

1 <?php if ( ! defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed'); 2 /** 3 * CodeIgniter 4 * 5 * An open source application development framework for PHP 5.1.6 or newer 6 * 7 * @package CodeIgniter 8 * @author EllisLab Dev Team 9 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2008 - 2014, EllisLab, Inc. 10 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2014 - 2015, British Columbia Institute of Technology (http://bcit.ca/) 11 * @license http://codeigniter.com/user_guide/license.html 12 * @link http://codeigniter.com 13 * @since Version 1.0 14 * @filesource 15 */ 16 17 // ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 18 19 /** 20 * CodeIgniter Application Controller Class 21 * 22 * This class object is the super class that every library in 23 * CodeIgniter will be assigned to. 24 * 25 * @package CodeIgniter 26 * @subpackage Libraries 27 * @category Libraries 28 * @author EllisLab Dev Team 29 * @link http://codeigniter.com/user_guide/general/controllers.html 30 */ 31 class CI_Controller { 32 33 private static $instance; 34 35 /** 36 * Constructor 37 */ 38 public function __construct() 39 { 40 self::$instance =& $this; 41 42 // Assign all the class objects that were instantiated by the 43 // bootstrap file (CodeIgniter.php) to local class variables 44 // so that CI can run as one big super object. 45 foreach (is_loaded() as $var => $class) 46 { 47 $this->$var =& load_class($class); 48 } 49 50 $this->load =& load_class('Loader', 'core'); 51 52 $this->load->initialize(); 53 54 log_message('debug', "Controller Class Initialized"); 55 } 56 57 public static function &get_instance() 58 { 59 return self::$instance; 60 } 61 } 62 // END Controller class 63 64 /* End of file Controller.php */ 65 /* Location: ./system/core/Controller.php */
看它的构造函数,先循环is_loaded方法返回的数组(参见核心类文件夹system/core/Common.php),前面说过每当通过load_class加载一个核心类时,load_class内部调用is_loaded,传递类名将加载过的核心类对象放入一个静态数组,并返回该静态数组,所以这里调用is_loaded返回加载的核心类数组并循环它,将它们一一置为CI_Controller类的属性成员($this->$var =& load_class($class);),然后直接$this->load =& load_class('Loader', 'core');将加载类Loader也置为它的成员。
下边的get_instance方法返回本类实例,而它是被全局get_instance方法调用的(system/core/CodeIgniter.php),因此全局方法get_instance直接获得了CI_Controller的实例,因此可以调用这些核心类的方法,所以get_instance才有超级方法的称呼。
在CI_Controller构造的方法的倒数第二句:$this->load->initialize();,那些库、辅助函数、语言、第三方包(package)、配置文件等等,如果是需要自动加载的,就是在这里初始化加载的,当然它们虽是自动加载,还是通过我们手动加载比如$this->load->model('someModel')的形式,调用的是model方法加载Model类,自动加载的Model类最后也是通过它来加载的。
回忆下,CI有一个这样的自动加载形式,即不是通过临时手动来调用的,而是当这个框架来加载时就已经加载或初始化的一些类或者文件,在application/config可以找到一个autoload.php(第一次看我还以为是放的__autoload()方法的文件,名字类似),打开它可以看到就是定义一个$autoload数组,以要加载的文件类型名作为键,对应的子数组元素存放文件名(是类的话根类名相关),要加载几个则向该数组中添加几个,典型的方式是:

添加之后,将需要自动加载的文件放在指定目录就给自动加载了。
知道这么一种机制后,再来看看CI_Controller中的$this->load->initialize();,来到Loder核心类,展(tui)开(dao)看看,在Loader中,有这么一些属性成员,典型的如这么两种
protected $_ci_model_paths = array();
protected $_ci_models = array();
前一个是要加载的Model类所在的路径,后一个是存放已加载的Model类,它们不一定是对应的,即有一个加载变量的数组就要有个路径数组,也可能名字不是对应命名的。

1 <?php if ( ! defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed'); 2 /** 3 * CodeIgniter 4 * 5 * An open source application development framework for PHP 5.1.6 or newer 6 * 7 * @package CodeIgniter 8 * @author EllisLab Dev Team 9 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2008 - 2014, EllisLab, Inc. 10 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2014 - 2015, British Columbia Institute of Technology (http://bcit.ca/) 11 * @license http://codeigniter.com/user_guide/license.html 12 * @link http://codeigniter.com 13 * @since Version 1.0 14 * @filesource 15 */ 16 17 // ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 18 19 /** 20 * Loader Class 21 * 22 * Loads views and files 23 * 24 * @package CodeIgniter 25 * @subpackage Libraries 26 * @author EllisLab Dev Team 27 * @category Loader 28 * @link http://codeigniter.com/user_guide/libraries/loader.html 29 */ 30 class CI_Loader { 31 32 // All these are set automatically. Don't mess with them. 33 /** 34 * Nesting level of the output buffering mechanism 35 * 36 * @var int 37 * @access protected 38 */ 39 protected $_ci_ob_level; 40 /** 41 * List of paths to load views from 42 * 43 * @var array 44 * @access protected 45 */ 46 protected $_ci_view_paths = array(); 47 /** 48 * List of paths to load libraries from 49 * 50 * @var array 51 * @access protected 52 */ 53 protected $_ci_library_paths = array(); 54 /** 55 * List of paths to load models from 56 * 57 * @var array 58 * @access protected 59 */ 60 protected $_ci_model_paths = array(); 61 /** 62 * List of paths to load helpers from 63 * 64 * @var array 65 * @access protected 66 */ 67 protected $_ci_helper_paths = array(); 68 /** 69 * List of loaded base classes 70 * Set by the controller class 71 * 72 * @var array 73 * @access protected 74 */ 75 protected $_base_classes = array(); // Set by the controller class 76 /** 77 * List of cached variables 78 * 79 * @var array 80 * @access protected 81 */ 82 protected $_ci_cached_vars = array(); 83 /** 84 * List of loaded classes 85 * 86 * @var array 87 * @access protected 88 */ 89 protected $_ci_classes = array(); 90 /** 91 * List of loaded files 92 * 93 * @var array 94 * @access protected 95 */ 96 protected $_ci_loaded_files = array(); 97 /** 98 * List of loaded models 99 * 100 * @var array 101 * @access protected 102 */ 103 protected $_ci_models = array(); 104 /** 105 * List of loaded helpers 106 * 107 * @var array 108 * @access protected 109 */ 110 protected $_ci_helpers = array(); 111 /** 112 * List of class name mappings 113 * 114 * @var array 115 * @access protected 116 */ 117 protected $_ci_varmap = array('unit_test' => 'unit', 118 'user_agent' => 'agent'); 119 120 /** 121 * Constructor 122 * 123 * Sets the path to the view files and gets the initial output buffering level 124 */ 125 public function __construct() 126 { 127 $this->_ci_ob_level = ob_get_level(); 128 $this->_ci_library_paths = array(APPPATH, BASEPATH); 129 $this->_ci_helper_paths = array(APPPATH, BASEPATH); 130 $this->_ci_model_paths = array(APPPATH); 131 $this->_ci_view_paths = array(APPPATH.'views/' => TRUE); 132 133 log_message('debug', "Loader Class Initialized"); 134 } 135 136 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 137 138 /** 139 * Initialize the Loader 140 * 141 * This method is called once in CI_Controller. 142 * 143 * @param array 144 * @return object 145 */ 146 public function initialize() 147 { 148 $this->_ci_classes = array(); 149 $this->_ci_loaded_files = array(); 150 $this->_ci_models = array(); 151 $this->_base_classes =& is_loaded(); 152 153 $this->_ci_autoloader(); 154 155 return $this; 156 } 157 158 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 159 160 /** 161 * Is Loaded 162 * 163 * A utility function to test if a class is in the self::$_ci_classes array. 164 * This function returns the object name if the class tested for is loaded, 165 * and returns FALSE if it isn't. 166 * 167 * It is mainly used in the form_helper -> _get_validation_object() 168 * 169 * @param string class being checked for 170 * @return mixed class object name on the CI SuperObject or FALSE 171 */ 172 public function is_loaded($class) 173 { 174 if (isset($this->_ci_classes[$class])) 175 { 176 return $this->_ci_classes[$class]; 177 } 178 179 return FALSE; 180 } 181 182 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 183 184 /** 185 * Class Loader 186 * 187 * This function lets users load and instantiate classes. 188 * It is designed to be called from a user's app controllers. 189 * 190 * @param string the name of the class 191 * @param mixed the optional parameters 192 * @param string an optional object name 193 * @return void 194 */ 195 public function library($library = '', $params = NULL, $object_name = NULL) 196 { 197 if (is_array($library)) 198 { 199 foreach ($library as $class) 200 { 201 $this->library($class, $params); 202 } 203 204 return; 205 } 206 207 if ($library == '' OR isset($this->_base_classes[$library])) 208 { 209 return FALSE; 210 } 211 212 if ( ! is_null($params) && ! is_array($params)) 213 { 214 $params = NULL; 215 } 216 217 $this->_ci_load_class($library, $params, $object_name); 218 } 219 220 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 221 222 /** 223 * Model Loader 224 * 225 * This function lets users load and instantiate models. 226 * 227 * @param string the name of the class 228 * @param string name for the model 229 * @param bool database connection 230 * @return void 231 */ 232 public function model($model, $name = '', $db_conn = FALSE) 233 { 234 if (is_array($model)) 235 { 236 foreach ($model as $babe) 237 { 238 $this->model($babe); 239 } 240 return; 241 } 242 243 if ($model == '') 244 { 245 return; 246 } 247 248 $path = ''; 249 250 // Is the model in a sub-folder? If so, parse out the filename and path. 251 if (($last_slash = strrpos($model, '/')) !== FALSE) 252 { 253 // The path is in front of the last slash 254 $path = substr($model, 0, $last_slash + 1); 255 256 // And the model name behind it 257 $model = substr($model, $last_slash + 1); 258 } 259 260 if ($name == '') 261 { 262 $name = $model; 263 } 264 265 if (in_array($name, $this->_ci_models, TRUE)) 266 { 267 return; 268 } 269 270 $CI =& get_instance(); 271 if (isset($CI->$name)) 272 { 273 show_error('The model name you are loading is the name of a resource that is already being used: '.$name); 274 } 275 276 $model = strtolower($model); 277 278 foreach ($this->_ci_model_paths as $mod_path) 279 { 280 if ( ! file_exists($mod_path.'models/'.$path.$model.'.php')) 281 { 282 continue; 283 } 284 285 if ($db_conn !== FALSE AND ! class_exists('CI_DB')) 286 { 287 if ($db_conn === TRUE) 288 { 289 $db_conn = ''; 290 } 291 292 $CI->load->database($db_conn, FALSE, TRUE); 293 } 294 295 if ( ! class_exists('CI_Model')) 296 { 297 load_class('Model', 'core'); 298 } 299 300 require_once($mod_path.'models/'.$path.$model.'.php'); 301 302 $model = ucfirst($model); 303 304 $CI->$name = new $model(); 305 306 $this->_ci_models[] = $name; 307 return; 308 } 309 310 // couldn't find the model 311 show_error('Unable to locate the model you have specified: '.$model); 312 } 313 314 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 315 316 /** 317 * Database Loader 318 * 319 * @param string the DB credentials 320 * @param bool whether to return the DB object 321 * @param bool whether to enable active record (this allows us to override the config setting) 322 * @return object 323 */ 324 public function database($params = '', $return = FALSE, $active_record = NULL) 325 { 326 // Grab the super object 327 $CI =& get_instance(); 328 329 // Do we even need to load the database class? 330 if (class_exists('CI_DB') AND $return == FALSE AND $active_record == NULL AND isset($CI->db) AND is_object($CI->db)) 331 { 332 return FALSE; 333 } 334 335 require_once(BASEPATH.'database/DB.php'); 336 337 if ($return === TRUE) 338 { 339 return DB($params, $active_record); 340 } 341 342 // Initialize the db variable. Needed to prevent 343 // reference errors with some configurations 344 $CI->db = ''; 345 346 // Load the DB class 347 $CI->db =& DB($params, $active_record); 348 } 349 350 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 351 352 /** 353 * Load the Utilities Class 354 * 355 * @return string 356 */ 357 public function dbutil() 358 { 359 if ( ! class_exists('CI_DB')) 360 { 361 $this->database(); 362 } 363 364 $CI =& get_instance(); 365 366 // for backwards compatibility, load dbforge so we can extend dbutils off it 367 // this use is deprecated and strongly discouraged 368 $CI->load->dbforge(); 369 370 require_once(BASEPATH.'database/DB_utility.php'); 371 require_once(BASEPATH.'database/drivers/'.$CI->db->dbdriver.'/'.$CI->db->dbdriver.'_utility.php'); 372 $class = 'CI_DB_'.$CI->db->dbdriver.'_utility'; 373 374 $CI->dbutil = new $class(); 375 } 376 377 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 378 379 /** 380 * Load the Database Forge Class 381 * 382 * @return string 383 */ 384 public function dbforge() 385 { 386 if ( ! class_exists('CI_DB')) 387 { 388 $this->database(); 389 } 390 391 $CI =& get_instance(); 392 393 require_once(BASEPATH.'database/DB_forge.php'); 394 require_once(BASEPATH.'database/drivers/'.$CI->db->dbdriver.'/'.$CI->db->dbdriver.'_forge.php'); 395 $class = 'CI_DB_'.$CI->db->dbdriver.'_forge'; 396 397 $CI->dbforge = new $class(); 398 } 399 400 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 401 402 /** 403 * Load View 404 * 405 * This function is used to load a "view" file. It has three parameters: 406 * 407 * 1. The name of the "view" file to be included. 408 * 2. An associative array of data to be extracted for use in the view. 409 * 3. TRUE/FALSE - whether to return the data or load it. In 410 * some cases it's advantageous to be able to return data so that 411 * a developer can process it in some way. 412 * 413 * @param string 414 * @param array 415 * @param bool 416 * @return void 417 */ 418 public function view($view, $vars = array(), $return = FALSE) 419 { 420 return $this->_ci_load(array('_ci_view' => $view, '_ci_vars' => $this->_ci_object_to_array($vars), '_ci_return' => $return)); 421 } 422 423 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 424 425 /** 426 * Load File 427 * 428 * This is a generic file loader 429 * 430 * @param string 431 * @param bool 432 * @return string 433 */ 434 public function file($path, $return = FALSE) 435 { 436 return $this->_ci_load(array('_ci_path' => $path, '_ci_return' => $return)); 437 } 438 439 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 440 441 /** 442 * Set Variables 443 * 444 * Once variables are set they become available within 445 * the controller class and its "view" files. 446 * 447 * @param array 448 * @param string 449 * @return void 450 */ 451 public function vars($vars = array(), $val = '') 452 { 453 if ($val != '' AND is_string($vars)) 454 { 455 $vars = array($vars => $val); 456 } 457 458 $vars = $this->_ci_object_to_array($vars); 459 460 if (is_array($vars) AND count($vars) > 0) 461 { 462 foreach ($vars as $key => $val) 463 { 464 $this->_ci_cached_vars[$key] = $val; 465 } 466 } 467 } 468 469 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 470 471 /** 472 * Get Variable 473 * 474 * Check if a variable is set and retrieve it. 475 * 476 * @param array 477 * @return void 478 */ 479 public function get_var($key) 480 { 481 return isset($this->_ci_cached_vars[$key]) ? $this->_ci_cached_vars[$key] : NULL; 482 } 483 484 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 485 486 /** 487 * Load Helper 488 * 489 * This function loads the specified helper file. 490 * 491 * @param mixed 492 * @return void 493 */ 494 public function helper($helpers = array()) 495 { 496 foreach ($this->_ci_prep_filename($helpers, '_helper') as $helper) 497 { 498 if (isset($this->_ci_helpers[$helper])) 499 { 500 continue; 501 } 502 503 $ext_helper = APPPATH.'helpers/'.config_item('subclass_prefix').$helper.'.php'; 504 505 // Is this a helper extension request? 506 if (file_exists($ext_helper)) 507 { 508 $base_helper = BASEPATH.'helpers/'.$helper.'.php'; 509 510 if ( ! file_exists($base_helper)) 511 { 512 show_error('Unable to load the requested file: helpers/'.$helper.'.php'); 513 } 514 515 include_once($ext_helper); 516 include_once($base_helper); 517 518 $this->_ci_helpers[$helper] = TRUE; 519 log_message('debug', 'Helper loaded: '.$helper); 520 continue; 521 } 522 523 // Try to load the helper 524 foreach ($this->_ci_helper_paths as $path) 525 { 526 if (file_exists($path.'helpers/'.$helper.'.php')) 527 { 528 include_once($path.'helpers/'.$helper.'.php'); 529 530 $this->_ci_helpers[$helper] = TRUE; 531 log_message('debug', 'Helper loaded: '.$helper); 532 break; 533 } 534 } 535 536 // unable to load the helper 537 if ( ! isset($this->_ci_helpers[$helper])) 538 { 539 show_error('Unable to load the requested file: helpers/'.$helper.'.php'); 540 } 541 } 542 } 543 544 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 545 546 /** 547 * Load Helpers 548 * 549 * This is simply an alias to the above function in case the 550 * user has written the plural form of this function. 551 * 552 * @param array 553 * @return void 554 */ 555 public function helpers($helpers = array()) 556 { 557 $this->helper($helpers); 558 } 559 560 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 561 562 /** 563 * Loads a language file 564 * 565 * @param array 566 * @param string 567 * @return void 568 */ 569 public function language($file = array(), $lang = '') 570 { 571 $CI =& get_instance(); 572 573 if ( ! is_array($file)) 574 { 575 $file = array($file); 576 } 577 578 foreach ($file as $langfile) 579 { 580 $CI->lang->load($langfile, $lang); 581 } 582 } 583 584 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 585 586 /** 587 * Loads a config file 588 * 589 * @param string 590 * @param bool 591 * @param bool 592 * @return void 593 */ 594 public function config($file = '', $use_sections = FALSE, $fail_gracefully = FALSE) 595 { 596 $CI =& get_instance(); 597 $CI->config->load($file, $use_sections, $fail_gracefully); 598 } 599 600 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 601 602 /** 603 * Driver 604 * 605 * Loads a driver library 606 * 607 * @param string the name of the class 608 * @param mixed the optional parameters 609 * @param string an optional object name 610 * @return void 611 */ 612 public function driver($library = '', $params = NULL, $object_name = NULL) 613 { 614 if ( ! class_exists('CI_Driver_Library')) 615 { 616 // we aren't instantiating an object here, that'll be done by the Library itself 617 require BASEPATH.'libraries/Driver.php'; 618 } 619 620 if ($library == '') 621 { 622 return FALSE; 623 } 624 625 // We can save the loader some time since Drivers will *always* be in a subfolder, 626 // and typically identically named to the library 627 if ( ! strpos($library, '/')) 628 { 629 $library = ucfirst($library).'/'.$library; 630 } 631 632 return $this->library($library, $params, $object_name); 633 } 634 635 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 636 637 /** 638 * Add Package Path 639 * 640 * Prepends a parent path to the library, model, helper, and config path arrays 641 * 642 * @param string 643 * @param boolean 644 * @return void 645 */ 646 public function add_package_path($path, $view_cascade=TRUE) 647 { 648 $path = rtrim($path, '/').'/'; 649 650 array_unshift($this->_ci_library_paths, $path); 651 array_unshift($this->_ci_model_paths, $path); 652 array_unshift($this->_ci_helper_paths, $path); 653 654 $this->_ci_view_paths = array($path.'views/' => $view_cascade) + $this->_ci_view_paths; 655 656 // Add config file path 657 $config =& $this->_ci_get_component('config'); 658 array_unshift($config->_config_paths, $path); 659 } 660 661 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 662 663 /** 664 * Get Package Paths 665 * 666 * Return a list of all package paths, by default it will ignore BASEPATH. 667 * 668 * @param string 669 * @return void 670 */ 671 public function get_package_paths($include_base = FALSE) 672 { 673 return $include_base === TRUE ? $this->_ci_library_paths : $this->_ci_model_paths; 674 } 675 676 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 677 678 /** 679 * Remove Package Path 680 * 681 * Remove a path from the library, model, and helper path arrays if it exists 682 * If no path is provided, the most recently added path is removed. 683 * 684 * @param type 685 * @param bool 686 * @return type 687 */ 688 public function remove_package_path($path = '', $remove_config_path = TRUE) 689 { 690 $config =& $this->_ci_get_component('config'); 691 692 if ($path == '') 693 { 694 $void = array_shift($this->_ci_library_paths); 695 $void = array_shift($this->_ci_model_paths); 696 $void = array_shift($this->_ci_helper_paths); 697 $void = array_shift($this->_ci_view_paths); 698 $void = array_shift($config->_config_paths); 699 } 700 else 701 { 702 $path = rtrim($path, '/').'/'; 703 foreach (array('_ci_library_paths', '_ci_model_paths', '_ci_helper_paths') as $var) 704 { 705 if (($key = array_search($path, $this->{$var})) !== FALSE) 706 { 707 unset($this->{$var}[$key]); 708 } 709 } 710 711 if (isset($this->_ci_view_paths[$path.'views/'])) 712 { 713 unset($this->_ci_view_paths[$path.'views/']); 714 } 715 716 if (($key = array_search($path, $config->_config_paths)) !== FALSE) 717 { 718 unset($config->_config_paths[$key]); 719 } 720 } 721 722 // make sure the application default paths are still in the array 723 $this->_ci_library_paths = array_unique(array_merge($this->_ci_library_paths, array(APPPATH, BASEPATH))); 724 $this->_ci_helper_paths = array_unique(array_merge($this->_ci_helper_paths, array(APPPATH, BASEPATH))); 725 $this->_ci_model_paths = array_unique(array_merge($this->_ci_model_paths, array(APPPATH))); 726 $this->_ci_view_paths = array_merge($this->_ci_view_paths, array(APPPATH.'views/' => TRUE)); 727 $config->_config_paths = array_unique(array_merge($config->_config_paths, array(APPPATH))); 728 } 729 730 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 731 732 /** 733 * Loader 734 * 735 * This function is used to load views and files. 736 * Variables are prefixed with _ci_ to avoid symbol collision with 737 * variables made available to view files 738 * 739 * @param array 740 * @return void 741 */ 742 protected function _ci_load($_ci_data) 743 { 744 // Set the default data variables 745 foreach (array('_ci_view', '_ci_vars', '_ci_path', '_ci_return') as $_ci_val) 746 { 747 $$_ci_val = ( ! isset($_ci_data[$_ci_val])) ? FALSE : $_ci_data[$_ci_val]; 748 } 749 750 $file_exists = FALSE; 751 752 // Set the path to the requested file 753 if ($_ci_path != '') 754 { 755 $_ci_x = explode('/', $_ci_path); 756 $_ci_file = end($_ci_x); 757 } 758 else 759 { 760 $_ci_ext = pathinfo($_ci_view, PATHINFO_EXTENSION); 761 $_ci_file = ($_ci_ext == '') ? $_ci_view.'.php' : $_ci_view; 762 763 foreach ($this->_ci_view_paths as $view_file => $cascade) 764 { 765 if (file_exists($view_file.$_ci_file)) 766 { 767 $_ci_path = $view_file.$_ci_file; 768 $file_exists = TRUE; 769 break; 770 } 771 772 if ( ! $cascade) 773 { 774 break; 775 } 776 } 777 } 778 779 if ( ! $file_exists && ! file_exists($_ci_path)) 780 { 781 show_error('Unable to load the requested file: '.$_ci_file); 782 } 783 784 // This allows anything loaded using $this->load (views, files, etc.) 785 // to become accessible from within the Controller and Model functions. 786 787 $_ci_CI =& get_instance(); 788 foreach (get_object_vars($_ci_CI) as $_ci_key => $_ci_var) 789 { 790 if ( ! isset($this->$_ci_key)) 791 { 792 $this->$_ci_key =& $_ci_CI->$_ci_key; 793 } 794 } 795 796 /* 797 * Extract and cache variables 798 * 799 * You can either set variables using the dedicated $this->load_vars() 800 * function or via the second parameter of this function. We'll merge 801 * the two types and cache them so that views that are embedded within 802 * other views can have access to these variables. 803 */ 804 if (is_array($_ci_vars)) 805 { 806 $this->_ci_cached_vars = array_merge($this->_ci_cached_vars, $_ci_vars); 807 } 808 extract($this->_ci_cached_vars); 809 810 /* 811 * Buffer the output 812 * 813 * We buffer the output for two reasons: 814 * 1. Speed. You get a significant speed boost. 815 * 2. So that the final rendered template can be 816 * post-processed by the output class. Why do we 817 * need post processing? For one thing, in order to 818 * show the elapsed page load time. Unless we 819 * can intercept the content right before it's sent to 820 * the browser and then stop the timer it won't be accurate. 821 */ 822 ob_start(); 823 824 // If the PHP installation does not support short tags we'll 825 // do a little string replacement, changing the short tags 826 // to standard PHP echo statements. 827 828 if ((bool) @ini_get('short_open_tag') === FALSE AND config_item('rewrite_short_tags') == TRUE) 829 { 830 echo eval('?>'.preg_replace("/;*s*?>/", "; ?>", str_replace('<?=', '<?php echo ', file_get_contents($_ci_path)))); 831 } 832 else 833 { 834 include($_ci_path); // include() vs include_once() allows for multiple views with the same name 835 } 836 837 log_message('debug', 'File loaded: '.$_ci_path); 838 839 // Return the file data if requested 840 if ($_ci_return === TRUE) 841 { 842 $buffer = ob_get_contents(); 843 @ob_end_clean(); 844 return $buffer; 845 } 846 847 /* 848 * Flush the buffer... or buff the flusher? 849 * 850 * In order to permit views to be nested within 851 * other views, we need to flush the content back out whenever 852 * we are beyond the first level of output buffering so that 853 * it can be seen and included properly by the first included 854 * template and any subsequent ones. Oy! 855 * 856 */ 857 if (ob_get_level() > $this->_ci_ob_level + 1) 858 { 859 ob_end_flush(); 860 } 861 else 862 { 863 $_ci_CI->output->append_output(ob_get_contents()); 864 @ob_end_clean(); 865 } 866 } 867 868 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 869 870 /** 871 * Load class 872 * 873 * This function loads the requested class. 874 * 875 * @param string the item that is being loaded 876 * @param mixed any additional parameters 877 * @param string an optional object name 878 * @return void 879 */ 880 protected function _ci_load_class($class, $params = NULL, $object_name = NULL) 881 { 882 // Get the class name, and while we're at it trim any slashes. 883 // The directory path can be included as part of the class name, 884 // but we don't want a leading slash 885 $class = str_replace('.php', '', trim($class, '/')); 886 887 // Was the path included with the class name? 888 // We look for a slash to determine this 889 $subdir = ''; 890 if (($last_slash = strrpos($class, '/')) !== FALSE) 891 { 892 // Extract the path 893 $subdir = substr($class, 0, $last_slash + 1); 894 895 // Get the filename from the path 896 $class = substr($class, $last_slash + 1); 897 } 898 899 // We'll test for both lowercase and capitalized versions of the file name 900 foreach (array(ucfirst($class), strtolower($class)) as $class) 901 { 902 $subclass = APPPATH.'libraries/'.$subdir.config_item('subclass_prefix').$class.'.php'; 903 904 // Is this a class extension request? 905 if (file_exists($subclass)) 906 { 907 $baseclass = BASEPATH.'libraries/'.ucfirst($class).'.php'; 908 909 if ( ! file_exists($baseclass)) 910 { 911 log_message('error', "Unable to load the requested class: ".$class); 912 show_error("Unable to load the requested class: ".$class); 913 } 914 915 // Safety: Was the class already loaded by a previous call? 916 if (in_array($subclass, $this->_ci_loaded_files)) 917 { 918 // Before we deem this to be a duplicate request, let's see 919 // if a custom object name is being supplied. If so, we'll 920 // return a new instance of the object 921 if ( ! is_null($object_name)) 922 { 923 $CI =& get_instance(); 924 if ( ! isset($CI->$object_name)) 925 { 926 return $this->_ci_init_class($class, config_item('subclass_prefix'), $params, $object_name); 927 } 928 } 929 930 $is_duplicate = TRUE; 931 log_message('debug', $class." class already loaded. Second attempt ignored."); 932 return; 933 } 934 935 include_once($baseclass); 936 include_once($subclass); 937 $this->_ci_loaded_files[] = $subclass; 938 939 return $this->_ci_init_class($class, config_item('subclass_prefix'), $params, $object_name); 940 } 941 942 // Lets search for the requested library file and load it. 943 $is_duplicate = FALSE; 944 foreach ($this->_ci_library_paths as $path) 945 { 946 $filepath = $path.'libraries/'.$subdir.$class.'.php'; 947 948 // Does the file exist? No? Bummer... 949 if ( ! file_exists($filepath)) 950 { 951 continue; 952 } 953 954 // Safety: Was the class already loaded by a previous call? 955 if (in_array($filepath, $this->_ci_loaded_files)) 956 { 957 // Before we deem this to be a duplicate request, let's see 958 // if a custom object name is being supplied. If so, we'll 959 // return a new instance of the object 960 if ( ! is_null($object_name)) 961 { 962 $CI =& get_instance(); 963 if ( ! isset($CI->$object_name)) 964 { 965 return $this->_ci_init_class($class, '', $params, $object_name); 966 } 967 } 968 969 $is_duplicate = TRUE; 970 log_message('debug', $class." class already loaded. Second attempt ignored."); 971 return; 972 } 973 974 include_once($filepath); 975 $this->_ci_loaded_files[] = $filepath; 976 return $this->_ci_init_class($class, '', $params, $object_name); 977 } 978 979 } // END FOREACH 980 981 // One last attempt. Maybe the library is in a subdirectory, but it wasn't specified? 982 if ($subdir == '') 983 { 984 $path = strtolower($class).'/'.$class; 985 return $this->_ci_load_class($path, $params); 986 } 987 988 // If we got this far we were unable to find the requested class. 989 // We do not issue errors if the load call failed due to a duplicate request 990 if ($is_duplicate == FALSE) 991 { 992 log_message('error', "Unable to load the requested class: ".$class); 993 show_error("Unable to load the requested class: ".$class); 994 } 995 } 996 997 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 998 999 /** 1000 * Instantiates a class 1001 * 1002 * @param string 1003 * @param string 1004 * @param bool 1005 * @param string an optional object name 1006 * @return null 1007 */ 1008 protected function _ci_init_class($class, $prefix = '', $config = FALSE, $object_name = NULL) 1009 { 1010 // Is there an associated config file for this class? Note: these should always be lowercase 1011 if ($config === NULL) 1012 { 1013 // Fetch the config paths containing any package paths 1014 $config_component = $this->_ci_get_component('config'); 1015 1016 if (is_array($config_component->_config_paths)) 1017 { 1018 // Break on the first found file, thus package files 1019 // are not overridden by default paths 1020 foreach ($config_component->_config_paths as $path) 1021 { 1022 // We test for both uppercase and lowercase, for servers that 1023 // are case-sensitive with regard to file names. Check for environment 1024 // first, global next 1025 if (defined('ENVIRONMENT') AND file_exists($path .'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/'.strtolower($class).'.php')) 1026 { 1027 include($path .'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/'.strtolower($class).'.php'); 1028 break; 1029 } 1030 elseif (defined('ENVIRONMENT') AND file_exists($path .'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/'.ucfirst(strtolower($class)).'.php')) 1031 { 1032 include($path .'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/'.ucfirst(strtolower($class)).'.php'); 1033 break; 1034 } 1035 elseif (file_exists($path .'config/'.strtolower($class).'.php')) 1036 { 1037 include($path .'config/'.strtolower($class).'.php'); 1038 break; 1039 } 1040 elseif (file_exists($path .'config/'.ucfirst(strtolower($class)).'.php')) 1041 { 1042 include($path .'config/'.ucfirst(strtolower($class)).'.php'); 1043 break; 1044 } 1045 } 1046 } 1047 } 1048 1049 if ($prefix == '') 1050 { 1051 if (class_exists('CI_'.$class)) 1052 { 1053 $name = 'CI_'.$class; 1054 } 1055 elseif (class_exists(config_item('subclass_prefix').$class)) 1056 { 1057 $name = config_item('subclass_prefix').$class; 1058 } 1059 else 1060 { 1061 $name = $class; 1062 } 1063 } 1064 else 1065 { 1066 $name = $prefix.$class; 1067 } 1068 1069 // Is the class name valid? 1070 if ( ! class_exists($name)) 1071 { 1072 log_message('error', "Non-existent class: ".$name); 1073 show_error("Non-existent class: ".$class); 1074 } 1075 1076 // Set the variable name we will assign the class to 1077 // Was a custom class name supplied? If so we'll use it 1078 $class = strtolower($class); 1079 1080 if (is_null($object_name)) 1081 { 1082 $classvar = ( ! isset($this->_ci_varmap[$class])) ? $class : $this->_ci_varmap[$class]; 1083 } 1084 else 1085 { 1086 $classvar = $object_name; 1087 } 1088 1089 // Save the class name and object name 1090 $this->_ci_classes[$class] = $classvar; 1091 1092 // Instantiate the class 1093 $CI =& get_instance(); 1094 if ($config !== NULL) 1095 { 1096 $CI->$classvar = new $name($config); 1097 } 1098 else 1099 { 1100 $CI->$classvar = new $name; 1101 } 1102 } 1103 1104 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 1105 1106 /** 1107 * Autoloader 1108 * 1109 * The config/autoload.php file contains an array that permits sub-systems, 1110 * libraries, and helpers to be loaded automatically. 1111 * 1112 * @param array 1113 * @return void 1114 */ 1115 private function _ci_autoloader() 1116 { 1117 if (defined('ENVIRONMENT') AND file_exists(APPPATH.'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/autoload.php')) 1118 { 1119 include(APPPATH.'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/autoload.php'); 1120 } 1121 else 1122 { 1123 include(APPPATH.'config/autoload.php'); 1124 } 1125 1126 if ( ! isset($autoload)) 1127 { 1128 return FALSE; 1129 } 1130 1131 // Autoload packages 1132 if (isset($autoload['packages'])) 1133 { 1134 foreach ($autoload['packages'] as $package_path) 1135 { 1136 $this->add_package_path($package_path); 1137 } 1138 } 1139 1140 // Load any custom config file 1141 if (count($autoload['config']) > 0) 1142 { 1143 $CI =& get_instance(); 1144 foreach ($autoload['config'] as $key => $val) 1145 { 1146 $CI->config->load($val); 1147 } 1148 } 1149 1150 // Autoload helpers and languages 1151 foreach (array('helper', 'language') as $type) 1152 { 1153 if (isset($autoload[$type]) AND count($autoload[$type]) > 0) 1154 { 1155 $this->$type($autoload[$type]); 1156 } 1157 } 1158 1159 // A little tweak to remain backward compatible 1160 // The $autoload['core'] item was deprecated 1161 if ( ! isset($autoload['libraries']) AND isset($autoload['core'])) 1162 { 1163 $autoload['libraries'] = $autoload['core']; 1164 } 1165 1166 // Load libraries 1167 if (isset($autoload['libraries']) AND count($autoload['libraries']) > 0) 1168 { 1169 // Load the database driver. 1170 if (in_array('database', $autoload['libraries'])) 1171 { 1172 $this->database(); 1173 $autoload['libraries'] = array_diff($autoload['libraries'], array('database')); 1174 } 1175 1176 // Load all other libraries 1177 foreach ($autoload['libraries'] as $item) 1178 { 1179 $this->library($item); 1180 } 1181 } 1182 1183 // Autoload models 1184 if (isset($autoload['model'])) 1185 { 1186 $this->model($autoload['model']); 1187 } 1188 } 1189 1190 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 1191 1192 /** 1193 * Object to Array 1194 * 1195 * Takes an object as input and converts the class variables to array key/vals 1196 * 1197 * @param object 1198 * @return array 1199 */ 1200 protected function _ci_object_to_array($object) 1201 { 1202 return (is_object($object)) ? get_object_vars($object) : $object; 1203 } 1204 1205 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 1206 1207 /** 1208 * Get a reference to a specific library or model 1209 * 1210 * @param string 1211 * @return bool 1212 */ 1213 protected function &_ci_get_component($component) 1214 { 1215 $CI =& get_instance(); 1216 return $CI->$component; 1217 } 1218 1219 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 1220 1221 /** 1222 * Prep filename 1223 * 1224 * This function preps the name of various items to make loading them more reliable. 1225 * 1226 * @param mixed 1227 * @param string 1228 * @return array 1229 */ 1230 protected function _ci_prep_filename($filename, $extension) 1231 { 1232 if ( ! is_array($filename)) 1233 { 1234 return array(strtolower(str_replace('.php', '', str_replace($extension, '', $filename)).$extension)); 1235 } 1236 else 1237 { 1238 foreach ($filename as $key => $val) 1239 { 1240 $filename[$key] = strtolower(str_replace('.php', '', str_replace($extension, '', $val)).$extension); 1241 } 1242 1243 return $filename; 1244 } 1245 } 1246 } 1247 1248 /* End of file Loader.php */ 1249 /* Location: ./system/core/Loader.php */
125行:它的构造函数,主要是对几个类型文件的路径变量初始化,如library库文件的是array(APPPATH, BASEPATH),预示着它会到这两个目下取搜索,model数组是array(APPPATH),就只在供我们开发的APPPATH下边去搜索加载。
146行:就是它的initialize()函数,主要做两件事,前面几行将即将放要加载的类或文件的数组置空,如$this->_ci_models = array();,对装载基础类的变量填满核心类,如$this->_base_classes =& is_loaded();(前面说过is_loaded可返回所有加载过的核心类),后面的 $this->_ci_autoloader(); 则开始执行自动CI需要自动加载的文件的流程了。
1115行:转到_ci_autoloader()的定义,看看它的注释,意思是config/autoload.php包含了一个数组,允许子系统(sub-systems)、库、辅助函数等的自动加载。
它先试图加载APPPATH.'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/autoload.php'(这两个变量参考前面),默认CI的文件目录中是没有development这个目录的, 所以无论你把他放在哪个目录下,再在它下面寻找autoload文件肯定是不存在的,然后,它加载的是APPPATH.'config/autoload.php',供我们开发的application目录下的配置信息目录下的autoload.php。
1131行:成功找到autoload.php并include后,第一个加载的脚本类型是package(包),package这个键的元素应该是目录,例如APPPATH.'third_party',也就是第三方的扩展包,如果要用这个,那么就得在application下新建一个third_party目录,里边存放这些东西,,在$autoload['package']中添加对应目录字符串,名字可以改。foreach调用了add_package_path方法,看看它在干啥。
646行:先将传进来的$path变量,即存放package的目录,分别添加到_ci_library_paths(存放库文件目录的数组,后面类似)、_ci_model_paths、_ci_helper_paths的开头,包括存放视图的数组也加进去了在第三方包目录下的对应的视图变量array($path.'view'=>TRUE),关于这个存放视图的数组成员,还没看过它是干啥的。然后通过_ci_get_component得到Config核心类的对象,将$path加入到它的成员_config_paths数组中,这个数组原有的元素也是个路径:APPPATH。$path变量是“第三方”目录(APPPATH.'third_party'),从这里连续的将这个$path变量加到Model、Helper等数组中,这个第三方的package大有独立系统的意思,原本我们自己开发的话只是加载application目录下边的models、helpers、views等,这里好像是这些文件也要到$path目录下再去找一遍,当然咯,前提第你的application下面要有个third_party目录,并且里面也放了一些文件。回到1131行 // Autoload packages 下边的if就是将路径$path加到Loader类的路径成员变量中。
1140行:载入任何自定义的配置文件。检查$autoload['config']是否有元素,通过超级方法get_instance来调用核心类Config,并通过它的成员函数load加载这些配置文件。注意它主要是加载application/config下的文件。
1150行:加载helper和language文件。分别调用了helper和language成员方法,就相当于我们在控制器中这样用:$this->load->helper(...),所以这个_ci_autoloader方法实际调用还是最后、公共的加载方法。
494行:以helper为例,看它加载时都干了啥。辅助函数用到的几率也算多的,比如你自己单独就数组的一些特殊处理作为一个辅助函数文件。首先加载辅助函数传过来的参数可以是单个文件名字符串或多个名称组成的数组变量,调用_ci_prep_filename这个方法返回的数组进行foreach,1230行的_ci_prep_filename函数功能是对传入的辅助函数文件名去掉末尾的.php扩展名,加上_helper后缀。所以当我们加载辅助函数时直接是这样$this->load->helper('array');就行,传全名反而错了。

回到helper函数,如果已经加载过,continue至下一个helper变量。首先找的是这样的:$ext_helper = APPPATH.'helpers/'.config_item('subclass_prefix').$helper.'.php',子类前缀默认是MY_,这里的$helper已经是经过上面处理过的,而看变量名猜得到就是对已有的辅助函数的扩展,如上边的array_helper.php是在system/helpers目录下,我现在要对它扩展,就定义个MY_array_helper.php就行了,注意辅助函数只是定义一些函数,不是单个类。如果辅助函数扩展出现了,就要先加载原有的基础辅助函数文件(BASEPATH.'helpers/'.$helper.'.php',在系统目录下),因此518-513行对基础文件进行检查。只有基础文件也出现了才都include(实际用include_once)它们。假如我没有扩展,就要走到524行,循环_ci_helper_paths这个属性成员来寻找,前面提到CI的Loader核心类的一些成员,是已经加载过得类弄到一个数组中,这是一种类型变量,然后是另外一种将各种类型文件即将出现的目录弄到一起,是另外一种类型的,毫无疑问,它里面就是helper可能存在的目录集合。它初始化是这样的:

前面在看到加载package时也看到,如果存在package且$autoload写入了对应的目录名,这些目录是会加到_ci_helper_paths数组前面的,当然默认没有这个。所以在524行foreach这个变量时,首先找APPPATH.'helpers/'.$helper.'.php',再找BATHPATH.'helpers/'.$helper.'.php',所以就是说,在application/helpers目录下边不都是扩展原来的,新写的也可以。找到了就include,并且加入到装载已经加载过的辅助函数的数组_ci_helpers中(再次加载时就直接返回),没找到就show_error展示错误页面。
569行:回到自动加载函数_ci_autoloader的1151行,加载language脚本。同理在$autoload['language']下面如果定义有一些需要加载的语言脚本名称,则foreach每一个元素,然后跳到569行执行language函数。在language函数里面。先通过get_instance()函数获得超级对象,也就是控制器基类CI_Controller,直接调用核心类Lang对象成员(前面的打印结果中可以到,语言核心类作为基础类已经被加载完毕)的load方法加载,传入数组就扫描加载它们,那就进入到CI_Lang类这种看看这个load方法的大致流程。
传送到system/core/Lang.php里边,66行:首先如果有.php扩展名就去掉,然后给文件名加上_lang后缀,所以写语言脚本时在命名时就要加上_lang,而加载时传入参数你也不必写比如eng_lang,它会给你加,有也会去掉再加,所以完全没必要。然后连接上.php后缀,在CI_Lang核心类中有一个成员变量is_loaded会记录下所有已经加载过的语言文件,所以接下来先检查是否被加载过,若加载直接返回。然后获得config文件中的$config变量(Common.php中的get_config全局方法,加载application/config/config.php),然后根据$config['language']的值(默认是english)确定$deft_lang和$idiom的值,先不管它们来干什么,接下来就是寻找language file并加载它们。如果传入第二个参数$idiom,它将在比如application/language/$idiom这个目录下去寻找语言文件,所以这个参数决定了你将加载什么类型的文件,当然你不穿默认就是$config['language']的值。

注意到CI_Lang类的load方法的最后一个参数$alt_path表示一个可选的路径,所以接下来会以它来拼一个路径寻找语言文件(file_exists($alt_path.'language/'.$idiom.'/'.$langfile),$alt_path为空,$idom默认为english),这里不存在这个路径文件,走else,调用Loader类的get_package_paths方法返回一个路径数组,这个数组默认是array(APPPATH,BASEPATH),转了一圈还是先找application/language/下的语言文件,再找system/language/下的,所以如果自定义语言文件,大可以放在前者目录下就行了,可以少找一步。一旦找到了就加载并break退出循环,如果需要返回变量(122行)则返回$lang (这是定义语言文件时所用),否则将记录已加载过得语言文件(127),将新加入的$lang变量merge到Lang类的language成员中。
Lang还有个方法line,这个就是返回$lang这个数组中的某一个元素对应的值,比如传入'lovely',它将返回$lang['lovely']的值。
综上,语言文件的加载就是在找application/language和system/language两个目录,定义文件时比如现在定义一个汉语的放在迁移个目录下,可以这样:现在application/language下新建一个目录chinese,我现在翻译湖北话,文件名定义为hubei_lang.php,里边可以是$lang['have a meal'] = '七饭';,将该文件放在application/language/chinese目录下,然后在控制器某方法中,载入语言文件$this->lang->load('hubei', 'chinese'); echo $this->lang->line('have a meal');。一个湖北方言版的网页就此诞生-_-#。这就是CI所谓的“国际化”,使用不同的语言呈现同一页面。
这就是Loader中的language方法,对语言文件加载和使用的简单流程。
回到Loader核心类,1152行到1158行,就是加载辅助函数和语言脚本。
1162行:检查$autoload中是否有core为键名的元素,如果有,将它赋给libraries为键名的元素,这大概是CI以前将工具库的类的键名称为core,后来弃用,改为libraries。
1168行:开始加载library,先检查$autoload['libraries']是否有值database,即自动加载数据库,这里就调用了Loader类的database方法,然后将database元素从$autoload['libraries']去除。数据库加载单说。
1178行:开始加载所有需要自动加载的library。开始调用Loader的library方法。
195行:library函数的定义。第一个参数是待加载的库的名称,第二、三个参数默认为null。库名参数可以是单个string或者包含多个元素的数组(多维也行)。如果是数组,则要加载多个,这里使用了递归,如果是数组扫描数组继续调用该方法。以单个string库名为例。如果第一个$library参数为空或者已经存在于Loader的数据成员_base_classes(它记录着Loader类通过load_class加载过的类,所以library实际上和core文件夹中的核心类在这儿都归为了基础类)中,则直接返回false。第二个参数默认空,走217行,调用成员方法_ci_load_class执行加载。
880行:_ci_load_class函数定义。
首先,去.php扩展名。然后解析子目录,从890行到898行。关于子目录,就是允许在传递给library方法的类文件名时可以包含路径,例如现在A公司针对XML开发了几个类,针对Mail也开发了有,B公司也做了这些,它们各自使用方式稍有差别,各有好坏,把它们均放在application/libraries下面时,我们就会先建一个A目录,里边放A的各个类,再建个B目录,再放B的各个类,因此可以在加载时这样$this->load->library('A/Xml_1');,这里的A就是子目录。890行到898行做的工作就是提取子目录赋给$subdir变量,提取类名赋给$class变量。
从901行的foreach开始就开始加载了。首先将你传入的名称转为全小写或首字母大写,来查找指定目录下的文件,所以你的library文件名称要么全小写或首字母大写,最好跟CI原有方式保持一致。先是形成一个子类文件路径:$subclass = APPPATH.'libraries/'.$subdir.config_item('subclass_prefix').$class.'.php';,这个子类是在application/libraries下边的,之所以叫子类是因为它是CI自己的library类的扩展,即CI允许我们队原有的工具库进行扩展继承,添加我们自己想要的内容。如果这个子类文件存在的话,形成一个基类文件路径$baseclass = BASEPATH.'libraries/'.ucfirst($class).'.php';,基类就没有什么子目录了,CI的基类不允许你这么干,扩展或改变library类只能放在application/libraries下面,人家是这么规定的。接下来检测基类出现的可能性,如果不存在就报错,子类有父类没有当然错了。如果存在就要来一次安全检查:如果这个文件以前加载过,library方法传入了第三个参数$object_name,这个对象名如果不为空,先调get_instance获取超级对象控制器基类,并且$object_name不是超级对象的成员,就调用Loader类另一个方法_ci_init_class来实例化一次这个类$class(实例化后会加入到控制器基类的属性成员),然后就return了。如果这个文件以前没有加载过,鲜藕加载父类文件和子类文件,并将该文件路径加入到Loader类的一个属性成员中,以记录这个路径的文件被加载过一次(所以前面有检查这个文件是否以前加载过)。
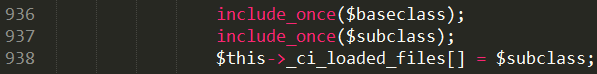
子类、父类文件均加载成功,接下来就调_ci_init_class实例化该类,返回。
944行:注意前面是子类存在的流程,如果不存在呢,刚开始下载一个CI程序,允许默认方法当然没有子类。当然也不会有子目录,$subdir就为空。
扫描Loader类属性成员_ci_library_paths(默认array(APPPATH,BASEPATH))来形成文件路径加载library类,这里的文件路径就正常多了$filepath = $path.'libraries/'.$subdir.$class.'.php';,$subdir默认空,这仍是在找application/libraries和system/libraries里边的文件。如果这个文件以前被加载过则又一次进行安全检查,然后继续在include_once这个文件并且实例化该类,返回。
982行:这是一个比较人性化的处理,它假设你在传参时少传了文件名,子目录不存在,就给深入一层再加载一次(递归),返回。就是加入传入$this->load->library('Xml');,加载的是system/libraries/xml/Xml.php,大致是这样。
如果还能往下走,那就不正常了,报错,996行结束。
回到_ci_autoloader函数,即将加载的是Model模型类,这也是_ci_autoloader自动加载的最后一种类型,它调用的也是model函数,就像我们在控制器类中加载Model一样:$this->load->model('info_model')。
====================================================================================
既然是加载Model,前面又打算把database数据库的加载单说,那我索性就最平常的,一个普通的控制器类,里边加载一个Model,在Model里边加载数据库,并读取数据返回,再加载view视图,这个过程何不就此回忆、梳理一下~
一个简单的自定义控制器类

对应的Model类

设置好数据库选项,一遍连接数据库

视图

控制器类的加载前面已经说过,就从Model类的加载说起。需要注意的一点是,在我们自己定义的,无论是Controller或Model类时,如果有构造函数需要强制(最好是)调用下父类的构造函数(parent::__construct()),前面说过CI_Controller的构造函数都要做些重要的准备工作,如果没有执行极可能出问题(好像不是可能而是一定会),比如CI_Controller会将核心类全部设置为控制器的属性成员,因此我们才可以$this->load->....这样去调用。
上面的自定义控制类中,最先加载的是staff_model模型类,回到system/core/Loader.php中看看model方法。
从大概223行起就是model方法的定义,第一个参数$model就是即将加载的Model类的文件名,它可能包含子路径(在application/models下面的子目录,视图多了我们可能会把它们分类存放),第二个参数$name允许为传入的类取一个别名,默认为空则表示按照CI默认对Model类的命名规则来,即设置为Controller类的成员后将名称全部转为小写,第三个参数$db_conn确定要不要在加载Model时连接数据库,默认为false则不连接,如果为true则会连接默认的数据库配置选项所指向的数据库,这个默认的数据库配置选项就是application/config/database.php中的default数组元素(下图),而上面自定义是我们指定其他的数据库连接信息。

初看到这个model的定义是不是很眼熟,是的,在前面说library的加载时也是这样的。首先检查$model是不是数组,若是数组递归调用该方法,$model为空直接return,250-258行就是解析出子目录(放在application/models的子文件夹下)和只包含类名的文件名,这根library基本一样,$path是子目录,$model是文件名。如果未指定$name则与$model一样。如果这个类已存在于CI_Loader类的成员变量_ci_models中,则直接返回,这个_ci_models是个数组,Loader类每加载一个Model类,均会在_ci_models中有相应的记录,当然这只是针对一次独立的访问而言,就像静态变量一样。
接下来270行调用超级方法,看看它是否跟CI_Controller中已存在的核心类重名,重名报错。接着会将类名转为全小写,从278行开始扫描成员变量_ci_model_paths加载Model类文件。
在Loader的构造函数中_ci_model_paths被初始化为array(APPPATH),意味着是在application下面去寻找的。首先检查$mod_path.'models/'.$path.$model.'.php'(APPPATH.'models/'.$path.$model.'php')是否有该文件,有的话检查$db_conn参数真假,为真则要连接数据库了,调用Loader的database方法,这个还是下面单说。再次检查CI_Model类的定义是否存在,走到这里就是基类CI_Model定义也在,自定义Model类文件也在,于是require_once正式加载这个Model文件。
然后类名变量转为首字母大写,实例化并作为控制器的属性成员,注意这个属性成员的变量名是$name,意味着model方法的第二个参数$name为空时,我们在如$this->a_model调用时a_model名字一定是全小写的,当然在实例化时类名是首字母大写的($CI->$name = new $model();),然后将这个类加入到已加载的类名称的集合数组中($this->_ci_models[] = $name;),加载完了直接return。如果跳到foreach循环外边去了,只有一个结果:error。
model方法就是以上。
回到自定义的控制器类staff_info中,调用staff_model类的getStaffsInfo方法,就是对数据库的简单查询,生成结果返回,看看这个$this->load->database...方法对数据库的加载如何执行。
定位到Loader.php文件大约324行,database方法的定义。
先调get_instance方法获取超级对象,然后检查CI_DB这个类是否出现过(联合一些条件)以判断是否需要加载数据库类,符合if条件则直接return。然后require文件BASEPATH.'database/DB.php',如果传入的第二个参数$return为真的话就返回一个由调用DB构造函数的构造的对象(直接return DB(...),还不是return new DB(...)),所以这里的DB是个方法,举的例子中第二个参数为TRUE,所以返回一个对象。如果$return为假的话,就实例化某个对象,并且作为核心控制器类对象的成员了,正是这样我们才可以$this->db->***这样用。这个数据库对象的实例化就根这个BASEPATH.'database/DB.php'脚本里的方法相关了。
打开system/database/DB.php,只有一个DB方法。

1 <?php if ( ! defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed'); 2 /** 3 * CodeIgniter 4 * 5 * An open source application development framework for PHP 5.1.6 or newer 6 * 7 * @package CodeIgniter 8 * @author EllisLab Dev Team 9 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2008 - 2014, EllisLab, Inc. 10 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2014 - 2015, British Columbia Institute of Technology (http://bcit.ca/) 11 * @license http://codeigniter.com/user_guide/license.html 12 * @link http://codeigniter.com 13 * @since Version 1.0 14 * @filesource 15 */ 16 17 // ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 18 19 /** 20 * Initialize the database 21 * 22 * @category Database 23 * @author EllisLab Dev Team 24 * @link http://codeigniter.com/user_guide/database/ 25 * @param string 26 * @param bool Determines if active record should be used or not 27 */ 28 function &DB($params = '', $active_record_override = NULL) 29 { 30 // Load the DB config file if a DSN string wasn't passed 31 if (is_string($params) AND strpos($params, '://') === FALSE) 32 { 33 // Is the config file in the environment folder? 34 if ( ! defined('ENVIRONMENT') OR ! file_exists($file_path = APPPATH.'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/database.php')) 35 { 36 if ( ! file_exists($file_path = APPPATH.'config/database.php')) 37 { 38 show_error('The configuration file database.php does not exist.'); 39 } 40 } 41 42 include($file_path); 43 44 if ( ! isset($db) OR count($db) == 0) 45 { 46 show_error('No database connection settings were found in the database config file.'); 47 } 48 49 if ($params != '') 50 { 51 $active_group = $params; 52 } 53 54 if ( ! isset($active_group) OR ! isset($db[$active_group])) 55 { 56 show_error('You have specified an invalid database connection group.'); 57 } 58 59 $params = $db[$active_group]; 60 } 61 elseif (is_string($params)) 62 { 63 64 /* parse the URL from the DSN string 65 * Database settings can be passed as discreet 66 * parameters or as a data source name in the first 67 * parameter. DSNs must have this prototype: 68 * $dsn = 'driver://username:password@hostname/database'; 69 */ 70 71 if (($dns = @parse_url($params)) === FALSE) 72 { 73 show_error('Invalid DB Connection String'); 74 } 75 76 $params = array( 77 'dbdriver' => $dns['scheme'], 78 'hostname' => (isset($dns['host'])) ? rawurldecode($dns['host']) : '', 79 'username' => (isset($dns['user'])) ? rawurldecode($dns['user']) : '', 80 'password' => (isset($dns['pass'])) ? rawurldecode($dns['pass']) : '', 81 'database' => (isset($dns['path'])) ? rawurldecode(substr($dns['path'], 1)) : '' 82 ); 83 84 // were additional config items set? 85 if (isset($dns['query'])) 86 { 87 parse_str($dns['query'], $extra); 88 89 foreach ($extra as $key => $val) 90 { 91 // booleans please 92 if (strtoupper($val) == "TRUE") 93 { 94 $val = TRUE; 95 } 96 elseif (strtoupper($val) == "FALSE") 97 { 98 $val = FALSE; 99 } 100 101 $params[$key] = $val; 102 } 103 } 104 } 105 106 // No DB specified yet? Beat them senseless... 107 if ( ! isset($params['dbdriver']) OR $params['dbdriver'] == '') 108 { 109 show_error('You have not selected a database type to connect to.'); 110 } 111 112 // Load the DB classes. Note: Since the active record class is optional 113 // we need to dynamically create a class that extends proper parent class 114 // based on whether we're using the active record class or not. 115 // Kudos to Paul for discovering this clever use of eval() 116 117 if ($active_record_override !== NULL) 118 { 119 $active_record = $active_record_override; 120 } 121 122 require_once(BASEPATH.'database/DB_driver.php'); 123 124 if ( ! isset($active_record) OR $active_record == TRUE) 125 { 126 require_once(BASEPATH.'database/DB_active_rec.php'); 127 128 if ( ! class_exists('CI_DB')) 129 { 130 eval('class CI_DB extends CI_DB_active_record { }'); 131 } 132 } 133 else 134 { 135 if ( ! class_exists('CI_DB')) 136 { 137 eval('class CI_DB extends CI_DB_driver { }'); 138 } 139 } 140 141 require_once(BASEPATH.'database/drivers/'.$params['dbdriver'].'/'.$params['dbdriver'].'_driver.php'); 142 143 // Instantiate the DB adapter 144 $driver = 'CI_DB_'.$params['dbdriver'].'_driver'; 145 $DB = new $driver($params); 146 147 if ($DB->autoinit == TRUE) 148 { 149 $DB->initialize(); 150 } 151 152 if (isset($params['stricton']) && $params['stricton'] == TRUE) 153 { 154 $DB->query('SET SESSION sql_mode="STRICT_ALL_TABLES"'); 155 } 156 157 return $DB; 158 } 159 160 161 162 /* End of file DB.php */ 163 /* Location: ./system/database/DB.php */
大约跟着DB方法走一遍,首先判断传入的第一个参数是字符串且其中没有'//'这样的字符,然后判断虽然ENVIRONMENT这个常量定义了,但默认情况下APPPATH.'config/'.ENVIRONMENT.'/database.php'这个路径的文件是不存在的。于是不出意外的话会加载APPPATH.'config/database.php'这个脚本,这是数据库配置信息的脚本,也就是前面举的例子中配置数据库连接选项所在的文件。检验$db变量是否存在,database.php这个配置文件中就是定义的$db这个数组。然后判断传入database方法的第一个参数不为空的话赋给$active_group(该变量定义在数据库配置文件中)。然后判断database.php脚本是否确实定义了$db[$active_group]这个元素,所谓的$active_group就是我们配置好的,可以用来连接需要的数据库的一套变量,规定为数组形式,整个数组的键名是$active_group,例如上边的'test',我连接的是test数组。最后将我们的配置信息数组赋给$params参数。
如果第一个if不成立,进入elseif,前提是传入的第一个参数是字符串,接着使用parse_url方法解析这个字符串,一看就知道parse_url专门解析类似于http://www.****的url,,为何在这儿解析传入的参数?看到注释里说DSN的时候就明白了,第一个参数还可以传入DSN连接字符串,这个可以看看PDO驱动的构造函数传入参数情况,很像,也可看看手册中parse_url解析后都返回些啥。
在这里,解析完后,CI得到的是scheme、host、user、pass、path这些选项,于是这个DSN字符串可能是这样的:mysql://root:password@localhost/test,重点是我们要通过这个字符串解析后得到dbdriver(驱动类型)、hostname(主机名)、username(用户名)、password(密码多少)、database(连的哪个数据库),测试下


右边是结果,注意path选项在CI中去掉了/。这样也得到了想要的信息,而不是通过加载数据库配置文件信息得到的,效果一样,不用也无所谓,反正配置文件信息更清楚嘛。
再来看这个elseif,首先parse_url解析$params,结果为false直接报错。然后解析相应选项,然后检索解析出的数组$dsn中是否有查询字符串($dsn['query']),因为是用解析url的方法,URL中当然可以有以get形式存在的查询字符串,在这里再使用解析查询字符串的方法parse_str,将查询字符串转化为数组形式,是bool型的转为字符串值"TRUE"和"FALSE",其他照旧。然后检查dbdriver选项的有效性,要使用哪种驱动?mysql?mssql?odbc?在这里就决定了,不通过的话当然就show_error了。
接下来从大约112行起,就是加载数据库类了。看看英文注释:因为active record类是可选的($active_record_override这个参数是非必传),我们需要动态的扩展一个合理的父类,基于是否用到active record类,团队中的人发现了eval这个巧妙的方法。
先检查$active_record_override这个参数(一般是不传这个参数的),存在的话将赋给$active_record。如果稍微用过CI的话,这个名字应该不陌生,在CI的数据库中有个玩意儿叫Active Record类(或者叫模式),CI就是靠它来最终对各个对应的数据库类里边的方法调用从而进行读写操作的。
加载system/database/DB_driver.php脚本(require_once(BASEPATH.'database/DB_driver.php')),这是一个总的驱动类文件,看看它的简略注释:这是一个基于平台的数据库基类,这个类不会被直接调用,当然,它是作为一个具体数据库类的适配器,由这个具体的数据库类来扩展和实例化它。看到这儿也还不怎么清楚它要干啥。
接着一个if-else语句,如果$active_record未定义或者为真,就加载system/database/DB_active_rec.php脚本,然后不出意外的话会运行这行 :eval('class CI_DB extends CI_DB_active_record { }')。eval这个函数的妙处就是直接把字符串当做php代码来执行,看它会发生什么直接去掉参数两边的引号就行,就是这样:
class CI_DB extends CI_DB_active_record
{ }
这是定义了一个CI_DB类,它继承自CI_DB_active_record,就是刚加载的文件,而CI_DB_active_record是继承自CI_DB_driver(DB_driver.php中定义)的,再看看system/database下面还有其他的文件,定义了其他的类。
然后会加载system/database/drivers/mysql/mysql_driver.php(BASEPATH.'database/drivers/'.$params['dbdriver'].'/'.$params['dbdriver'].'_driver.php')。
接着实例化mysql驱动类,$driver = 'CI_DB_'.$params['dbdriver'].'_driver'; $DB = new $driver($params);
147行是执行一个初始化方法,这个autoinit属性和initialize方法在CI_DB_driver类中(继承了几个类,得找一下在哪个里边~),做的主要是连接数据库。
OK,这里有几个类显得有点乱,以最常用的mysql为例,箭头所指为子类(UML懒得画了):

在system/database目录下面,可以看到几个文件DB_active_rec.php、DB_driver.php、DB_forge.php、DB_result.php、DB_utility.php,分别对应上图上靠上面的类,其中一个CI_DB类只是个空壳,过渡一下。我们最常用的就是最左边那条线下来的,而我们用到的mysql的驱动方法分布在这几个继承的类和它本身中(如query定义是在DB_driver.php中),当然也可能是子类override了父类的方法,我没全部看过。在database文件夹下边有个drivers子文件夹,里边放的就是各种数据库驱动对应的类文件,其中的mysql子目录就是上图中最下面的一排类。
这些所有的驱动都从system/database/DB.php中的DB方法开始加载和构造,比如例子中的查询,调用Loader类中的database方法后,加载DB.php,加载数据库配置文件,然后依次按照继承顺序加载DB_driver.php、DB_active_rec.php、mysql_driver.php。
=====================================================================================
回到最初举的例子的staff_model中,load玩数据库后,我执行了query方法,它的定义在DB_driver.php中大约251行,接着调用了query方法,你会发现mysql_driver等几个脚本中均没有这个方法,足够耐心的话,你可以看一下这个query方法。在query方法中调用了一个load_rdriver方法

估计你能看出来它加载了CI_DB_result类和CI_DB_mysql_result类,这是对父子类,最后query返回的就是这个CI_DB_mysql_result类,即query生成的结果实际上是一个单独的result类在处理,result_array(定义在DB_result.php中),free_result两个类都有,CI_DB_mysql_result中是真正的释放操作。释放结后就返回结果集,数据库类的调用结束。
对于其他类型数据库驱动,基本跟这一样。
在staff_model中获取完数据后,返回staff_info控制器类中,调用Loader核心类的view方法加载、展现视图。回到Loader.php文件,大约418行,第一个参数是需加载视图的文件名称(可包含子目录),第二个参数是传递给视图脚本的变量数组,第三个参数默认为false,传递true的话,CI将不会加载视图(所以看不到),而是将视图生成字符串内容返回。然后调用Loader类的_ci_load方法。在传递给_ci_load参数时,将前三个参数整合到了一个数组中,视图文件与键_ci_view对应,要使用的变量与键_ci_vars对应(若是对象将转为数组),是否只返回视图与键_ci_return对应。
Loader.php大约742行,则是一个protected访问属性的方法,只能在继承类中使用,还要注意一点带有下划线的前缀的方法,即便是公有访问属性的,也不能通过对象调用,这是CI的规则。一步步来看_ci_load方法。
首先是一个foreach扫描,将对应的键和值,定义为变量的名和值。然后是if检查$_ci_path这个变量是否有值,CI的view方法里传入_ci_load参数时是没有以_ci_path为键的元素的,因此走else。$_ci_ext变量获取传入视图文件名的扩展名,不写扩展名的话这里就是空串了,$_ci_file获取这个视图文件名,如果你传入视图时没有写.php后缀,我上面也没写,这里会给加上该扩展,所以完全不必加扩展名。
接下来是else中的一个foreach扫描,所做的工作就是寻找需要加载的视图,并确定其存在性。可以看到它扫描的是CI_Loader类的_ci_view_paths变量成员,这个成员在初始化是:array(APPPATH.'views/' => TRUE),约莫可以知道它是到application目录里边去找了。通过对这个数组的循环,$_ci_path = $view_file.$_ci_file;拼接一个视图的相对路径出来,确定存在则break跳出循环。如果不存在的话就走到779行的if报错了。
接着从787-794行,获取超级对象CI_Controller实例,扫描它所有的属性成员变量,把它们全部增加为CI_Loader类的属性成员,所以,即便是在view视图中,我们仍然能以$this->load->的形式调用控制器类所拥有的一切成员变量,当然也包括CI_Loader类自身的成员变量和成员方法,这是个非常方便的举措。
805-809行:当视图不是只由一个简单的脚本组成时,比如为了扩展性,前端可能会把一个页面分成head(头部)、中间实体、foot(尾部)三部分,头部和尾部基本相同,变化的是中间实体页面,这时就要保证在中间实体中加载的变量,在尾部中也能使用,这几行代码实现的就是这个效果。将我们传入的一些变量$_ci_vars,与Loader核心类的属性成员_ci_cached_vars进行合并,合并后的数组使用extract方法将键值提取出来,作为定义在当前脚本中的变量名和值,比如头部中有一个$title变量,它已经假如到_ci_cached_vars属性成员中了,当我们再 $this->load->view('body', array(‘var’ => 'val')) 时,这个var键对应的值又会合并到_ci_cached_vars中,再全部定义一遍,反正重复定义没什么影响。这样在中间实体部分仍然可以使用那个在头部中就加载了的$title变量,也可使用后来新加载进来的$var变量。
大约822行到方法结束,就是打开缓冲,加载视图脚本,然后有条件的清空或输出缓冲到页面了。
822行:打开缓存。
828-835行:检查服务器的配置短标记(短标记就是允许php脚本允许以<?开始,而不是最通用的<?php)是否开启,配置文件短标记选项($config['rewrite_short_tags'])是否允许,符合条件的话,将视图内容中的<?=(短标记时这个直接输出)替换为<?php echo ,正则将诸如 ;空格...空格?> 替换为 ;空格; (只有一个空格)的形式,默认是不走if条件的,走else就加载该脚本,呈现视图页面了,在这儿就是真正对视图脚本进行加载。
840行:如果当初传入$this->load->view方法的第三个参数为TRUE的话,就要走这个if语句,就是将整个页面内容返回,ob_get_contents获取这个文本,ob_end_clean清除缓存内容。注意:上面的加载并不能立即呈现页面,因为已经开启了缓存,除非脚本已经结束或输出缓冲。
857-结束:输出/清空缓存,展示页面。如果因为缓冲缓冲区是可以嵌套的,所以有个嵌套层次一说,最外面是1(未打开缓冲时),越嵌入里面层次值越深。如果当前缓冲区层次比Loader核心类的嵌套层次加1还大,就输出缓冲区,否写就附加到Output核心类的一个属性成员上(调用CI_Output类的append_output方法),这就是当有多个脚本共同组成一个页面时,把页面内容进行衔接,然后清除缓冲区。
当然,如果只是ob_start开启缓存了,没有手动关闭,到脚本结束时也会给你关闭掉,页面还是能展示出来滴。
~哎,就到这儿,得结合代码看,否则就一团糟。果然图表就简单明了。
