种群计数用于统计单位计算机字长所包含的1位的数量。
x是无符号整数,因此右移最高位填0
种群计数
基本方法1:
int x = 4;//大概208条指令
int pop = 0; for (int i = 0; i<32; i++) { if (x & 1)pop = pop + 1; x = x >> 1; }
基本方法2:
int x = 6;//大概120~160条指令
int pop = 0; while(x){ pop = pop + (x & 1); x = x >> 1; }
基本方法3:
int x = 6;
int pop = 0; while(x){//循环体需要4或者5条指令,但循环次数等于x中包含的一位数的数目 pop = pop + 1; x = x &(x-1);//x&(x-1)的作用是将x的最低1位清零 }
查表法:
int x = 6;//大概17条指令
static char table[256] = { 0,1,1,2,1,2,2,3,...8 };
int pop = table[x & 0xFF] + table[(x >> 8) & 0xff] + table[(x >> 16) & 0xFF] + table[x >> 24];
分治法:

int x = 7; x = (x & 0x55555555) + ((x >> 1) & 0x55555555); x = (x & 0x33333333) + ((x >> 2) & 0x33333333); x = (x & 0x0f0f0f0f) + ((x >> 4) & 0x0f0f0f0f); x = (x & 0x00ff00ff) + ((x >> 8) & 0x00ff00ff); x = (x & 0x0000ffff) + ((x >> 16) & 0x0000ffff);
int pop(unsigned x) {//21条指令
x = x-((x >> 1) & 0x55555555);
x = (x & 0x33333333) + ((x >> 2) & 0x33333333);
x = (x + (x >> 4)) & 0x0f0f0f0f;
x = x + (x >> 8);
x = x + (x >> 16);
return x & 0x0000003f;
}
另外一种方法:
int pop(unsigned x) {//最大适用于62位字长,无法只通过简单地扩展常数适用于64位字长
//15条指令,但有一条无符号模指令,速度较慢
unsigned n;
n = (x >> 1) & 033333333333;//对每个三位字段进行1位计数
x = x - n;
n = (n >> 1) & 033333333333;
x = x - n;
x = (x + (x >> 3)) & 030707070707;//6位字段的1位数目和
return x % 63; //将所以6位字段和相加
}
两个字种群计数的和与差
pop(x)-pop(y)=pop(x)-(32-pop(~y))
=pop(x)+pop(~y)-32
int popDiff(unsigned x, unsigned y) {//使用32条指令,若使用上面的分治法进行两次运算和一次减法则需要43条指令
x = x - ((x >> 1) & 0x55555555);
x = (x & 0x33333333) + ((x >> 2) & 0x33333333);
y = ~y;
y = y - ((y >> 1) & 0x555555555);
y= (y & 0x33333333) + ((y >> 2) & 0x33333333);
x = x + y;
x = (x & 0x0f0f0f0f) + ((x >> 4) & 0x0f0f0f0f);
x = x + (x >> 8);
x = x + (x >> 16);
return (x & 0x0000007f) - 32;
}
两个字的种群计数比较
程序返回负值表示pop(x)<pop(y),
返回0则表示pop(x)=pop(y),
返回正值表示pop(x)>pop(y)。
int popCmpr(unsigned xp, unsigned yp) {//对每个字中的单个比特位轮流清零,直到某个字的比特位全为0,那么剩下的非零种群计数值的字就是较大者。大概50条指令
unsigned x, y;
x = xp&~yp;//清除同是1的比特位
y = yp&~xp;//是1的比特位
while (1) {
if (x == 0)return y | -int(y);
if (y == 0)return 1;
x = x&(x - 1);//每个字
y = y&(y - 1);//清除一个1位
}
}
数组中的1位种群计数
//处理2个一组的元素
#define CSA(h,l,a,b,c)//处理进位 {unsigned u=a^b;unsigned v=c; h=(a&b)|(u&v);l=u^v;} int pop(unsigned x) {//21条指令 x = x - ((x >> 1) & 0x55555555); x = (x & 0x33333333) + ((x >> 2) & 0x33333333); x = (x + (x >> 4)) & 0x0f0f0f0f; x = x + (x >> 8); x = x + (x >> 16); return x & 0x0000003f; } int popArray(unsigned A[], int n) {//平均每字10.5条指令 int tot, i; unsigned ones, twos; tot = 0;//初始化 ones = 0; for (i = 0; i <= n - 2; i = i + 2) { CSA(twos, ones, ones, A[i], A[i + 1]); tot = tot + pop(twos); } tot = 2 * tot + pop(ones); if (n & 1)//如果还剩最后一个字,则把它的种群计数也加上 tot = tot + pop(A[i]); return tot; }
//CSA操作展开为:
u = ones^A[i]; v = A[i + 1]; twos = (ones&A[i]) | (u&v); ones = u^v;
//处理8个一组的元素
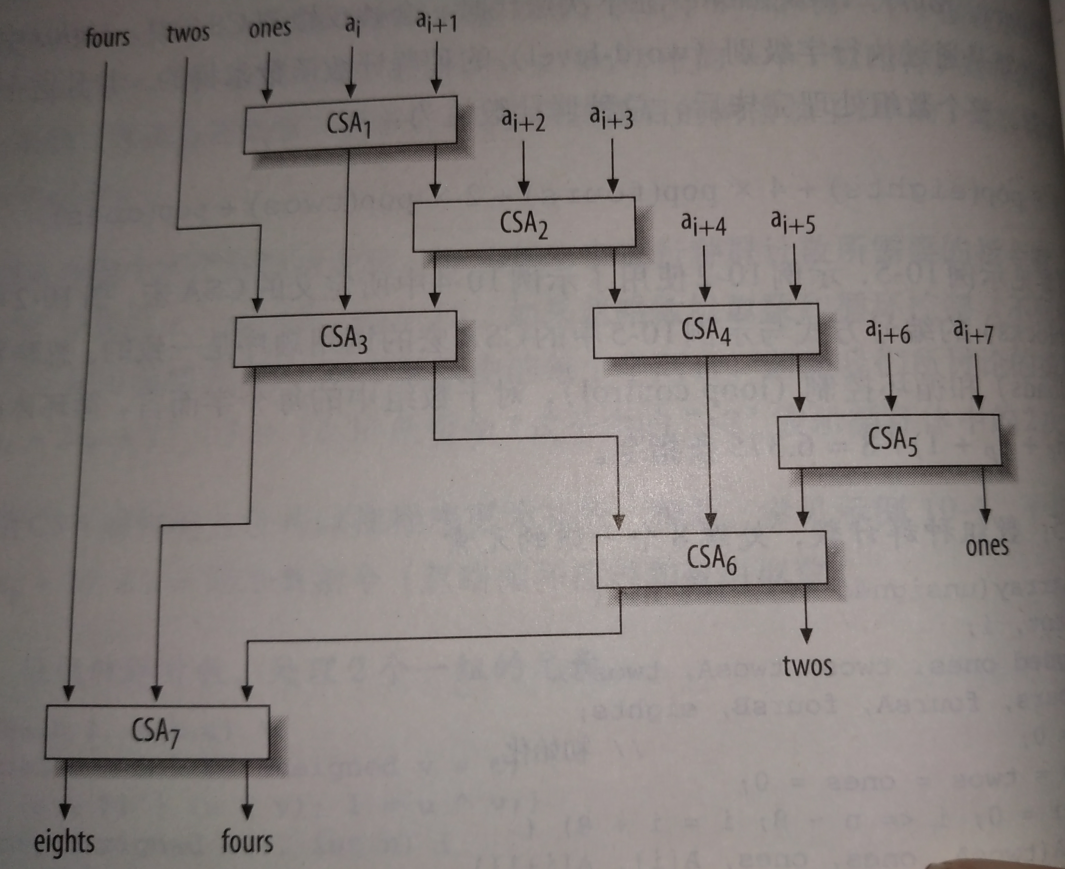
#define CSA(h,l,a,b,c) {unsigned u=a^b;unsigned v=c; h=(a&b)|(u&v);l=u^v;} int pop(unsigned x) {//21条指令 x = x - ((x >> 1) & 0x55555555); x = (x & 0x33333333) + ((x >> 2) & 0x33333333); x = (x + (x >> 4)) & 0x0f0f0f0f; x = x + (x >> 8); x = x + (x >> 16); return x & 0x0000003f; } int popArray(unsigned A[], int n) {//平均每字6.3条指令 int tot, i; unsigned ones, twos, twosA, twosB, fours, foursA, foursB, eights; tot = 0;//初始化 fours = twos = ones = 0; for (i = 0; i <= n - 8; i = i + 8) { CSA(twosA, ones, ones, A[i], A[i + 1]); CSA(twosB, ones, ones, A[i + 2], A[i + 3]); CSA(foursA, twos, twos, twosA, twosB); CSA(twosA, ones, ones, A[i + 4], A[i + 5]); CSA(twosB, ones, ones, A[i + 6], A[i + 7]); CSA(foursB, twos, twos, twosA, twosB); CSA(eights, fours, fours, foursA, foursB); tot = tot + pop(eights); } tot = 8 * tot + 4 * pop(fours) + 2 * pop(twos) + pop(ones); for(;i<n;i++)//n不一定能模8整除,所以简单的加上最后的0~7个元素。 tot = tot + pop(A[i]); return tot; }