一、Bean生命周期
Spring IOC容器可以管理Bean的生命周期,允许在Bean生命周期的特定点执行定制的任务。
Spring IOC容器对Bean的生命周期进行管理的过程如下:
- 通过构造器或工厂方法创建Bean实例
- 为Bean的属性设置值和对其它Bean的引用
- 调用Bean的初始化方法
- Bean可以使用了
- 当容器关闭时,调用Bean的销毁方法
在 Bean 的声明里设置 init-method 和 destroy-method 属性, 为 Bean 指定初始化和销毁方法。
具体过程:
-
Spring容器 从XML 文件中读取bean的定义,并实例化bean。
-
Spring根据bean的定义填充所有的属性。
-
如果bean实现了BeanNameAware 接口,Spring 传递bean 的ID 到 setBeanName方法。
-
如果Bean 实现了 BeanFactoryAware 接口, Spring传递beanfactory 给setBeanFactory 方法。
-
如果有任何与bean相关联的BeanPostProcessors,Spring会在postProcesserBeforeInitialization()方法内调用它们。
-
如果bean实现IntializingBean了,调用它的afterPropertySet方法,如果bean声明了初始化方法,调用此初始化方法。
-
如果有BeanPostProcessors 和bean 关联,这些bean的postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法将被调用。
-
如果bean实现了 DisposableBean,它将调用destroy()方法。
下面通过示例来实现上述的过程:
首先,编写一个Person类:
1 public class Person 2 { 3 String name; 4 int age; 5 String sex; 6 public String getName() 7 { 8 return name; 9 } 10 public void setName(String name) 11 { 12 System.out.println("执行name属性"); 13 this.name = name; 14 } 15 public int getAge() 16 { 17 return age; 18 } 19 public void setAge(int age) 20 { 21 this.age = age; 22 } 23 public String getSex() 24 { 25 return sex; 26 } 27 public void setSex(String sex) 28 { 29 this.sex = sex; 30 } 31 @Override 32 public String toString() 33 { 34 return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + "]"; 35 } 36 public void init() 37 { 38 System.out.println("执行初始化方法!"); 39 } 40 public Person() 41 { 42 System.out.println("执行构造函数"); 43 } 44 public void destory() 45 { 46 System.out.println("执行销毁方法"); 47 } 48 public void fun() 49 { 50 System.out.println("正在使用bean实例"); 51 } 52 }
配置文件person.xml为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="Person" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"> <property name="name" value="ktao"></property> <property name="age" value="20"></property> <property name="sex" value="male"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试函数:
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("person.xml"); 4 Person person=(Person)context.getBean("person"); 5 person.fun(); 6 context.close(); 7 } 8 }
运行结果:
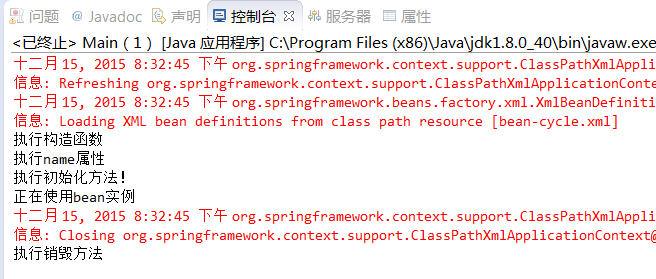
从上图可以看到,首先通过构造函数来创建bean的实例,然后通过setter方法设置属性,在使用bean实例之前,执行了init初始化方法,使用之后又执行了destroy方法。