闲的无聊,随便写写。随便说说自己看到的spring boot启动到结束的过程。
众所周知spring boot是运行springApplication.run()来运行的,那我们的故事就从这开始说起。(例子为spring boot 2.1.8版本)
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); }
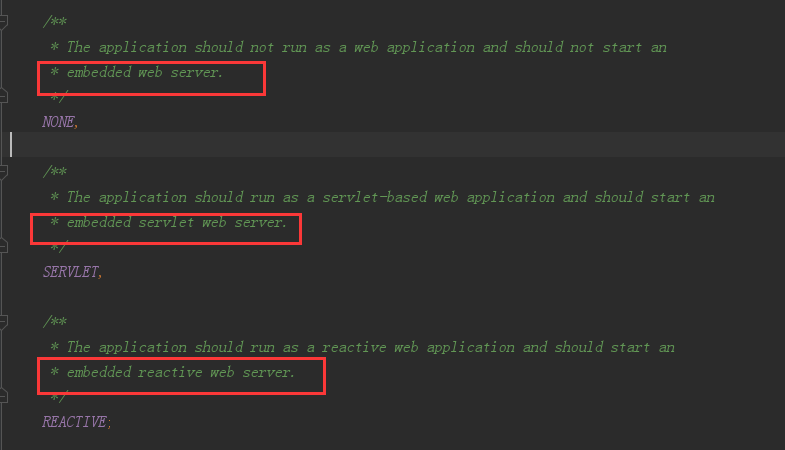
上面就是我们的springApplication,他先将源路径也就是你的运行类拿到,判断webApplication的类型,类型有3.
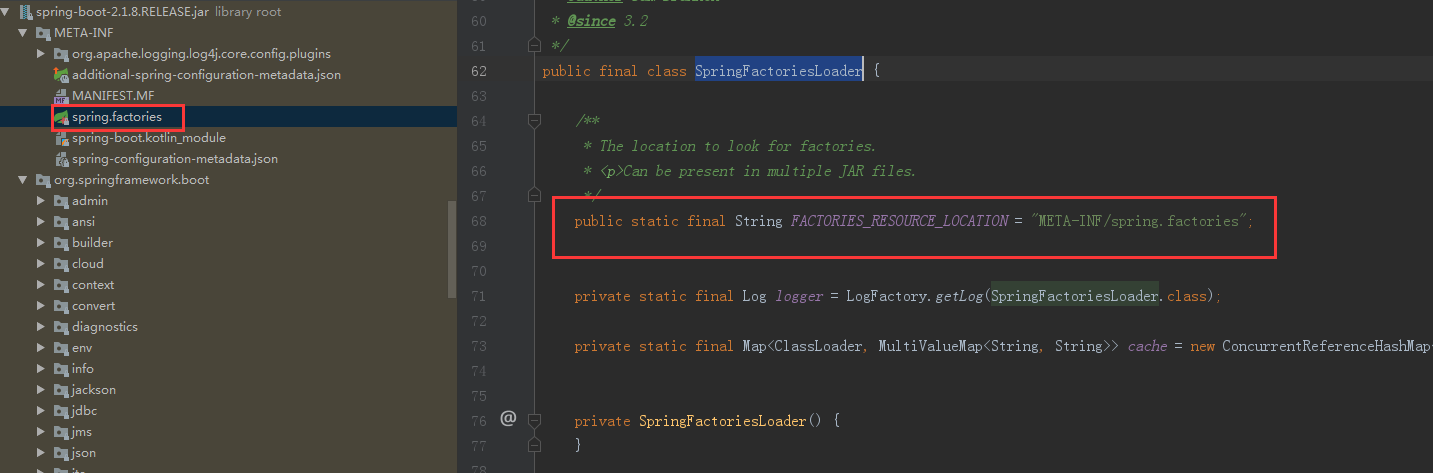
再将定义好的Initializer,Listener通过SpringFactoriesLoader加载,加载spring.factories里面的各种属性(也就算spi模式)。
判断完之后,就来说我们的run方法了,下面就是我们的run方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); configureHeadlessProperty(); SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); context = createApplicationContext(); exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); refreshContext(context); afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } listeners.started(context); callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { listeners.running(context); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return context; }
前几行可以不用管,主要是SpringApplicationRunListeners,SpringApplicationRunListeners告诉了我们springApplication的几种状态。他也对应了springApplicationEvent的事件。
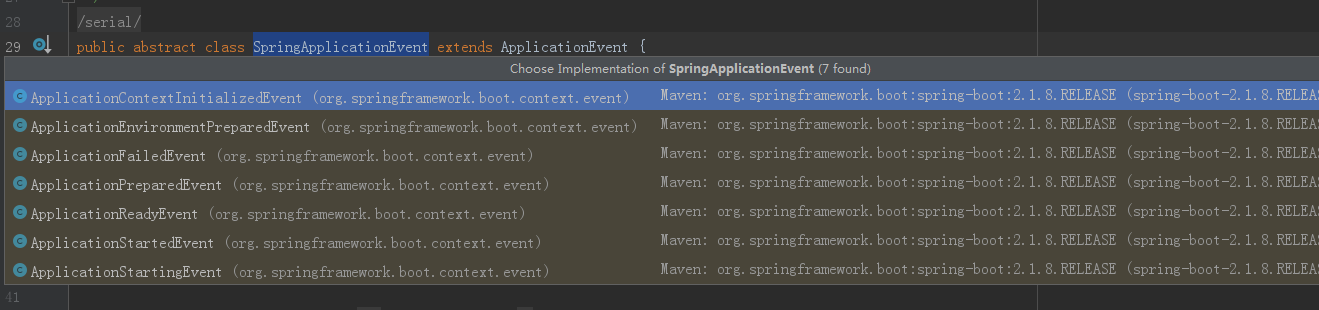
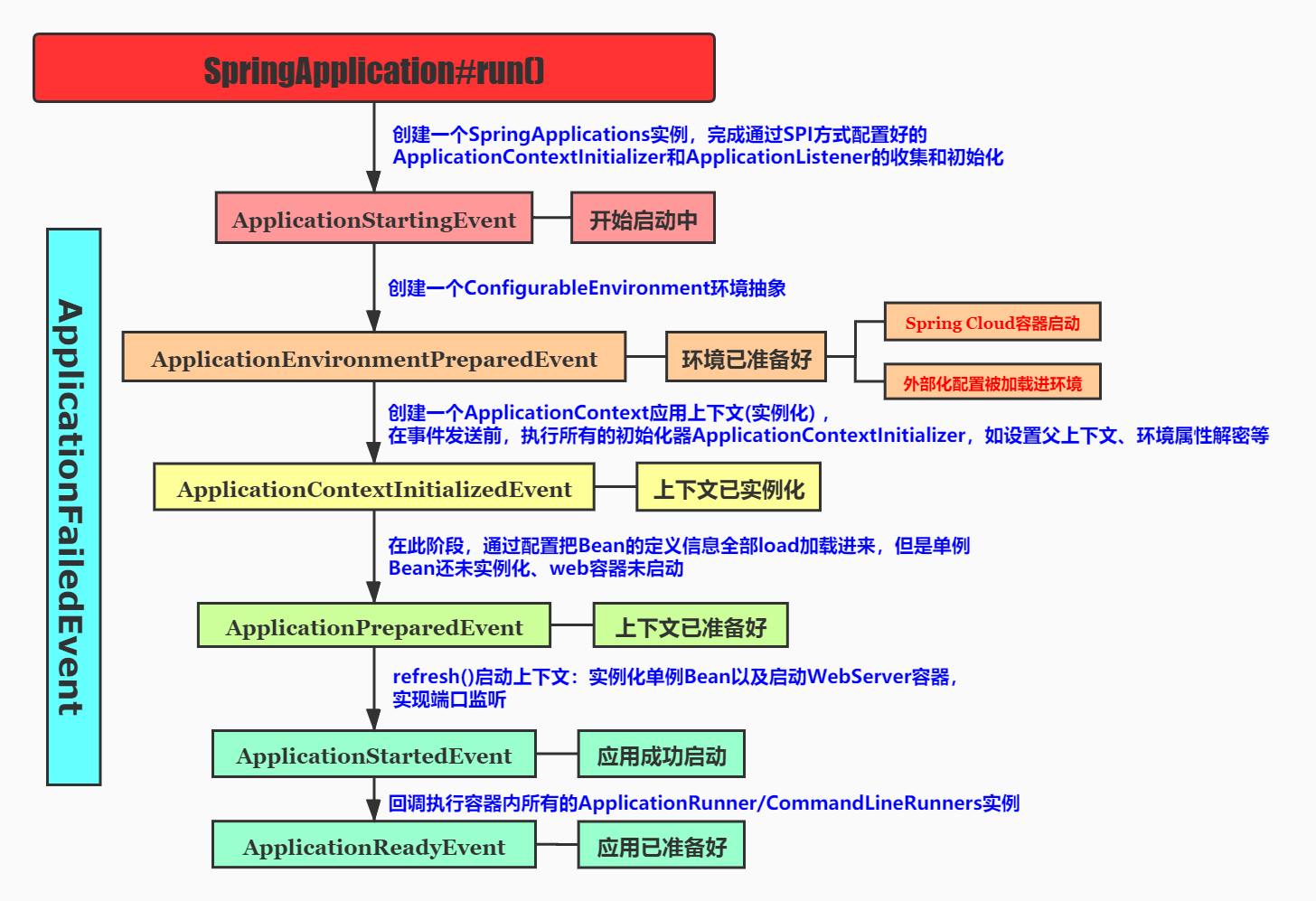
他们的顺序是这样的(图源来着yourbatman的csdn博客)
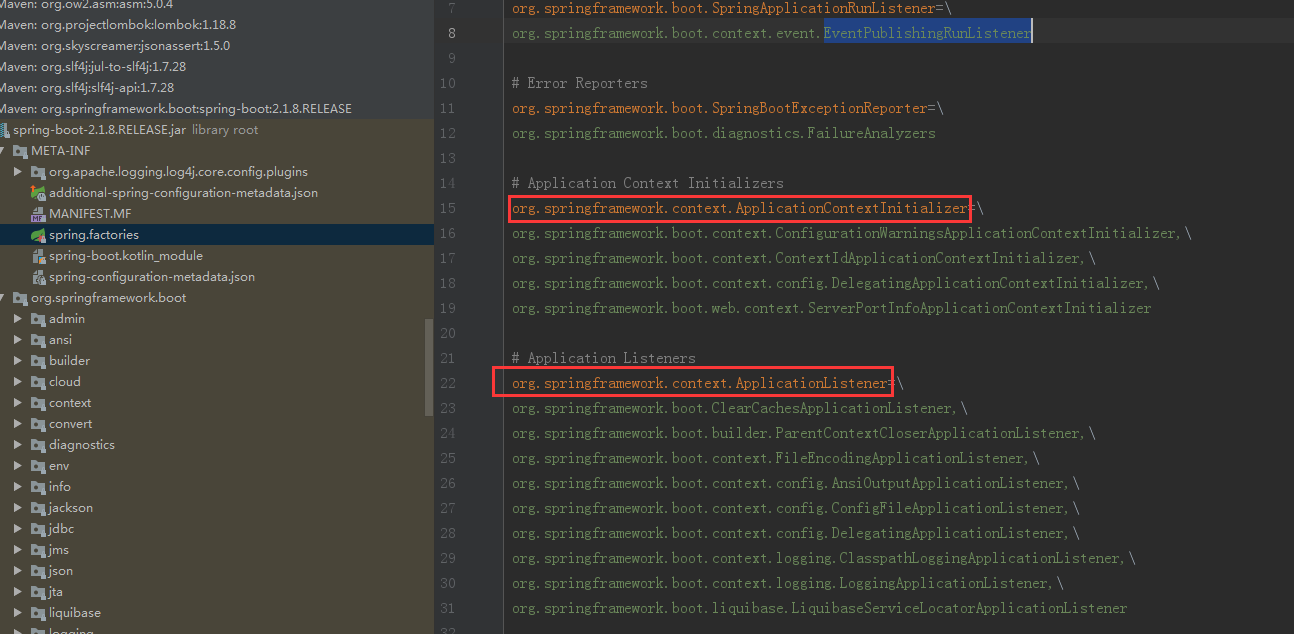
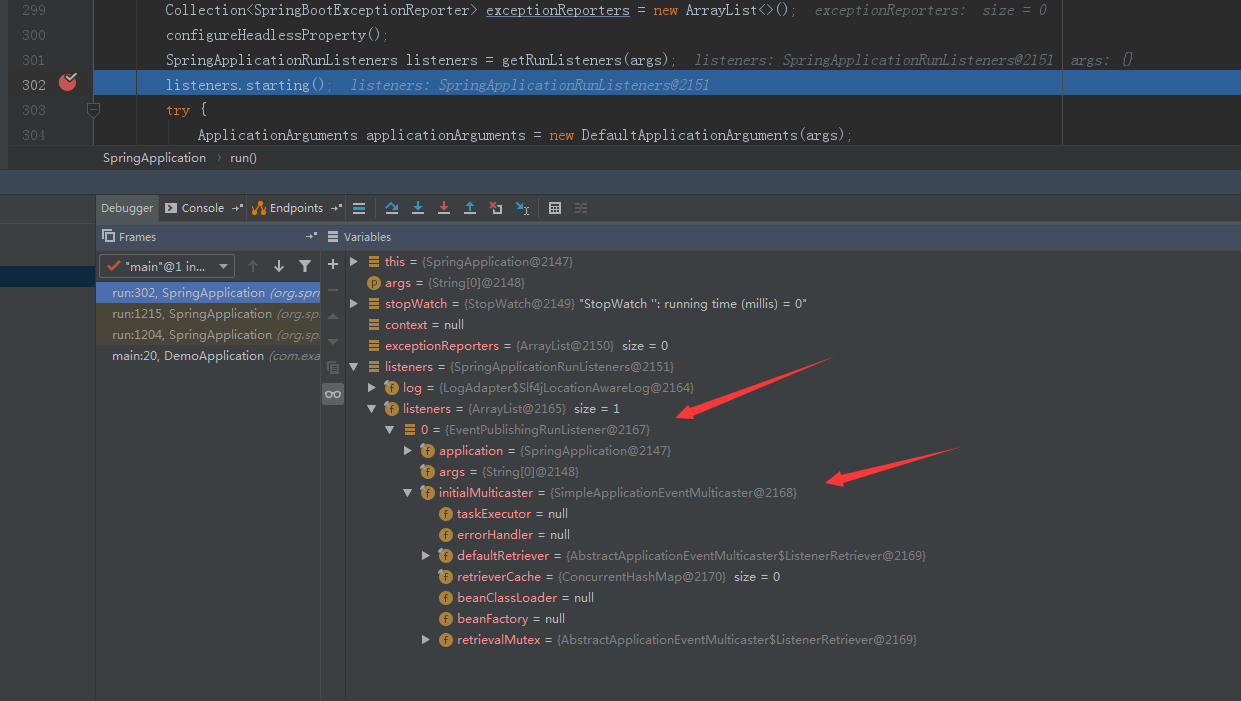
下面就是运行时listeners的东西,注意标注的地方。EventPublishingRunListeners也是由spring.factories里面配置的(最开始的截图可以看到),他再由SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster将事件传播出去。
未完,待续。。。。。。。