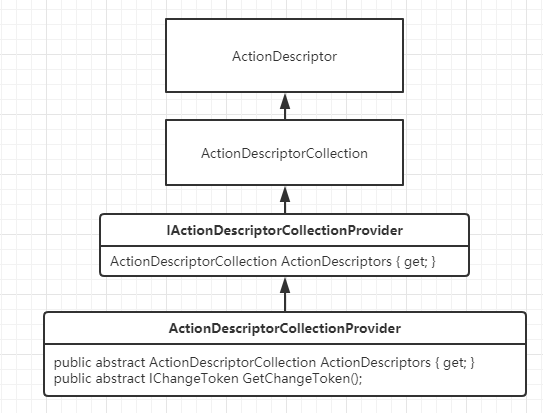
看下应用如何构建出对应的ActionDescriptor
DefaultActionDescriptorCollectionProvider
internal class DefaultActionDescriptorCollectionProvider : ActionDescriptorCollectionProvider { private readonly IActionDescriptorProvider[] _actionDescriptorProviders; private readonly IActionDescriptorChangeProvider[] _actionDescriptorChangeProviders; // The lock is used to protect WRITES to the following (do not need to protect reads once initialized). private readonly object _lock; private ActionDescriptorCollection _collection; private IChangeToken _changeToken; private CancellationTokenSource _cancellationTokenSource; private int _version = 0; public DefaultActionDescriptorCollectionProvider( IEnumerable<IActionDescriptorProvider> actionDescriptorProviders, IEnumerable<IActionDescriptorChangeProvider> actionDescriptorChangeProviders) { _actionDescriptorProviders = actionDescriptorProviders .OrderBy(p => p.Order) .ToArray(); _actionDescriptorChangeProviders = actionDescriptorChangeProviders.ToArray(); _lock = new object(); // IMPORTANT: this needs to be the last thing we do in the constructor. Change notifications can happen immediately! ChangeToken.OnChange( GetCompositeChangeToken, UpdateCollection); } /// <summary> /// Returns a cached collection of <see cref="ActionDescriptor" />. /// </summary> public override ActionDescriptorCollection ActionDescriptors { get { Initialize(); Debug.Assert(_collection != null); Debug.Assert(_changeToken != null); return _collection; } } /// <summary> /// Gets an <see cref="IChangeToken"/> that will be signaled after the <see cref="ActionDescriptors"/> /// collection has changed. /// </summary> /// <returns>The <see cref="IChangeToken"/>.</returns> public override IChangeToken GetChangeToken() { Initialize(); Debug.Assert(_collection != null); Debug.Assert(_changeToken != null); return _changeToken; } private IChangeToken GetCompositeChangeToken() { if (_actionDescriptorChangeProviders.Length == 1) { return _actionDescriptorChangeProviders[0].GetChangeToken(); } var changeTokens = new IChangeToken[_actionDescriptorChangeProviders.Length]; for (var i = 0; i < _actionDescriptorChangeProviders.Length; i++) { changeTokens[i] = _actionDescriptorChangeProviders[i].GetChangeToken(); } return new CompositeChangeToken(changeTokens); } private void Initialize() { // Using double-checked locking on initialization because we fire change token callbacks // when the collection changes. We don't want to do that repeatedly for redundant changes. // // The main call path of this code on the first call is async initialization from Endpoint Routing // which is done in a non-blocking way so in practice no caller will ever block here. if (_collection == null) { lock (_lock) { if (_collection == null) { UpdateCollection(); } } } } private void UpdateCollection() { // Using the lock to initialize writes means that we serialize changes. This eliminates // the potential for changes to be processed out of order - the risk is that newer data // could be overwritten by older data. lock (_lock) { var context = new ActionDescriptorProviderContext(); for (var i = 0; i < _actionDescriptorProviders.Length; i++) { _actionDescriptorProviders[i].OnProvidersExecuting(context); } for (var i = _actionDescriptorProviders.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { _actionDescriptorProviders[i].OnProvidersExecuted(context); } // The sequence for an update is important because we don't want anyone to obtain // the new change token but the old action descriptor collection. // 1. Obtain the old cancellation token source (don't trigger it yet) // 2. Set the new action descriptor collection // 3. Set the new change token // 4. Trigger the old cancellation token source // // Consumers who poll will observe a new action descriptor collection at step 2 - they will see // the new collection and ignore the change token. // // Consumers who listen to the change token will re-query at step 4 - they will see the new collection // and new change token. // // Anyone who acquires the collection and change token between steps 2 and 3 will be notified of // a no-op change at step 4. // Step 1. var oldCancellationTokenSource = _cancellationTokenSource; // Step 2. _collection = new ActionDescriptorCollection( new ReadOnlyCollection<ActionDescriptor>(context.Results), _version++); // Step 3. _cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource(); _changeToken = new CancellationChangeToken(_cancellationTokenSource.Token); // Step 4 - might be null if it's the first time. oldCancellationTokenSource?.Cancel(); } } }
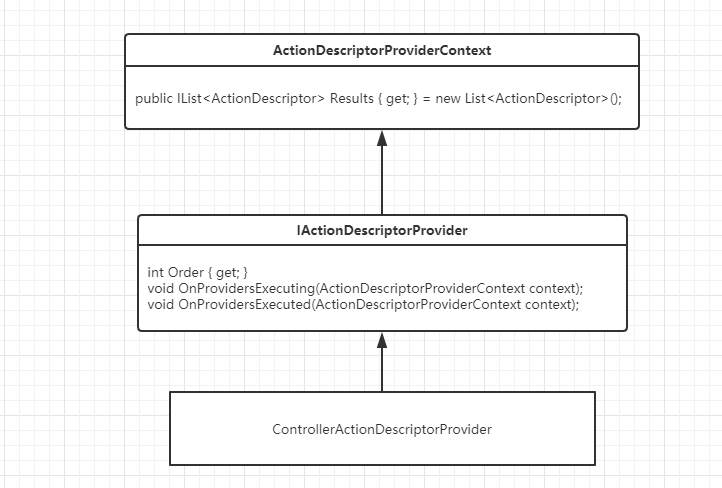
在UpdateCollection方法中,会遍历已经注册IActionDescriptorProvider的服务,分别调用OnProvidersExecuting、OnProvidersExecuted方法构建ActionDescriptor
IActionDescriptorProvider的默认实现类有ControllerActionDescriptorProvider
internal class ControllerActionDescriptorProvider : IActionDescriptorProvider { private readonly ApplicationPartManager _partManager; private readonly ApplicationModelFactory _applicationModelFactory; public ControllerActionDescriptorProvider( ApplicationPartManager partManager, ApplicationModelFactory applicationModelFactory) { if (partManager == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(partManager)); } if (applicationModelFactory == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(applicationModelFactory)); } _partManager = partManager; _applicationModelFactory = applicationModelFactory; } public int Order => -1000; /// <inheritdoc /> public void OnProvidersExecuting(ActionDescriptorProviderContext context) { if (context == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(context)); } foreach (var descriptor in GetDescriptors()) { context.Results.Add(descriptor); } } /// <inheritdoc /> public void OnProvidersExecuted(ActionDescriptorProviderContext context) { // After all of the providers have run, we need to provide a 'null' for each all of route values that // participate in action selection. // // This is important for scenarios like Razor Pages, that use the 'page' route value. An action that // uses 'page' shouldn't match when 'action' is set, and an action that uses 'action' shouldn't match when // 'page is specified. // // Or for another example, consider areas. A controller that's not in an area needs a 'null' value for // area so it can't match when the route produces an 'area' value. var keys = new HashSet<string>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase); for (var i = 0; i < context.Results.Count; i++) { var action = context.Results[i]; foreach (var key in action.RouteValues.Keys) { keys.Add(key); } } for (var i = 0; i < context.Results.Count; i++) { var action = context.Results[i]; foreach (var key in keys) { if (!action.RouteValues.ContainsKey(key)) { action.RouteValues.Add(key, null); } } } } internal IEnumerable<ControllerActionDescriptor> GetDescriptors() { var controllerTypes = GetControllerTypes(); var application = _applicationModelFactory.CreateApplicationModel(controllerTypes); return ControllerActionDescriptorBuilder.Build(application); } private IEnumerable<TypeInfo> GetControllerTypes() { var feature = new ControllerFeature(); _partManager.PopulateFeature(feature); return feature.Controllers; } }
GetControllerTypes方法获取应用中的Controller类型
这里涉及到ApplicationPartManager对象
public class ApplicationPartManager { /// <summary> /// Gets the list of <see cref="IApplicationFeatureProvider"/>s. /// </summary> public IList<IApplicationFeatureProvider> FeatureProviders { get; } = new List<IApplicationFeatureProvider>(); /// <summary> /// Gets the list of <see cref="ApplicationPart"/> instances. /// <para> /// Instances in this collection are stored in precedence order. An <see cref="ApplicationPart"/> that appears /// earlier in the list has a higher precedence. /// An <see cref="IApplicationFeatureProvider"/> may choose to use this an interface as a way to resolve conflicts when /// multiple <see cref="ApplicationPart"/> instances resolve equivalent feature values. /// </para> /// </summary> public IList<ApplicationPart> ApplicationParts { get; } = new List<ApplicationPart>(); /// <summary> /// Populates the given <paramref name="feature"/> using the list of /// <see cref="IApplicationFeatureProvider{TFeature}"/>s configured on the /// <see cref="ApplicationPartManager"/>. /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="TFeature">The type of the feature.</typeparam> /// <param name="feature">The feature instance to populate.</param> public void PopulateFeature<TFeature>(TFeature feature) { if (feature == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(feature)); } foreach (var provider in FeatureProviders.OfType<IApplicationFeatureProvider<TFeature>>()) { provider.PopulateFeature(ApplicationParts, feature); } } internal void PopulateDefaultParts(string entryAssemblyName) { var assemblies = GetApplicationPartAssemblies(entryAssemblyName); var seenAssemblies = new HashSet<Assembly>(); foreach (var assembly in assemblies) { if (!seenAssemblies.Add(assembly)) { // "assemblies" may contain duplicate values, but we want unique ApplicationPart instances. // Note that we prefer using a HashSet over Distinct since the latter isn't // guaranteed to preserve the original ordering. continue; } var partFactory = ApplicationPartFactory.GetApplicationPartFactory(assembly); foreach (var applicationPart in partFactory.GetApplicationParts(assembly)) { ApplicationParts.Add(applicationPart); } } } private static IEnumerable<Assembly> GetApplicationPartAssemblies(string entryAssemblyName) { var entryAssembly = Assembly.Load(new AssemblyName(entryAssemblyName)); // Use ApplicationPartAttribute to get the closure of direct or transitive dependencies // that reference MVC. var assembliesFromAttributes = entryAssembly.GetCustomAttributes<ApplicationPartAttribute>() .Select(name => Assembly.Load(name.AssemblyName)) .OrderBy(assembly => assembly.FullName, StringComparer.Ordinal) .SelectMany(GetAsemblyClosure); // The SDK will not include the entry assembly as an application part. We'll explicitly list it // and have it appear before all other assemblies ApplicationParts. return GetAsemblyClosure(entryAssembly) .Concat(assembliesFromAttributes); } private static IEnumerable<Assembly> GetAsemblyClosure(Assembly assembly) { yield return assembly; var relatedAssemblies = RelatedAssemblyAttribute.GetRelatedAssemblies(assembly, throwOnError: false) .OrderBy(assembly => assembly.FullName, StringComparer.Ordinal); foreach (var relatedAssembly in relatedAssemblies) { yield return relatedAssembly; } } }
ApplicationPartManager有IList<IApplicationFeatureProvider>类型的FeatureProviders属性、IList<ApplicationPart>类型的ApplicationParts属性

ControllerFeatureProvider获取应用中的所有Controller
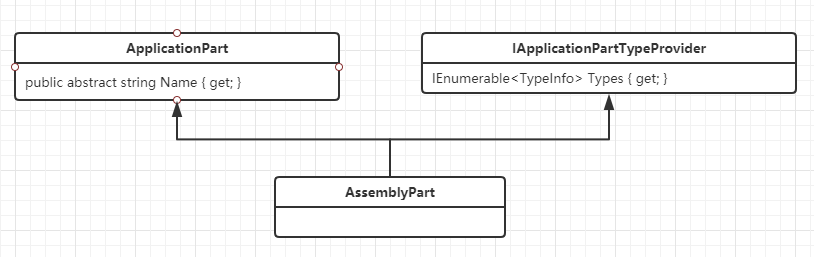
从ApplicationParts加载所有的Controller
然后调用ApplicationModelFactory类的CreateApplicationModel创建ApplicationModel对象
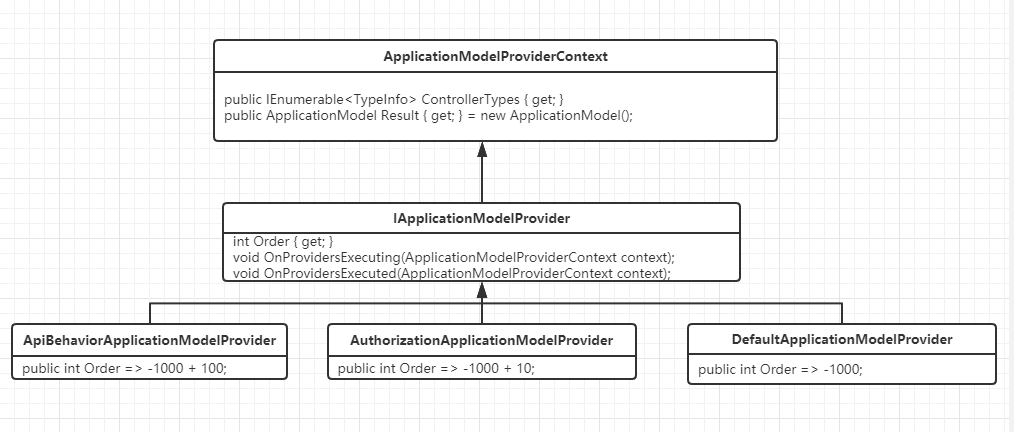
遍历注册的IApplicationModelProvider服务,调用OnProvidersExecuting、OnProvidersExecuted创建ApplicationModel
再调用ApplicationModelConventions的ApplyConventions
创建好ApplicationModel之后,再调用ControllerActionDescriptorBuilder类的Build方法创建ControllerActionDescriptor列表